lombok使用基础教程
- 本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/woshimrf/p/lombok-usage.html
- 版权声明: 本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
前言
lombok是一个编译级别的插件,它可以在项目编译的时候生成一些代码。在很多工具类的项目中都有这个功能。比如dagger。
通俗的说,lombok可以通过注解来标示生成getter settter等代码。我们自然可以通过编译器比如IDEA的Generate生成,为啥要用这个?
在项目开发阶段,一个class的属性是一直变化的,今天可能增加一个字段,明天可能删除一个字段。每次变化都需要修改对应的模板代码。另外,有的class的字段超级多,多到一眼看不完。如果加上模板代码,更难一眼看出来。更有甚者,由于字段太多,想要使用builder来创建。手动创建builder和字段和原来的类夹杂在一起,看起来真的难受。lombok的@Builder即可解决这个问题。
引入
引入就是加入lombok的jar包。
在maven中
直接加入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.16.20</version>
</dependency>在gradle中
这里比较麻烦,需要添加一个编译时生成代码的插件。gradle里有几个这样的插件。但为了简化过程,lombok提供了新插件。
首先,添加一个plugin
plugins {
id 'io.franzbecker.gradle-lombok' version '1.11'
}然后,就可以了。还可以配置lombok的版本:
lombok { // optional: values below are the defaults
version = "1.16.20"
sha256 = ""
}IntelIJ IDEA 插件
在IDEA里使用需要添加一个插件。在插件里搜索lombok,安装,重启。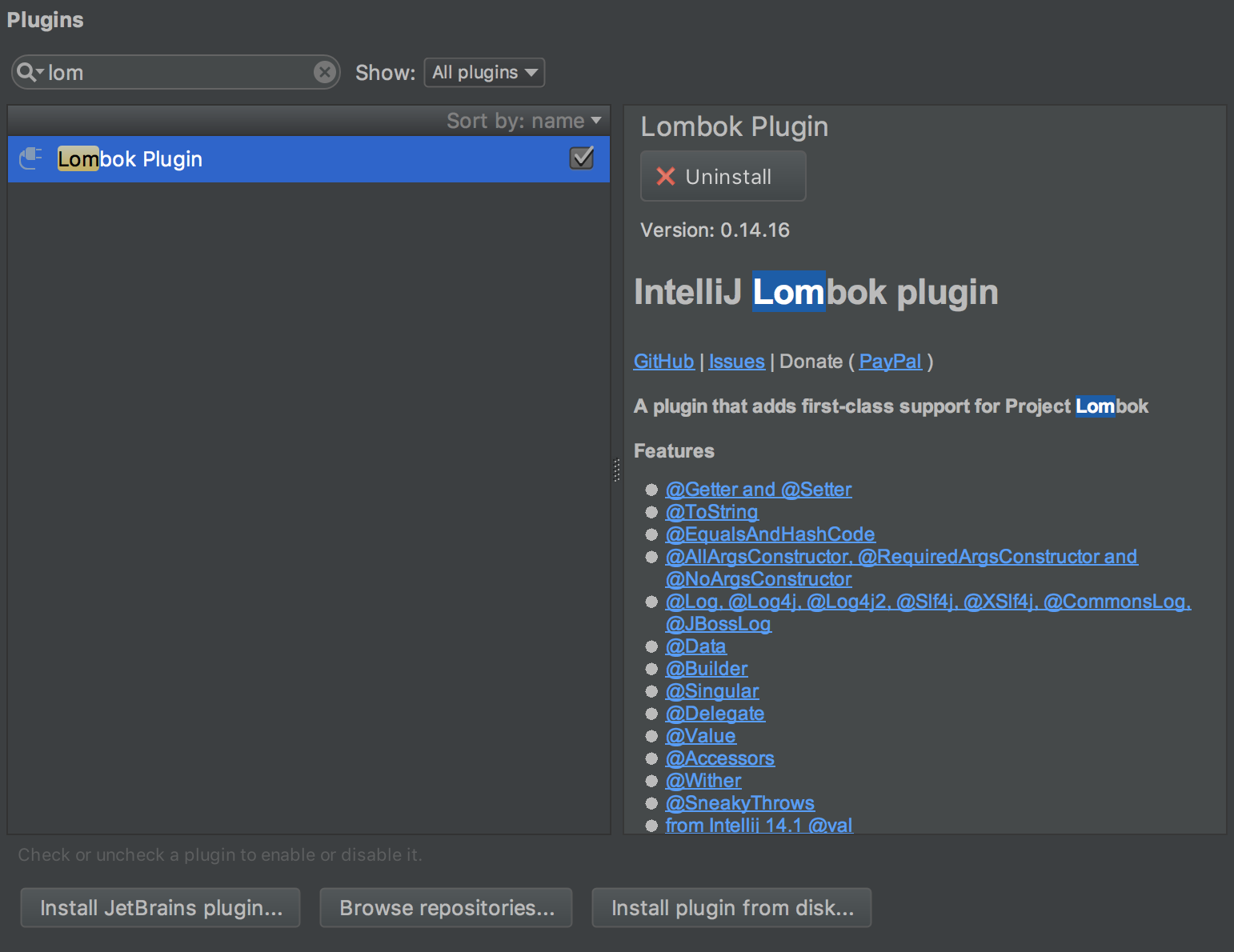
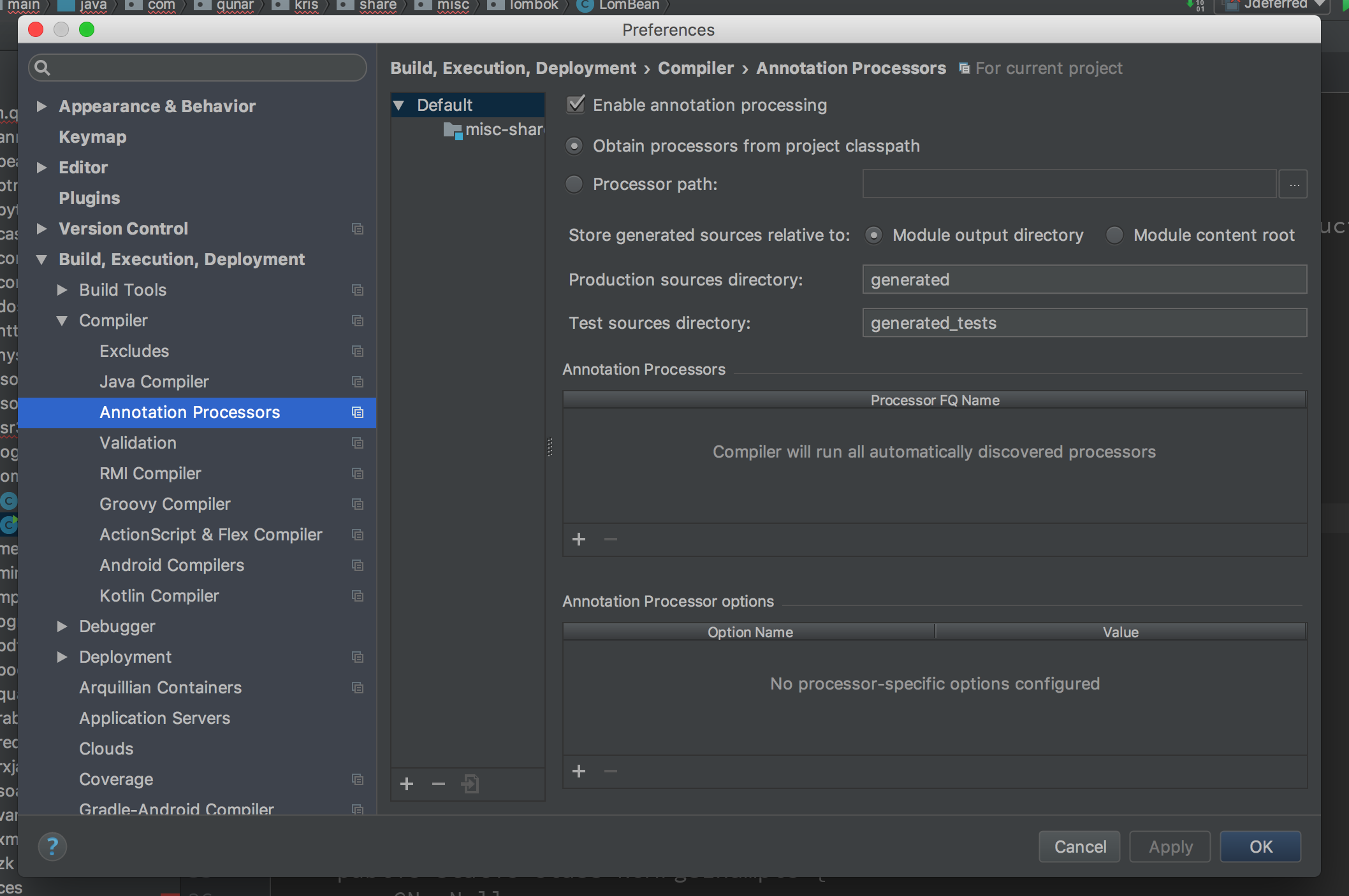
IDEA里需要在设置中启用annotation processors。
基本用法
测试代码: https://github.com/Ryan-Miao/someTest/tree/master/src/main/java/com/test/lombok
Geeter Setter
最简单的,最常用的,最直观的使用就是getter setter方法。
package com.test.lombok; import lombok.AccessLevel; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter; import java.util.Date; /** * Created by Ryan Miao on 1/18/18. */ public class GetterSetterExample { /** * Age of the person. Water is wet. * * @param age New value for this person's age. Sky is blue. * @return The current value of this person's age. Circles are round. */ @Getter @Setter private int age = 10; @Getter @Setter private boolean active; @Getter @Setter private Boolean none; @Getter @Setter private Date date; /** * Name of the person. * -- SETTER -- * Changes the name of this person. * * @param name The new value. */ @Setter(AccessLevel.PROTECTED) private String name; @Override public String toString() { return String.format("%s (age: %d)", name, age); } public static void main(String[] args) { GetterSetterExample example = new GetterSetterExample(); example.setActive(true); example.setAge(123); example.setDate(new Date()); example.setName("abc"); example.setNone(false); Date date = example.getDate(); Boolean none = example.getNone(); boolean active = example.isActive(); } }
简单使用没有问题,深入一点可以看到有些特殊设定。比如javadoc.
Getter声明创建getter方法;Setter声明创建setter方法;@Setter(AccessLevel.PROTECTED)可以添加参数,指定权限为私有;- Attention!关于
boolean的set前缀都是set,但getter不同,小写的boolean,即基本类型,前缀是is;Boolean,即包装类型,前缀是get;
编译后的结果如下:
1 // 2 // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA 3 // (powered by Fernflower decompiler) 4 // 5 6 package com.test.lombok; 7 8 import java.util.Date; 9 10 public class GetterSetterExample { 11 private int age = 10; 12 private boolean active; 13 private Boolean none; 14 private Date date; 15 private String name; 16 17 public GetterSetterExample() { 18 } 19 20 public String toString() { 21 return String.format("%s (age: %d)", this.name, this.age); 22 } 23 24 public static void main(String[] args) { 25 GetterSetterExample example = new GetterSetterExample(); 26 example.setActive(true); 27 example.setAge(123); 28 example.setDate(new Date()); 29 example.setName("abc"); 30 example.setNone(false); 31 Date date = example.getDate(); 32 Boolean none = example.getNone(); 33 boolean active = example.isActive(); 34 } 35 36 public int getAge() { 37 return this.age; 38 } 39 40 public void setAge(int age) { 41 this.age = age; 42 } 43 44 public boolean isActive() { 45 return this.active; 46 } 47 48 public void setActive(boolean active) { 49 this.active = active; 50 } 51 52 public Boolean getNone() { 53 return this.none; 54 } 55 56 public void setNone(Boolean none) { 57 this.none = none; 58 } 59 60 public Date getDate() { 61 return this.date; 62 } 63 64 public void setDate(Date date) { 65 this.date = date; 66 } 67 68 protected void setName(String name) { 69 this.name = name; 70 } 71 }
ToString
虽然ToString在生产环境貌似没什么卵用。但是,很多情况下,我们还是需要这个的。因为记log。不想每次看log的时候是一串@地址,那就好好把toString()加上。
package com.test.lombok; import lombok.Setter; import lombok.ToString; /** * Created by Ryan Miao on 1/18/18. */ @Setter @ToString(exclude="id") public class ToStringExample { private static final int STATIC_VAR = 10; private String name; private Shape shape = new Square(5, 10); private String[] tags; private int id; @ToString(callSuper=true, includeFieldNames=true) public static class Square extends Shape { private final int width, height; public Square(int width, int height) { this.width = width; this.height = height; } } @ToString public static class Shape { private int color; } public static void main(String[] args) { final ToStringExample example = new ToStringExample(); example.setId(1); example.setName("abc"); example.setTags(new String[]{"a","b","c"}); final Shape shape = new Square(1,2); example.setShape(shape); System.out.println(example.toString()); } }
1.@ToString最简单使用即可
打印结果如下:
ToStringExample(name=abc, shape=ToStringExample.Square(super=ToStringExample.Shape(color=0), width=1, height=2), tags=[a, b, c])
编译后的代码如下:
1 // 2 // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA 3 // (powered by Fernflower decompiler) 4 // 5 6 package com.test.lombok; 7 8 import java.util.Arrays; 9 10 public class ToStringExample { 11 private static final int STATIC_VAR = 10; 12 private String name; 13 private ToStringExample.Shape shape = new ToStringExample.Square(5, 10); 14 private String[] tags; 15 private int id; 16 17 public ToStringExample() { 18 } 19 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 ToStringExample example = new ToStringExample(); 22 example.setId(1); 23 example.setName("abc"); 24 example.setTags(new String[]{"a", "b", "c"}); 25 ToStringExample.Shape shape = new ToStringExample.Square(1, 2); 26 example.setShape(shape); 27 System.out.println(example.toString()); 28 } 29 30 public void setName(String name) { 31 this.name = name; 32 } 33 34 public void setShape(ToStringExample.Shape shape) { 35 this.shape = shape; 36 } 37 38 public void setTags(String[] tags) { 39 this.tags = tags; 40 } 41 42 public void setId(int id) { 43 this.id = id; 44 } 45 46 public String toString() { 47 return "ToStringExample(name=" + this.name + ", shape=" + this.shape + ", tags=" + Arrays.deepToString(this.tags) + ")"; 48 } 49 50 public static class Shape { 51 private int color; 52 53 public Shape() { 54 } 55 56 public String toString() { 57 return "ToStringExample.Shape(color=" + this.color + ")"; 58 } 59 } 60 61 public static class Square extends ToStringExample.Shape { 62 private final int width; 63 private final int height; 64 65 public Square(int width, int height) { 66 this.width = width; 67 this.height = height; 68 } 69 70 public String toString() { 71 return "ToStringExample.Square(super=" + super.toString() + ", width=" + this.width + ", height=" + this.height + ")"; 72 } 73 } 74 }
@EqualsAndHashCode
equals()和hashCode()在Java中有着举足轻重的基地作用,虽然通常很少关注。但是,这个必须不可省。不知道有几个可以手写出来的。
1 package com.test.lombok; 2 3 import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode; 4 5 /** 6 * Created by Ryan Miao on 1/18/18. 7 */ 8 @EqualsAndHashCode(exclude={"id", "shape"}) 9 public class EqualsAndHashCodeExample { 10 private transient int transientVar = 10; 11 private String name; 12 private double score; 13 private ToStringExample.Shape shape = new Square(5, 10); 14 private String[] tags; 15 private int id; 16 17 public String getName() { 18 return this.name; 19 } 20 21 @EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper=true) 22 public static class Square extends ToStringExample.Shape { 23 private final int width, height; 24 25 public Square(int width, int height) { 26 this.width = width; 27 this.height = height; 28 } 29 } 30 31 public static void main(String[] args) { 32 EqualsAndHashCodeExample example = new EqualsAndHashCodeExample(); 33 EqualsAndHashCodeExample example1 = new EqualsAndHashCodeExample(); 34 boolean equals = example.equals(example1); 35 boolean b = example.canEqual(example); 36 int i = example.hashCode(); 37 } 38 }
编译后的结果为:
1 // 2 // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA 3 // (powered by Fernflower decompiler) 4 // 5 6 package com.test.lombok; 7 8 import com.test.lombok.ToStringExample.Shape; 9 import java.util.Arrays; 10 11 public class EqualsAndHashCodeExample { 12 private transient int transientVar = 10; 13 private String name; 14 private double score; 15 private Shape shape = new EqualsAndHashCodeExample.Square(5, 10); 16 private String[] tags; 17 private int id; 18 19 public EqualsAndHashCodeExample() { 20 } 21 22 public String getName() { 23 return this.name; 24 } 25 26 public static void main(String[] args) { 27 EqualsAndHashCodeExample example = new EqualsAndHashCodeExample(); 28 EqualsAndHashCodeExample example1 = new EqualsAndHashCodeExample(); 29 example.equals(example1); 30 boolean b = example.canEqual(example); 31 int i = example.hashCode(); 32 } 33 34 public boolean equals(Object o) { 35 if (o == this) { 36 return true; 37 } else if (!(o instanceof EqualsAndHashCodeExample)) { 38 return false; 39 } else { 40 EqualsAndHashCodeExample other = (EqualsAndHashCodeExample)o; 41 if (!other.canEqual(this)) { 42 return false; 43 } else { 44 label31: { 45 Object this$name = this.getName(); 46 Object other$name = other.getName(); 47 if (this$name == null) { 48 if (other$name == null) { 49 break label31; 50 } 51 } else if (this$name.equals(other$name)) { 52 break label31; 53 } 54 55 return false; 56 } 57 58 if (Double.compare(this.score, other.score) != 0) { 59 return false; 60 } else { 61 return Arrays.deepEquals(this.tags, other.tags); 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 67 protected boolean canEqual(Object other) { 68 return other instanceof EqualsAndHashCodeExample; 69 } 70 71 public int hashCode() { 72 int PRIME = true; 73 int result = 1; 74 Object $name = this.getName(); 75 int result = result * 59 + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode()); 76 long $score = Double.doubleToLongBits(this.score); 77 result = result * 59 + (int)($score >>> 32 ^ $score); 78 result = result * 59 + Arrays.deepHashCode(this.tags); 79 return result; 80 } 81 82 public static class Square extends Shape { 83 private final int width; 84 private final int height; 85 86 public Square(int width, int height) { 87 this.width = width; 88 this.height = height; 89 } 90 91 public boolean equals(Object o) { 92 if (o == this) { 93 return true; 94 } else if (!(o instanceof EqualsAndHashCodeExample.Square)) { 95 return false; 96 } else { 97 EqualsAndHashCodeExample.Square other = (EqualsAndHashCodeExample.Square)o; 98 if (!other.canEqual(this)) { 99 return false; 100 } else if (!super.equals(o)) { 101 return false; 102 } else if (this.width != other.width) { 103 return false; 104 } else { 105 return this.height == other.height; 106 } 107 } 108 } 109 110 protected boolean canEqual(Object other) { 111 return other instanceof EqualsAndHashCodeExample.Square; 112 } 113 114 public int hashCode() { 115 int PRIME = true; 116 int result = super.hashCode(); 117 result = result * 59 + this.width; 118 result = result * 59 + this.height; 119 return result; 120 } 121 } 122 }
构造函数@NoArgsConstructor, @RequiredArgsConstructor, @AllArgsConstructor
Java中class的一切起源于构造器。大家最喜欢的还是构造函数创建对象。这里有一点比较坑的是无参构造函数。当你自己添加一个带有参数的构造函数后,无参构造函数则别隐藏。通常也没啥问题,但当你使用jackson反序列化对象的时候就被恶心到了。jackson通过无参构造函数创建对象。因此,当你考虑这个class会用来序列化为json的时候,即必须手动添加一个无参数构造函数。
@NoArgsConstructor
当你想要创建一个valueobject,DDD中的值对象,要求实现Immutable,那么无参数构造器就不合适了。@NoArgsConstructor会生成一个空的构造器。如果你设置了final field,那么编译会报错。如果你强制执行创建无参数构造器。即,@NoArgsConstructor(force = true),那么final的field会初始化为0/false/null。通常适合与@Data集成。
@NoArgsConstructor public static class NoArgsExample { @NonNull private String field; }
NonNull被忽略了
最终生成代码如下:
public static class NoArgsExample { @NonNull private String field; public NoArgsExample() { } }
对于final的字段,我认为我不会用空构造器来做这件事。所以,感觉这个参数force=true不要也罢,鸡肋。
@RequiredArgsConstructor
一个class可以有很多属性,但你可能只关心其中的几个字段,那么可以使用@RequiredArgsConstructor。@NonNull将标注这个字段不应为null,初始化的时候会检查是否为空,否则抛出NullPointException。在上面的无参构造函数中被忽略了。那么,对于关注的字段标注@NonNull, @RequiredArgsConstructor则会生成带有这些字段的构造器。
@RequiredArgsConstructor public class RequiredArgsExample { @NonNull private String field; private Date date; private Integer integer; private int i; private boolean b; private Boolean aBoolean; }
最终生成结果:
1 public class RequiredArgsExample { 2 @NonNull 3 private String field; 4 private Date date; 5 private Integer integer; 6 private int i; 7 private boolean b; 8 private Boolean aBoolean; 9 10 public RequiredArgsExample(@NonNull String field) { 11 if (field == null) { 12 throw new NullPointerException("field"); 13 } else { 14 this.field = field; 15 } 16 } 17 }
只有@NonNull会生成构造器。其他默认,Java的class初始化默认为null.false,0.
lombok提供了另一种初始化做法,静态初始化。即私有构造器,使用静态方法创建对象。这种做法看起来简单,但通常用的不多。因为静态初始化的东西很难mock,对测试不够友好。
@RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName = "of") public static class RequiredArgsStaticExample { @NonNull private String field; private Date date; private Integer integer; private int i; private boolean b; private Boolean aBoolean; }
最终生成代码如下:
public class ConstructorExample<T> { private int x; private int y; @NonNull private T description; private ConstructorExample(@NonNull T description) { if (description == null) { throw new NullPointerException("description"); } else { this.description = description; } } public static <T> ConstructorExample<T> of(@NonNull T description) { return new ConstructorExample(description); } }
@AllArgsConstructor
想要初始化所有字段。
@AllArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED) public class ConstructorExample<T> { private int x, y; @NonNull private T description; }
最终生成代码如下:
public class ConstructorExample<T> { private int x; private int y; @NonNull private T description; protected ConstructorExample(int x, int y, @NonNull T description) { if (description == null) { throw new NullPointerException("description"); } else { this.x = x; this.y = y; this.description = description; } } }
必用项@Data
@Data是一个集合体。包含Getter,Setter,RequiredArgsConstructor,ToString,EqualsAndHashCode
不可变对象valueobject @Value
这个看起来很美好,就是可以帮忙生成一个不可变对象。对于所有的字段都将生成final的。但我感觉有点失控。注解的优势应该是所见即所得,可以通过字面量来传递消息。而@Value字段给字段加final会让人困惑,因为这更改了我们的定义。当我想声明一个Immutable对象的时候,我会显示的给字段加一个限定final。
同@Data, @Value是一个集合体。包含Getter,AllArgsConstructor,ToString,EqualsAndHashCode。
/** * Created by Ryan Miao on 1/18/18. */ @Value public class Room { @NonNull private String id; private String name; private boolean active; private Date createTime; }
编译后
1 public final class Room { 2 @NonNull 3 private final String id; 4 private final String name; 5 private final boolean active; 6 private final Date createTime; 7 8 public Room(@NonNull String id, String name, boolean active, Date createTime) { 9 if (id == null) { 10 throw new NullPointerException("id"); 11 } else { 12 this.id = id; 13 this.name = name; 14 this.active = active; 15 this.createTime = createTime; 16 } 17 } 18 19 @NonNull 20 public String getId() { 21 return this.id; 22 } 23 24 public String getName() { 25 return this.name; 26 } 27 28 public boolean isActive() { 29 return this.active; 30 } 31 32 public Date getCreateTime() { 33 return this.createTime; 34 } 35 36 public boolean equals(Object o) { 37 if (o == this) { 38 return true; 39 } else if (!(o instanceof Room)) { 40 return false; 41 } else { 42 Room other = (Room)o; 43 Object this$id = this.getId(); 44 Object other$id = other.getId(); 45 if (this$id == null) { 46 if (other$id != null) { 47 return false; 48 } 49 } else if (!this$id.equals(other$id)) { 50 return false; 51 } 52 53 label41: { 54 Object this$name = this.getName(); 55 Object other$name = other.getName(); 56 if (this$name == null) { 57 if (other$name == null) { 58 break label41; 59 } 60 } else if (this$name.equals(other$name)) { 61 break label41; 62 } 63 64 return false; 65 } 66 67 if (this.isActive() != other.isActive()) { 68 return false; 69 } else { 70 Object this$createTime = this.getCreateTime(); 71 Object other$createTime = other.getCreateTime(); 72 if (this$createTime == null) { 73 if (other$createTime != null) { 74 return false; 75 } 76 } else if (!this$createTime.equals(other$createTime)) { 77 return false; 78 } 79 80 return true; 81 } 82 } 83 } 84 85 public int hashCode() { 86 int PRIME = true; 87 int result = 1; 88 Object $id = this.getId(); 89 int result = result * 59 + ($id == null ? 43 : $id.hashCode()); 90 Object $name = this.getName(); 91 result = result * 59 + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode()); 92 result = result * 59 + (this.isActive() ? 79 : 97); 93 Object $createTime = this.getCreateTime(); 94 result = result * 59 + ($createTime == null ? 43 : $createTime.hashCode()); 95 return result; 96 } 97 98 public String toString() { 99 return "Room(id=" + this.getId() + ", name=" + this.getName() + ", active=" + this.isActive() + ", createTime=" + this.getCreateTime() + ")"; 100 } 101 }
最喜欢的项 @Builder
对于喜欢builder模式的人来说,声明式简化对象创建流程让一切看得美好。但是,手动复制字段,手动创建方法很让人不喜。@Builder解决了刚需。
/** * Created by Ryan Miao on 1/18/18. */ @Data @Builder(toBuilder = true) public class Room { @NonNull private String id; private String name; private boolean active; private Date createTime; @Singular private Set<String> occupations; public static void main(String[] args) { Room room = Room.builder().active(true) .name("name") .id("id") .createTime(new Date()) .occupation("1") .occupation("2") .build(); Assert.assertEquals(2, room.getOccupations().size()); } }
这才是我们想要的建造者。对应生成的代码为:
1 // 2 // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA 3 // (powered by Fernflower decompiler) 4 // 5 6 package com.test.lombok; 7 8 import java.util.ArrayList; 9 import java.util.Collection; 10 import java.util.Collections; 11 import java.util.Date; 12 import java.util.LinkedHashSet; 13 import java.util.Set; 14 import lombok.NonNull; 15 import org.junit.Assert; 16 17 public class Room { 18 @NonNull 19 private String id; 20 private String name; 21 private boolean active; 22 private Date createTime; 23 private Set<String> occupations; 24 25 public static void main(String[] args) { 26 Room room = builder().active(true).name("name").id("id").createTime(new Date()).occupation("1").occupation("2").build(); 27 Assert.assertEquals(2L, (long)room.getOccupations().size()); 28 } 29 30 Room(@NonNull String id, String name, boolean active, Date createTime, Set<String> occupations) { 31 if (id == null) { 32 throw new NullPointerException("id"); 33 } else { 34 this.id = id; 35 this.name = name; 36 this.active = active; 37 this.createTime = createTime; 38 this.occupations = occupations; 39 } 40 } 41 42 public static Room.RoomBuilder builder() { 43 return new Room.RoomBuilder(); 44 } 45 46 public Room.RoomBuilder toBuilder() { 47 return (new Room.RoomBuilder()).id(this.id).name(this.name).active(this.active).createTime(this.createTime).occupations(this.occupations); 48 } 49 50 @NonNull 51 public String getId() { 52 return this.id; 53 } 54 55 public String getName() { 56 return this.name; 57 } 58 59 public boolean isActive() { 60 return this.active; 61 } 62 63 public Date getCreateTime() { 64 return this.createTime; 65 } 66 67 public Set<String> getOccupations() { 68 return this.occupations; 69 } 70 71 public void setId(@NonNull String id) { 72 if (id == null) { 73 throw new NullPointerException("id"); 74 } else { 75 this.id = id; 76 } 77 } 78 79 public void setName(String name) { 80 this.name = name; 81 } 82 83 public void setActive(boolean active) { 84 this.active = active; 85 } 86 87 public void setCreateTime(Date createTime) { 88 this.createTime = createTime; 89 } 90 91 public void setOccupations(Set<String> occupations) { 92 this.occupations = occupations; 93 } 94 95 public boolean equals(Object o) { 96 if (o == this) { 97 return true; 98 } else if (!(o instanceof Room)) { 99 return false; 100 } else { 101 Room other = (Room)o; 102 if (!other.canEqual(this)) { 103 return false; 104 } else { 105 label63: { 106 Object this$id = this.getId(); 107 Object other$id = other.getId(); 108 if (this$id == null) { 109 if (other$id == null) { 110 break label63; 111 } 112 } else if (this$id.equals(other$id)) { 113 break label63; 114 } 115 116 return false; 117 } 118 119 Object this$name = this.getName(); 120 Object other$name = other.getName(); 121 if (this$name == null) { 122 if (other$name != null) { 123 return false; 124 } 125 } else if (!this$name.equals(other$name)) { 126 return false; 127 } 128 129 if (this.isActive() != other.isActive()) { 130 return false; 131 } else { 132 Object this$createTime = this.getCreateTime(); 133 Object other$createTime = other.getCreateTime(); 134 if (this$createTime == null) { 135 if (other$createTime != null) { 136 return false; 137 } 138 } else if (!this$createTime.equals(other$createTime)) { 139 return false; 140 } 141 142 Object this$occupations = this.getOccupations(); 143 Object other$occupations = other.getOccupations(); 144 if (this$occupations == null) { 145 if (other$occupations != null) { 146 return false; 147 } 148 } else if (!this$occupations.equals(other$occupations)) { 149 return false; 150 } 151 152 return true; 153 } 154 } 155 } 156 } 157 158 protectedbooleancanEqual(Object other) { 159 return other instanceof Room; 160 } 161 162 publicinthashCode() { 163 int PRIME = true; 164 int result = 1; 165 Object $id = this.getId(); 166 int result = result * 59 + ($id == null ? 43 : $id.hashCode()); 167 Object $name = this.getName(); 168 result = result * 59 + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode()); 169 result = result * 59 + (this.isActive() ? 79 : 97); 170 Object $createTime = this.getCreateTime(); 171 result = result * 59 + ($createTime == null ? 43 : $createTime.hashCode()); 172 Object $occupations = this.getOccupations(); 173 result = result * 59 + ($occupations == null ? 43 : $occupations.hashCode()); 174 return result; 175 } 176 177 public String toString() { 178 return "Room(id=" + this.getId() + ", name=" + this.getName() + ", active=" + this.isActive() + ", createTime=" + this.getCreateTime() + ", occupations=" + this.getOccupations() + ")"; 179 } 180 181 public static classRoomBuilder { 182 private String id; 183 private String name; 184 private boolean active; 185 private Date createTime; 186 private ArrayList<String> occupations; 187 188 RoomBuilder() { 189 } 190 191 public Room.RoomBuilderid(String id) { 192 this.id = id; 193 return this; 194 } 195 196 public Room.RoomBuildername(String name) { 197 this.name = name; 198 return this; 199 } 200 201 public Room.RoomBuilderactive(boolean active) { 202 this.active = active; 203 return this; 204 } 205 206 public Room.RoomBuildercreateTime(Date createTime) { 207 this.createTime = createTime; 208 return this; 209 } 210 211 public Room.RoomBuilderoccupation(String occupation) { 212 if (this.occupations == null) { 213 this.occupations = new ArrayList(); 214 } 215 216 this.occupations.add(occupation); 217 return this; 218 } 219 220 public Room.RoomBuilderoccupations(Collection<? extends String> occupations) { 221 if (this.occupations == null) { 222 this.occupations = new ArrayList(); 223 } 224 225 this.occupations.addAll(occupations); 226 return this; 227 } 228 229 public Room.RoomBuilderclearOccupations() { 230 if (this.occupations != null) { 231 this.occupations.clear(); 232 } 233 234 return this; 235 } 236 237 public Room build() { 238 Set occupations; 239 switch(this.occupations == null ? 0 : this.occupations.size()) { 240 case 0: 241 occupations = Collections.emptySet(); 242 break; 243 case 1: 244 occupations = Collections.singleton(this.occupations.get(0)); 245 break; 246 default: 247 Set<String> occupations = new LinkedHashSet(this.occupations.size() < 1073741824 ? 1 + this.occupations.size() + (this.occupations.size() - 3) / 3 : 2147483647); 248 occupations.addAll(this.occupations); 249 occupations = Collections.unmodifiableSet(occupations); 250 } 251 252 return new Room(this.id, this.name, this.active, this.createTime, occupations); 253 } 254 255 public String toString() { 256 return "Room.RoomBuilder(id=" + this.id + ", name=" + this.name + ", active=" + this.active + ", createTime=" + this.createTime + ", occupations=" + this.occupations + ")"; 257 } 258 } 259 }
总结
lombok还提供了其他几个注解,以及还有好多内置的参数没有讲解。但是,根据2-8原理,我们根本不需要。上面这几个足够了。更多的注解只会增加理解阅读难度。
参考
https://projectlombok.org/features/all


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号