19Java基础之异常
异常
什么是异常?
- 异常就是代表程序出现的问题。
常见的异常
//目标:认识异常
public class ExceptionDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
System.out.println("程序开始");
System.out.println(arr[0]);
System.out.println(arr[1]);
System.out.println(arr[2]);
// System.out.println(arr[3]);// 报ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException异常
System.out.println("程序结束");
String s = null;
// System.out.println(s.length());// 报NullPointerException异常,空指针异常
// System.out.println(10/0); //报ArithmeticException异常,算术异常
Object o = "张麻子";
Integer i = (Integer) o;
// System.out.println(i); // 报ClassCastException异常,类型转换异常
String s1 = "23a";
int it = Integer.valueOf(s1);
// System.out.println(it); // 报NumberFormatException异常,数字格式化异常
parseDate("2025-08-06 21:22:23");
}
public static void parseDate(String date) throws ParseException {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Date d = sdf.parse(date); // 编译时错误,写代码时就会报错。
}
}
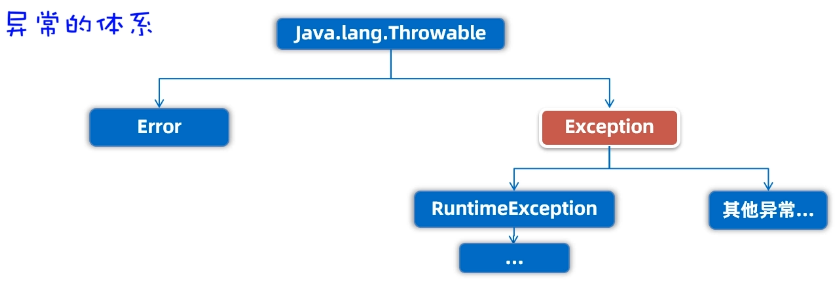
-
Error:代表的系统级别错误(属于严重问题),也就是说系统一旦出现问题,sun公司会把这些问题封装成Error对象给出来,说白了,Error是给sun公司自己用的,不是给我们程序员用的,因此我们开发人员不用管它。
-
Exception:叫异常,它代表的才是我们程序可能出现的问题,所以,我们程序员通常会用Exception以及它的孩子来封装程序出现的问题。
- 运行时异常:RuntimeException及其子类,编译阶段不会出现错误提醒,运行时出现的异常(如数组索引越界异常)
- 编译时异常:编译阶段就会出现错误提醒的。(如:日期解析异常)
异常处理方式
- 抛出异常(throws)
- 在方法上使用throws关键字,可以将方法内部出现的异常抛出去给调用者处理。
- 格式:
方法 throws 异常1,异常2,异常3{
...
}
- 捕获异常(try...catch)
- 直接捕获程序出现的异常。
- 格式:
try{
// 监视可能出现异常的代码!
}catch(异常类型1 变量){
// 处理异常
}catch(异常类型2 变量){
// 处理异常
}
异常有什么作用?
- 异常是用来查询系统Bug的关键参考信息!
- 异常可以作为方法内部的一种特殊返回值,以便通知上层调用者底层的执行情况。
案例:
// 目标:搞清楚异常的作用。
public class ExceptionDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 监视代码
divide(2, 1);
System.out.println("成功了!");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("失败了!");
// 捕获异常,并打印出异常的信息。
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static int divide(int a, int b){
if(b == 0){
System.out.println("参数有问题!");
// return -1;
// 抛出一个异常作为返回值,通知上层这里出现了bug。
throw new RuntimeException("/ by 0!");
}
int c = a / b;
return c;
}
}
小技巧
- 在IDEA中,在要抛出异常的语句上按ctrl+ alt + T,从弹出的下拉表单中找到try/catch,回车,就可以直接生成异常捕获。
自定义异常
- Java无法为这个世界上全部的问题都提供异常类来代表,如果企业自己的某种问题,想通过异常来表示,以便用异常来管理该问题,那就需要自己来定义异常类。
自定义异常的种类
- 自定义运行时异常
- 自定义编译时异常
![image]()
注意:
- 自定义异常时,建议使用自定义运行时异常。这种异常对程序员干扰性少,如果定义编译时异常,连锁反应太多,容易干扰程序员。
- 要注意throw和throws的区别。throw是方法内部使用,创建异常并从此点抛出异常;throws是在方法上,抛出方法内部的异常给调用者。
案例:
自定义运行时异常类:
// 自定义运行时异常
/*
* 1. 继承RuntimeException
* 2. 重写构造器
* 3. 通过throw new 自定义异常对象抛出异常
* */
public class AgeIllegalRuntimeException extends RuntimeException {
public AgeIllegalRuntimeException() {
}
public AgeIllegalRuntimeException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
自定义异常类:
// 自定义编译时异常
/*
* 1. 继承Exception
* 2. 重写构造器
* 3. 通过throw new 自定义异常对象抛出异常
* */
public class AgeIllegalException extends Exception {
public AgeIllegalException() {
}
public AgeIllegalException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
测试:
//目标:自定义异常
public class ExceptionDemo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws AgeIllegalException {
System.out.println("start...");
try {
save(100);
System.out.println("执行成功!");
} catch (AgeIllegalException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("执行失败!");
}
System.out.println("end...");
}
public static void save(int age) throws AgeIllegalException {
// throw 方法内部使用,创建异常并从此点抛出异常
// throws 方法上,抛出方法内部的异常给调用者。
if(age <= 0 || age > 65){
//这个年龄非法!创建异常时对象来抛出异常
throw new AgeIllegalException("年龄非法!");
}
System.out.println("年龄合法:" + age);
}
}
异常的常见处理方式

- 捕获异常,记录异常并响应合适的信息给用户。(推荐)
- 捕获异常,尝试重新修复。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号