Another Filling the Grid
Another Filling the Grid
题目信息
题目链接
题目描述
You have $ n \times n $ square grid and an integer $ k $ . Put an integer in each cell while satisfying the conditions below.
- All numbers in the grid should be between $ 1 $ and $ k $ inclusive.
- Minimum number of the $ i $ -th row is $ 1 $ ( $ 1 \le i \le n $ ).
- Minimum number of the $ j $ -th column is $ 1 $ ( $ 1 \le j \le n $ ).
Find the number of ways to put integers in the grid. Since the answer can be very large, find the answer modulo $ (10^{9} + 7) $ .
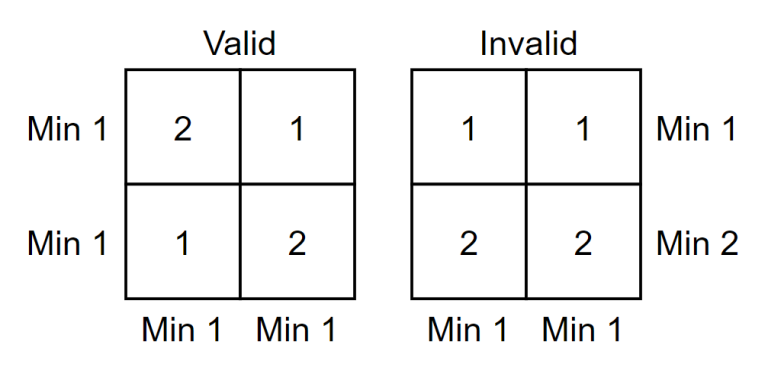
These are the examples of valid and invalid grid when $ n=k=2 $ .
输入格式
The only line contains two integers $ n $ and $ k $ ( $ 1 \le n \le 250 $ , $ 1 \le k \le 10^{9} $ ).
输出格式
Print the answer modulo $ (10^{9} + 7) $ .
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
2 2
样例输出 #1
7
样例 #2
样例输入 #2
123 456789
样例输出 #2
689974806
提示
In the first example, following $ 7 $ cases are possible.
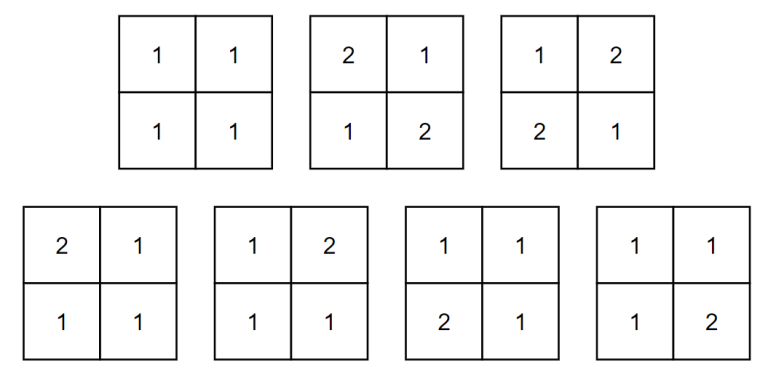
In the second example, make sure you print the answer modulo $ (10^{9} + 7) $ .
题面翻译
给定一个 \(n\times n\) 的矩阵,用 \(1\sim k\) 的数填充,每行每列最小值均为 \(1\),问有多少填法,对 \(10^9+7\) 取模。
\(1\le n\le 250,1\le k\le 10^9\)。
思路分析
\(S_i\) 表示第 \(i\) 行不合法的方案集合。
\(T_i\) 表示第 \(i\) 列不合法的方案集合。
答案就是:\(k^{n^2}-|\displaystyle\bigcup_{1}^n S_i\displaystyle\bigcup_{1}^n T_i|\)。
\(O(2^n)\) 显然过不了,考虑优化,发现可以合并(不要只想着 1 个 \(\sum\) 的合并,要想一想多个 \(\sum\) 的合并)。
则答案为:
\[\sum_{i=0}^n\sum_{j=0}^n(-1)^{i+j}{n\choose i}{n\choose j}(k-1)^{(i+j)n-ij}k^{(n^2-(i+j)n+ij)}
\]
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 2e5+10;
const int MOD = 1e9+7;
namespace math{
int mu[MAXN],prime[MAXN];
bitset<MAXN> is_prime;
int frac[MAXN];
int qpow(int a,int b){
if(b==0) return 1;
if(b==1) return a;
int k = qpow(a,b>>1);
k*=k;k%=MOD;
if(b&1) k*=a;k%=MOD;
return k;
}
int exgcd(int a,int b,int &x,int &y){
if(b==0){
x = 1;y = 0;
return a;
}
int t = exgcd(b,a%b,x,y);
int g = x;
x = y;
y = g-a/b*y;
return t;
}
int inv(int a){
return qpow(a,MOD-2);
}
int ex_inv(int a){
int x,y;
exgcd(a,MOD,x,y);
return (x%MOD+MOD)%MOD;
}
int C(int n,int m){
if(n<m) return 0;
return frac[n]*inv(frac[m]*frac[n-m]%MOD)%MOD;
}
int get(int n,int m){
return C(m+n-1,m);
}
void frac_init(){
frac[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1;i<MAXN;i++){
frac[i] = frac[i-1]*i;
frac[i]%=MOD;
}
}
int lowbit(int k){
return k&(-k);
}
int bit(int k){
int sum = 0;
while(k){
sum ++;
k -= lowbit(k);
}
return sum;
}
int log2(int k){
for(int i = 0;i<=64;i++){
int p = 1;
if(p<<i==k) return i;
}
return 0;
}
void Euler_sieve(){
mu[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2;i<MAXN;i++){
if(!is_prime[i]){
prime[++prime[0]] = i;
mu[i] = -1;
}
for(int j = 1;j<=prime[0]&&i*prime[j]<MAXN;j++){
is_prime[i*prime[j]] = 1;
if(i%prime[j]==0){
mu[i*prime[j]] = 0;
break;
}else{
mu[i*prime[j]] = -mu[i];
}
}
}
}
}
using namespace math;
int n,k,ans;
signed main(){
scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&k);
frac_init();
for(int i = 0;i<=n;i++){
for(int j = 0;j<=n;j++){
ans +=
qpow(-1,i+j)
*C(n,i)%MOD
*C(n,j)%MOD
*qpow(k-1,(i+j)*n-i*j)%MOD
*qpow(k,n*n-(i+j)*n+i*j)%MOD
;
ans%=MOD;
}
}
printf("%lld",(ans%MOD+MOD)%MOD);
return 0;
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号