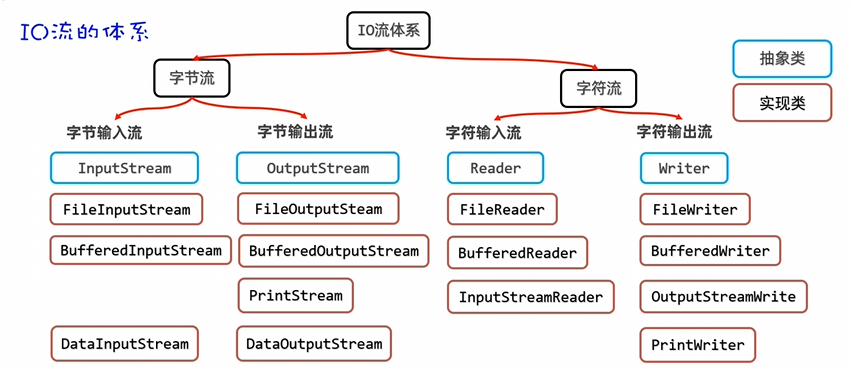
25Java基础之IO(二)
IO流-字符流
FileReader(文件字符输入流)
- 作用:以内存为基准,可以把文件中的数据以字符的形式读入到内存中去。
![image]()
案例:读取一个字符
//目标:文件字符输入流的使用,每次读取一个字符。
public class FileReaderDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args){
//1. 创建字符输入流管道与源文件接通
try(Reader reader = new FileReader("day10-io-code\\src\\chartest.txt");
){
//2. 读取一个字符,返回编号,没有字符可读时返回-1。
int c;
while((c = reader.read()) != -1) {
char ch = (char) c;
System.out.print(ch);
}
}
catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//拓展:解决了乱码的问题,2.性能较差。
}
}
案例:读取多个字符
//目标:文件字符输入流的使用:每次读取多个字符
public class FileReaderDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建字符输入流管道与源文件接通
try(Reader reader = new FileReader("day10-io-code\\src\\chartest.txt");
){
//2. 定义一个字符数组
char[] buf = new char[3];
int len;
while((len = reader.read(buf)) != -1) {
String str = new String(buf, 0, len);
System.out.print(str);
}
}
catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//拓展:解决了乱码的问题,2.性能挺好。这是目前来说学到过的读取文本文件的最好的方式。
}
}
FileWriter(文件字符输出流)
- 作用:以内存为基准,把内存中的数据以字符的形式写出到文件中去。
![image]()
案例
//目标:文件字符输出流的使用
public class FileReaderDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建字符输出流管道与源文件接通
try(//Writer rt = new FileWriter("day10-io-code\\src\\chartest1.txt");//覆盖管道
Writer rt = new FileWriter("day10-io-code\\src\\chartest1.txt", true);//追加管道
){
//2. 写一个字符出去
rt.write(98);
rt.write("\r\n");
rt.write('王');
rt.write("我是中国人,我爱我的祖国!",3 ,6);
rt.write("\r\n");
// //3. 刷新
// rt.flush();
}
catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
字符输出流使用的注意事项
- 字符输出流写出数据后,必须刷新流,或者关闭流,写出去的数据才能生效。
![image]()
字节流、字符流的使用场景小结:
- 字节流适合做一切文件数据的拷贝(音视频、文本);字节流不适合读取中文内容输出。
- 字符流适合做文本文件的操作(读、写)。
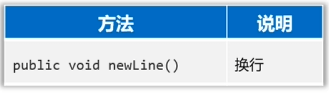
IO流-缓冲流
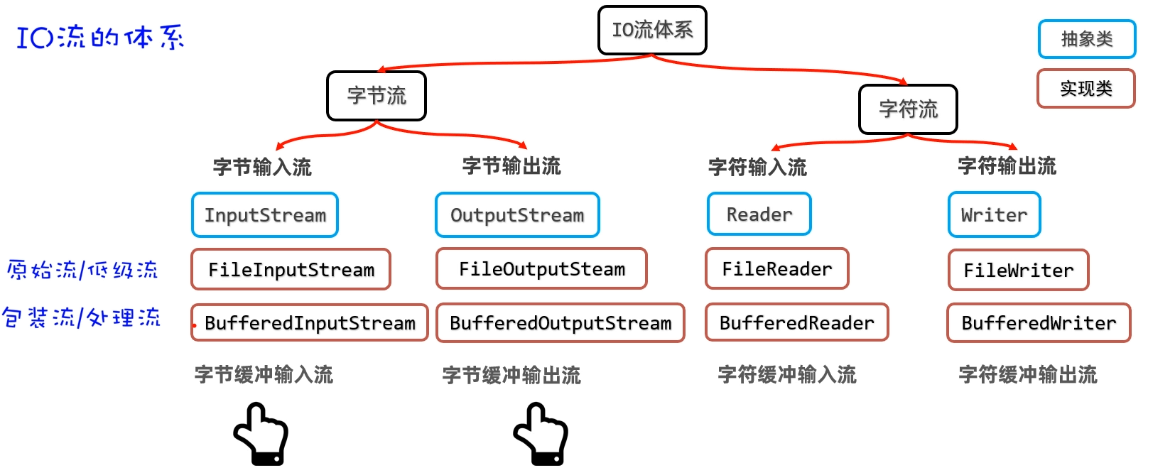
字节缓冲流的作用
- 提高字节流读写数据的性能。
- 原理:字节缓冲输入流自带了8KB缓冲池;字节缓冲输出流也自带了8KB缓冲池。
![image]()
案例
//目标:使用字节缓冲流提升原始字节流读写数据的性能。
public class BufferedInputStreamDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建字节流输入流管道与源文件接通
try(InputStream in = new FileInputStream("F:\\360安全浏览器下载\\4b60c2c15cad30091caa0940e15fadb4.jpeg");
//2. 使用高级的缓冲流包装低级的字节输入流
InputStream bin = new BufferedInputStream(in);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("F:\\360安全浏览器下载\\4b60c2c15cad30091caa0940e15fadb4_bak.jpeg");
//3. 使用高级的缓冲流包装低级的字节输出流
OutputStream bout = new BufferedOutputStream(out);
){
//准备一个字节数组
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = bin.read(buf)) != -1){
bout.write(buf, 0, len);
}
}
catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
字符缓冲输入流(BufferReader)
- 作用:自带8K(8192)的字符缓冲池,可以提高字符输入流读取字符数据的性能。
![image]()
字符缓冲输入流新增的功能:按照行读取字符

案例
public class BufferedReaderDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建字符输入流管道与源文件接通
try(Reader fr = new FileReader("day10-io-code\\src\\chartest2.txt");
// 把低级的字符输入流包装成一个高级的缓冲字符输入流
BufferedReader fr2 = new BufferedReader(fr);
){
//2. 定义一个字符数组用于读取多个字符
/* char[] buf = new char[1024];
int len;
while((len = fr2.read(buf)) != -1){
String rs = new String(buf, 0, len);
System.out.print(rs);
}*/
//3. 缓冲字符输入流多了一个按照行读取内容的方式功能。
String ln;
while((ln = fr2.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(ln);
}
}
catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
字符缓冲输出流(BufferedWriter)
- 作用:自带8K的字符缓冲池,可以提高字符输出流写字符数据的性能。
![image]()
字符缓冲输出流新增的功能:换行
案例
//目标:掌握缓冲字符流的使用
public class BufferedWirterDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(
//1. 创建一个文件字符输出流管道与源文件接通
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("day10-io-code\\src\\chartest2.txt");
BufferedWriter br = new BufferedWriter(fw);
){
//2. 写一个字符出去
br.write(98);
br.write('c');
br.newLine();
br.write("我是中国人,我爱我的祖国!");
br.newLine();
}
catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
案例:原始流、缓冲流的性能分析
测试用例:
- 分别使用原始的字节流,以及字节缓冲流复制一个很大视频。
测试步骤:
- 使用低级的字节流按照一个一个字节的形式复制文件。
- 使用低级的字节流按照字节数组的形式复制文件。
- 使用高级的缓冲字节流按照一个一个字节的形式复制文件。
- 使用高级的缓冲字节流按照字节数组的形式复制文件。
//目标:原始流和缓冲流的性能分析
//1. 使用低级的字节流按照一个一个字节的形式复制文件。
//2. 使用低级的字节流按照字节数组的形式复制文件。
//3. 使用高级的缓冲字节流按照一个一个字节的形式复制文件。
//4. 使用高级的缓冲字节流按照字节数组的形式复制文件。
public class TimeTest05 {
public static final String SRC_VIDEO = "F:\\BaiduNetdiskDownload\\0412 天才的学习方法\\0412 天才的学习方法.mp4";
public static final String DEST_VIDEO = "D:\\WEMedia\\";
public static void main(String[] args) {
// copy01(); //使用低级的字节流按照一个一个字节的形式复制文件:速度非常慢,禁止使用,直接淘汰!
copy02(); //使用低级的字节流按照字节数组的形式复制文件:速度还可以,相对来说比较慢。
// copy03(); //使用高级的缓冲字节流按照一个一个字节的形式复制文件:特别慢,不推荐使用。
copy04(); //使用高级的缓冲字节流按照字节数组的形式复制文件:极快,推荐使用!
}
public static void copy01(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//1. 使用低级的字节流按照一个一个字节的形式复制文件。
try (
//1. 创建字节流输入流管道与源文件接通
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(SRC_VIDEO);
//2. 创建字节输出流管道与目标文件接通
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(DEST_VIDEO + "01.mp4");
) {
int len;
while ((len = in.read()) != -1) {
out.write(len);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("1.使用低级的字节流总耗时:" + (end - start) / 1000.0 + "s");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void copy02(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//2. 使用低级的字节流按照字节数组的形式复制文件。
try (
//1. 创建字节流输入流管道与源文件接通
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(SRC_VIDEO);
//2. 创建字节输出流管道与目标文件接通
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(DEST_VIDEO + "02.mp4");
) {
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = in.read(buf)) != -1) {
out.write(len);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("2.使用低级的字节流按照字符数组的形式,总耗时:" + (end - start) / 1000.0 + "s");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void copy03(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//3. 使用高级的缓冲字节流按照一个一个字节的形式复制文件。
try (
//1. 创建字节流输入流管道与源文件接通
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(SRC_VIDEO);
InputStream bin = new BufferedInputStream(in);
//2. 创建字节输出流管道与目标文件接通
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(DEST_VIDEO + "03.mp4");
OutputStream bout = new BufferedOutputStream(out);
) {
int len;
while ((len = bin.read()) != -1) {
bout.write(len);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("3.使用高级的缓冲字节流总耗时:" + (end - start) / 1000.0 + "s");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void copy04(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//3. 使用高级的缓冲字节流按照一个一个字节的形式复制文件。
try (
//1. 创建字节流输入流管道与源文件接通
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(SRC_VIDEO);
InputStream bin = new BufferedInputStream(in);
//2. 创建字节输出流管道与目标文件接通
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(DEST_VIDEO + "04.mp4");
OutputStream bout = new BufferedOutputStream(out);
) {
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bin.read(buf)) != -1) {
bout.write(len);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("3.使用高级的缓冲字节流总耗时:" + (end - start) / 1000.0 + "s");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
IO流-转换流
不同编码读取出现乱码的问题
- 如果代码编码和被读取的文本文件的编码是一致的,使用字符流读取文本文件时不会出现乱码!
- 如果代码编码和被读取的文本文件的编码是不一致的,使用字符流读取文本文件就会出现乱码!
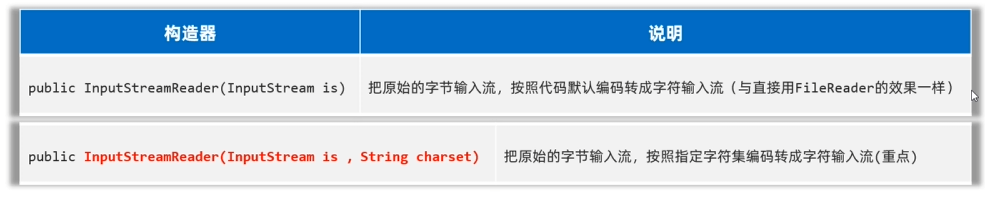
字符输入转换流(InputStreamReader)
- 解决不同编码时,字符流读取文本内容乱码的问题。
- 解决思路:先获取文件的原始字节流,再将其按照真实的字符集编码转成字符输入流,这样字符输入流中的字符就不会乱码了。
![image]()
案例
//目标:字符输入转换流
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(//1. 得到GBK文件的原始字节输入流
InputStream in = new FileInputStream("D:\\java_project\\resource\\ds.txt");
//2. 通过字符输入转换流把原始字节流按照指定编码转换成字符输入流。
Reader ir = new InputStreamReader(in, "GBK");
//3. 把字符输入流包装成高级的缓冲字符输入流
BufferedReader isr = new BufferedReader(ir);
){
//4. 按照行读取
String ln ;
while((ln = isr.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(ln);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
字符输出转换流(OutputStreamWriter)
-
需要控制写出去的字符使用什么字符集编码该怎么办?
- 调用String提供的getBytes方法解决。
![image]()
- 使用“字符输出转换流”实现。
- 调用String提供的getBytes方法解决。
-
作用:可以控制写出去的字符使用什么字符集编码。
-
解决思路:获取字节输出流,在按照指定的字符集编码将其转换成字符输出流,以后写出去的字符就会用该字符集编码了。
![image]()
案例
//目标:掌握字符输出转换流的使用
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
//1.创建一个输出字节流于源文件连通
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("D:\\java_project\\resource\\ds1.txt");
//2.创建一个字符输出转换流,把字节输出流按照指定编码转换成字符输出流
Writer ow = new OutputStreamWriter(out, "GBK");
//3.把字符输出流包装成高级的缓冲字符输出流
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(ow);
){
bw.write("hello world!");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("我是中国人,我爱我的祖国!");
bw.newLine();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
IO流-打印流
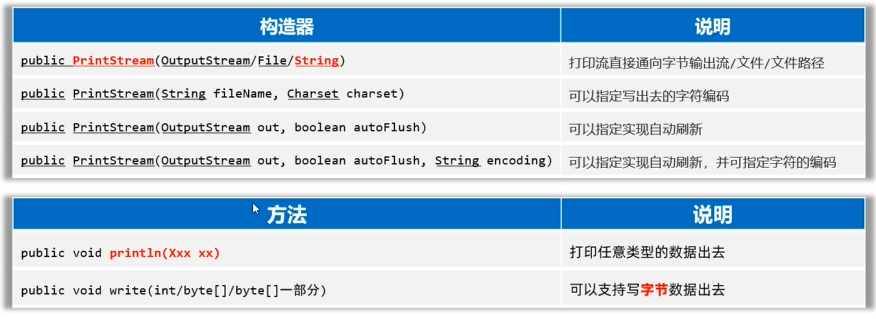
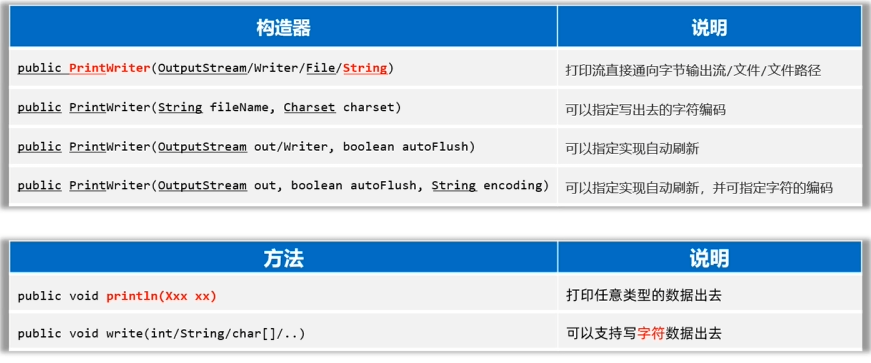
PrintStream/PrintWriter(打印流)
- 作用:打印流可以实现更方便、更高效的打印数据出去,能实现打印啥出去就是啥出去。
PrintStream提供的打印数据的方案
PrintWriter提供的打印数据的方案
//目标:打印流,方便,高效的写数据出去
public class PrintStreamDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("day10-io-code\\src\\ps.txt");
// PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter("day10-io-code\\src\\ps.txt");//默认是覆盖
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("day10-io-code\\src\\ps.txt",true));//追加
){
//写数据出去
ps.println(97);
ps.println("2314asdf");
ps.println('A');
ps.println(16.5);
ps.println(true);
ps.println("------------------------------------");
pw.println(751);
pw.println('a');
pw.println("我是中国人,我爱我的祖国!");
pw.println(true);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
PrintStream和PrintWriter的区别
- 打印数据的功能上是一模一样的:都是使用方便,性能高效(核心优势)
- PrintStream继承自字节输出流OutputStream,因此支持写字节数据的方法。
- PrintWriter继承自字符输出流Writer,因此支持写字符数据出去。
打印流的一种应用:输出语句的重定向。

案例
//目标:输出语句的重定向
public class PrintStreamDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
System.out.println("红豆生南国");
System.out.println("春来发几枝");
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("day10-io-code\\src\\ps.txt", true));
System.setOut(ps); //把系统的打印流改成自己的打印流
System.out.println("愿君多采撷");
System.out.println("此物最相思");
}
}
IO特殊数据流---数据输出流(DataOutputStream)
- 允许把数据和其类型一并写出去。
![image]()
案例
public class DataOutputStreamDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("day10-io-code\\src\\dos.txt"));
){
//写入数据
dos.writeByte(97);
dos.writeBoolean(true);
dos.writeInt(4232);
dos.writeChar('c');
dos.writeChars("zcvsadf55");
dos.writeUTF("我是中国人!");
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
DataInputStream(数据输入流)
- 用于读取数据输出流写出去的数据。
![image]()
案例
//特殊数据输入流
public class DataInputStreamDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("day10-io-code\\src\\dos.txt"));
){
System.out.println(dis.readByte());
System.out.println(dis.readBoolean());
System.out.println(dis.readInt());
System.out.println(dis.readChar());
System.out.println(dis.readUTF());
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
注意:输出流和输入流的数据类型读写顺序必须保持一致,否则会报错。
IO流---序列化流
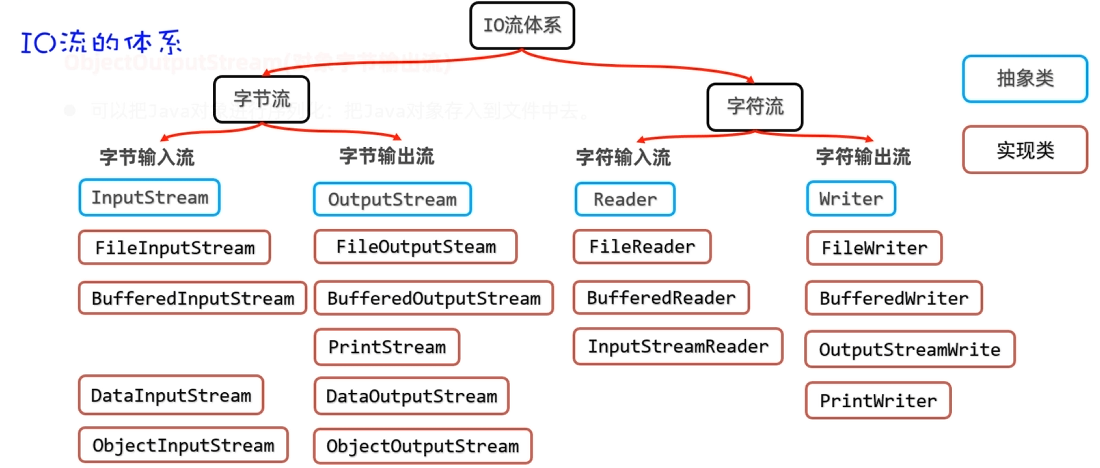
ObjectOutputStream(对象字节输出流)
- 对象序列化:把java对象写入到文件中去。
![image]()
注意:对象如果要参与序列化,必须实现序列化接口(java.io.Serializable)
案例
学生类:
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
//注意:如果学生对象要参与序列化,那么学生类必须实现Serializable接口,否则会抛出NotSerializableException异常。
public class Student implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
//transient:修饰的成员变量,不能参与序列化。
private transient String password;
private double height;
}
测试类:
//目标:完成对象的序列化:把java对象存储到文件中去。
public class ObjectOutputStreamDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建一个Student对象
Student s1 = new Student("电驴", 18, "123456", 1.78);
//2.创建对象字节输出流管道与目标文件接通
try(
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("day10-io-code\\src\\obj.txt"));
){
//3. 开始写对象出去
oos.writeObject(s1);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 对象反序列化:把文件里的java对象读出来。
案例
//目标:完成对象的反序列化:把文件中的数据恢复成java对象。
public class ObjectInputStreamDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1;
try (
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("day10-io-code\\src\\obj.txt"));
){
s1 = (Student) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(s1);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
如果要一次序列多个对象,怎么办?
- 用一个ArrayList集合存储多个对象,然后直接对结合进行序列化即可。
- 注意:ArrayList集合已经实现了序列化接口。
IO框架
什么是框架?
- 解决某类问题,编写的一套类、接口等,可以理解成一个半成品,大多数框架都是第三方开发的。
- 好处:在框架的基础上开发,可以得到优秀的软件架构,并能提高开发效率。
- 框架的形式:一般是把类、接口等编译成class形式,再压缩成一个.jar结尾的文件发行出去。
![image]()
什么是IO框架?
- 封装了Java提供的对文件、数据进行操作的代码,对外提供了更简单的方式来对文件进行操作,对数据进行读写等。
commons-io-2.11.0.jar框架
导入commons-io-2.11.0.jar框架到项目中去。
- 在项目中创建一个文件夹:lib
- 将commons-io-2.6.jar文件复制到lib文件夹
- 在jar文件上点右键,选择Add as Library->点击OK
- 在类中导包使用
下载地址:https://commons.apache.org/io/download_io.cgi
- Commons-io是apache开源基金组织提供的一组有关IO操作的小框架,目的是提高IO流的开发效率。
![image]()
![image]()
案例
//目标:使用Commons IO框架进行IO操作
public class CommonsIODemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileUtils.copyFile(new File("day10-io-code\\src\\dos.txt"), new File("day10-io-code\\src\\dos1.txt"));
// FileUtils.copyDirectory(new File("D:\\java_project\\resource\\b"), new File("D:\\java_project\\resource\\b1"));
// FileUtils.deleteDirectory(new File("D:\\java_project\\resource\\b"));
//JDK7开始也新增了单行复制相关的技术
Files.copy(Path.of("day10-io-code\\src\\dos.txt"), Path.of("day10-io-code\\src\\dos2.txt"));
}
}
案例:复制文件夹
//目标:复制文件夹
//源文件夹:D:\java_project\resource\
//目标文件夹:E:\
public class CopyDirectoryDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
copyDirectory(new File("D:\\java_project\\resource\\"), new File("E:\\"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void copyDirectory(File srcDir, File destDir) throws Exception {
//1.判断源文件夹是否存在
if(srcDir == null || destDir == null || !srcDir.exists()
|| !destDir.exists() || srcDir.isFile() || destDir.isFile()) {
return;
}
//2.开始拷贝之前,先在目标位置创建新的文件夹名和原文件夹名称一样。
File destNewDir = new File(destDir, srcDir.getName());
destNewDir.mkdirs();
//3. 提取原始目录的一级文件对象
File[] files = srcDir.listFiles();
//4. 判断这个目录是否可以拿到一级文件对象
if(files == null || files.length==0) return;
//5. 遍历全部一级文件对象,拷贝到新的目录中
for (File file : files) {
if(file.isFile()){
FileUtils.copyFile(file, new File(destNewDir, file.getName()));
}
else {
copyDirectory(file, destNewDir);
}
}
}
}
案例:删除文件夹
//目标:删除文件夹
public class DeleteDirDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
deleteDirectory(new File("e:\\resource\\"));
}
public static void deleteDirectory(File dir){
//1. 不删除的情况
if(dir == null || !dir.exists()) return;
//2. 如果是文件,直接删除
if(dir.isFile()) {
dir.delete();
return;
}
//3.文件夹
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
if(files == null) return;
if(files.length == 0){
dir.delete();
return;
}
//4.遍历全部一级文件对象,删除
for (File file : files) {
if(file.isFile()){
file.delete();
}
else {
deleteDirectory(file);
}
}
//5.删除自己
dir.delete();
}
}
课外拓展案例:啤酒问题
- 需求:啤酒2元一瓶,4个盖子可以换一瓶,2个空瓶可以换一瓶,10元可以买多少瓶?剩余多少个盖子和空瓶?
代码
//目标:啤酒问题:啤酒2元一瓶,4个盖子可以换一瓶,2个空瓶可以换一瓶,10元可以买多少瓶?剩余多少个盖子和空瓶?
public class BeerDemo03 {
public static int totalBeers;
public static int lastBottles;
public static int lastCovers;
public static void main(String[] args) {
buyBeers(10);
System.out.println("一共可以买"+ totalBeers + "瓶酒,"
+ "还剩" + lastBottles + "个空瓶子,还剩" + lastCovers + "个瓶盖子!");
}
public static void buyBeers(int money) {
//1.拿钱买酒
int beers = money /2;
totalBeers += beers;
//2.计算出本轮总共的空瓶和盖子数,换算成钱继续递归买酒。
int totalBottles = lastBottles + beers;
int totalCovers = lastCovers + beers;
//3. 换算成钱,继续买酒
int newMoney = 0;
if(totalBottles >= 2){
newMoney += (totalBottles / 2) * 2;
}
lastBottles = totalBottles % 2; //记录剩余瓶子数
if(totalCovers >= 4){
newMoney += (totalCovers / 4) * 2;
}
lastCovers = totalCovers % 4; //记录剩余盖子数
if(newMoney >= 2){
buyBeers(newMoney);//递归
}
}
}
















 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号