Blog-2总结
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String sc = input.nextLine(); String[] a = new String[10]; int flag = 0; int m = 0; int j = 0; int res = 0; int count = 0; for(int i = 0; i < sc.length() ;i++) { if(sc.charAt(i) == '+' || sc.charAt(i) == '-' ) { if(sc.charAt(i+1) == '+'|| sc.charAt(i+1) == '-') { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); flag = 1; break; } } } for(int i = 0; i < sc.length() ;i++) { if(sc.charAt(i) == '0' && sc.charAt(i+1) == '0') { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); flag = 1; break; } } for(int i = 0; i < sc.length() ;i++) { if(sc.charAt(i) == '.' && sc.charAt(i+1) == ' ') { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); flag = 1; break; } } for(int i = 0; i < sc.length() ;i++) { if(sc.charAt(i) == ',' || sc.charAt(i) == ' ') { a[j] = sc.substring(m,i); m = i + 1; j++; res = i; } } for(int i = 0; i < sc.length() ;i++) { if(sc.charAt(i) == ' ') { count++; } } if(j >= 4 && flag == 0) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); } else if(count != 1){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } if(flag == 0 && j == 3){ a[3] = sc.substring(res+1,sc.length()); double x1 = Double.parseDouble(a[0]); double y1 = Double.parseDouble(a[1]); double x2 = Double.parseDouble(a[2]); double y2 = Double.parseDouble(a[3]); Distance dis = new Distance(x1,y1,x2,y2); dis.distance(); } } } class Distance{ private double x1; private double y1; private double x2; private double y2; public Distance() { super(); } public Distance(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) { super(); this.x1 = x1; this.y1 = y1; this.x2 = x2; this.y2 = y2; } public double getX1() { return x1; } public void setX1(double x1) { this.x1 = x1; } public double getY1() { return y1; } public void setY1(double y1) { this.y1 = y1; } public double getX2() { return x2; } public void setX2(double x2) { this.x2 = x2; } public double getY2() { return y2; } public void setY2(double y2) { this.y2 = y2; } public void distance() { double distance = 0; distance = Math.sqrt((x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(y1-y2)*(y1-y2)); System.out.println(distance); } }
题目分析:本道题目写的时候因为没有学习正则表达式而导致每一个非法输入都需要去尝试,除此之外本题采用了两个类的形式,其中计算点到直线的距离写在Distance类中,在主类中进行非法输入和非法数量的判断。
采坑心得:非法输入永远的痛,其他的倒是没错什么,非法输入后面过不了,一个一个的试出来了。
7-2 点线形系列2-线的计算
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String sc = input.nextLine(); int flag = 0; int count = 0; int j =0; int m = 2; int res = 0; String[] a = new String[10]; if(sc.charAt(0) <= 0 && sc.charAt(0) >=6 ){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } if(sc.charAt(1) != ':'){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } for(int i = 2; i < sc.length() ;i++){ if(sc.charAt(i) == ' ') { count++; } } for(int k = 2; k < sc.length() ;k++) { if(sc.charAt(k) == ',' || sc.charAt(k) == ' ') { a[j] = sc.substring(m,k); m = k + 1; j++; res = k; } } if(j == 3) { a[3] = sc.substring(res+1,sc.length()); double x1 = Double.parseDouble(a[0]); double y1 = Double.parseDouble(a[1]); double x2 = Double.parseDouble(a[2]); double y2 = Double.parseDouble(a[3]); for(int i = 0; i < sc.length(); i++) { if(sc.charAt(i) == ':' && sc.charAt(i-1) == '1') { Point point = new Point(x1,y1,x2,y2); point.slope(); } if(count == 2){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); } } } else if(j == 5) { a[5] = sc.substring(res+1,sc.length()); double x1 = Double.parseDouble(a[0]); double y1 = Double.parseDouble(a[1]); double x2 = Double.parseDouble(a[2]); double y2 = Double.parseDouble(a[3]); double x3 = Double.parseDouble(a[4]); double y3 = Double.parseDouble(a[5]); if(sc.charAt(0) == '2') { Point point = new Point(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3); point.threePointDistance(); } if(sc.charAt(0) == '3') { Point point = new Point(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3); point.threePointLine(); } if (count == 3){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); } } else if(j == 7) { a[7] = sc.substring(res+1,sc.length()); double x1 = Double.parseDouble(a[0]); double y1 = Double.parseDouble(a[1]); double x2 = Double.parseDouble(a[2]); double y2 = Double.parseDouble(a[3]); double x3 = Double.parseDouble(a[4]); double y3 = Double.parseDouble(a[5]); double x4 = Double.parseDouble(a[6]); double y4 = Double.parseDouble(a[7]); if(sc.charAt(0) == '4') { Point point = new Point(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4); point.fourPointParallel(); } if(sc.charAt(0) == '5') { Point point = new Point(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4); point.intersection(); } if(count == 4){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); } } else if(j >= 8) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); } } } class Point{ private double x1; private double y1; private double x2; private double y2; private double x3; private double y3; private double x4; private double y4; public Point() { super(); } public Point(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) { super(); this.x1 = x1; this.y1 = y1; this.x2 = x2; this.y2 = y2; } public Point(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2, double x3, double y3) { super(); this.x1 = x1; this.y1 = y1; this.x2 = x2; this.y2 = y2; this.x3 = x3; this.y3 = y3; } public Point(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2, double x3, double y3, double x4, double y4) { super(); this.x1 = x1; this.y1 = y1; this.x2 = x2; this.y2 = y2; this.x3 = x3; this.y3 = y3; this.x4 = x4; this.y4 = y4; } public double getX1() { return x1; } public void setX1(double x1) { this.x1 = x1; } public double getY1() { return y1; } public void setY1(double y1) { this.y1 = y1; } public double getX2() { return x2; } public void setX2(double x2) { this.x2 = x2; } public double getY2() { return y2; } public void setY2(double y2) { this.y2 = y2; } public double getX3() { return x3; } public void setX3(double x3) { this.x3 = x3; } public double getY3() { return y3; } public void setY3(double y3) { this.y3 = y3; } public double getX4() { return x4; } public void setX4(double x4) { this.x4 = x4; } public double getY4() { return y4; } public void setY4(double y4) { this.y4 = y4; } public boolean superposition(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2){ if(x1 == x2 && y1 == y2){ return true; } else{ return false; } } public void slope() {//斜率 double k = 0; k = (y1 - y2)/(x1 - x2); if(superposition(x1,y1,x2,y2)){ System.out.println("points coincide"); } else{ if(x1 == x2){ System.out.println("Slope does not exist"); } else{ System.out.println(k); } } } public void threePointDistance() { double distance = 0; distance = Math.abs((y2 - y3)*x1+(x3-x2)*y1+x2*y3-y2*x3)/Math.sqrt((y2 - y3) *(y2 - y3)+(x2-x3)*(x2-x3)); if(!superposition(x2,y2,x3,y3)) { System.out.println(distance); } else{ System.out.println("points coincide"); } } public void threePointLine() { double k1=0; double k2=0; k1 = (y1-y2)/(x1-x2); k2 = (y2-y3)/(x2-x3); if (!superposition(x1, y1, x2, y2) && !superposition(x4, y4, x3, y3)){ if (x1==x2 && x3 == x4){ System.out.println("true"); } else{ if (k1 == k2){ System.out.println("true"); } else{ System.out.println("false"); } } } else{ System.out.println("points coincide"); } } public void fourPointParallel() { if(superposition(x1,y1,x2,y2) || superposition(x3,y3,x4,y4)){ System.out.println("points coincide"); } else{ if((x1-x2)*(y3-y4)-(x3-x4)*(y1-y2)==0){ System.out.println("true"); } else{ System.out.println("false"); } } } public double max(double x1,double x2) { if(x1 > x2) { return x1; } else { return x2; } } public double min(double x1,double x2) { if(x1 > x2) { return x2; } else { return x1; } } public boolean check(double x,double y) { double max1 = max(x1, x2); double max2 = max(x3, x4); double min1 = min(x1, x2); double min2 = min(x3, x4); if ((x > min1 || x > min2) && (x < max2 || x < max1)) { return true; } else { return false; } } public void intersection(){ double k1 = 0; double k2 = 0; double x = (y3*x2*x4-x3*y4*x2-y3*x1*x4+y4*x1*x3-y1*x4*x2+y2*x4*x1+y1*x2*x3-y2*x1*x3)/(x4*y2-x4*y1-x3*y2+x3*y1-x2*y4+x2*y3+x1*y4-x1*y3); double y = (-y2*x4*y3+y2*x3*y4+y3*x4*y1-y4*x3*y1+y4*x2*y1-y1*x2*y3-y4*x1*y2+y2*x1*y3)/(y4*x2-y4*x1-y3*x2+x1*y3-y2*x4+y2*x3+y1*x4-y1*x3); k1 = (y1-y2)/(x1-x2); k2 = (y4-y3)/(x4-x3); if(superposition(x1,y1,x2,y2) || superposition(x3,y3,x4,y4)){ System.out.println("points coincide"); } else{ if (k1 == k2 || (x1 == x2 && x3 == x4)){ System.out.println("is parallel lines,have no intersection point"); } else { System.out.println(x+","+y+" "+check(x,y)); } } } }
题目分析:本题采用两个类的形式,依然与第一题类似,主类判断,Point类来进行所需要的方法的编写,方法的编写并不是很难,难度依旧在于非法的判断。
采坑心得:这题与第一题相似,写这种题目的时候一定要想好正则表达式怎么写,要不然非法输入完全过不了。
源码如下:
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String sc = input.nextLine();
int count = 0;
int j =0;
int m = 2;
int res = 0;
String[] a = new String[10];
if(sc.charAt(0) <= 0 && sc.charAt(0) >=6 ){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return;
}
if(sc.charAt(1) != ':'){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return;
}
for(int i = 2; i < sc.length() ;i++){
if(sc.charAt(i) == ' ') {
count++;
}
}
for(int k = 2; k < sc.length() ;k++) {
if(sc.charAt(k) == ',' || sc.charAt(k) == ' ') {
a[j] = sc.substring(m,k);
m = k + 1;
j++;
res = k;
}
}
if(j == 5) {
a[5] = sc.substring(res+1,sc.length());
double x1 = Double.parseDouble(a[0]);
double y1 = Double.parseDouble(a[1]);
double x2 = Double.parseDouble(a[2]);
double y2 = Double.parseDouble(a[3]);
double x3 = Double.parseDouble(a[4]);
double y3 = Double.parseDouble(a[5]);
if(sc.charAt(0) == '1') {
Point point = new Point(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3);
point.threeTriangle();
}
if(sc.charAt(0) == '2') {
Point point = new Point(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3);
point.threeDate();
}
if(sc.charAt(0) == '3') {
Point point = new Point(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3);
point.judgeThreeTriangle();
}
}
else if(j == 7) {
a[7] = sc.substring(res+1,sc.length());
double x1 = Double.parseDouble(a[0]);
double y1 = Double.parseDouble(a[1]);
double x2 = Double.parseDouble(a[2]);
double y2 = Double.parseDouble(a[3]);
double x3 = Double.parseDouble(a[4]);
double y3 = Double.parseDouble(a[5]);
double x4 = Double.parseDouble(a[6]);
double y4 = Double.parseDouble(a[7]);
if(sc.charAt(0) == '5') {
Point point = new Point(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4);
point.fourPoint();
}
}
else if(j == 9) {
a[9] = sc.substring(res+1,sc.length());
double x1 = Double.parseDouble(a[0]);
double y1 = Double.parseDouble(a[1]);
double x2 = Double.parseDouble(a[2]);
double y2 = Double.parseDouble(a[3]);
double x3 = Double.parseDouble(a[4]);
double y3 = Double.parseDouble(a[5]);
double x4 = Double.parseDouble(a[6]);
double y4 = Double.parseDouble(a[7]);
double x5 = Double.parseDouble(a[8]);
double y5 = Double.parseDouble(a[9]);
if(sc.charAt(0) == '4') {
Point point = new Point(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4,x5,y5);
point.five();
}
}
else if(j >= 10) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
}
}
}
class Point{
private double x1;
private double y1;
private double x2;
private double y2;
private double x3;
private double y3;
private double x4;
private double y4;
private double x5;
private double y5;
public Point() {
super();
}
public Point(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2, double x3, double y3) {
super();
this.x1 = x1;
this.y1 = y1;
this.x2 = x2;
this.y2 = y2;
this.x3 = x3;
this.y3 = y3;
}
public Point(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2, double x3, double y3, double x4, double y4) {
super();
this.x1 = x1;
this.y1 = y1;
this.x2 = x2;
this.y2 = y2;
this.x3 = x3;
this.y3 = y3;
this.x4 = x4;
this.y4 = y4;
}
public Point(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2, double x3, double y3, double x4, double y4, double x5,
double y5) {
super();
this.x1 = x1;
this.y1 = y1;
this.x2 = x2;
this.y2 = y2;
this.x3 = x3;
this.y3 = y3;
this.x4 = x4;
this.y4 = y4;
this.x5 = x5;
this.y5 = y5;
}
public double getX1() {
return x1;
}
public void setX1(double x1) {
this.x1 = x1;
}
public double getY1() {
return y1;
}
public void setY1(double y1) {
this.y1 = y1;
}
public double getX2() {
return x2;
}
public void setX2(double x2) {
this.x2 = x2;
}
public double getY2() {
return y2;
}
public void setY2(double y2) {
this.y2 = y2;
}
public double getX3() {
return x3;
}
public void setX3(double x3) {
this.x3 = x3;
}
public double getY3() {
return y3;
}
public void setY3(double y3) {
this.y3 = y3;
}
public double getX4() {
return x4;
}
public void setX4(double x4) {
this.x4 = x4;
}
public double getY4() {
return y4;
}
public void setY4(double y4) {
this.y4 = y4;
}
public double getX5() {
return x5;
}
public void setX5(double x5) {
this.x5 = x5;
}
public double getY5() {
return y5;
}
public void setY5(double y5) {
this.y5 = y5;
}
public boolean superposition(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2){
if(x1 == x2 && y1 == y2){
return true;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
public boolean triangle(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3)
{
double a = 0;
double b = 0;
double c = 0;
a = Math.sqrt((x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2));
b = Math.sqrt((x1 - x3) * (x1 - x3) + (y1 - y3) * (y1 - y3));
c = Math.sqrt((x3 - x2) * (x3 - x2) + (y3 - y2) * (y3 - y2));
if (a + b > c && a + c > b && b + c > a ) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
public void threeTriangle() {
double a = 0;
double b = 0;
double c = 0;
a = Math.sqrt((x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2));
b = Math.sqrt((x1 - x3) * (x1 - x3) + (y1 - y3) * (y1 - y3));
c = Math.sqrt((x3 - x2) * (x3 - x2) + (y3 - y2) * (y3 - y2));
if(!triangle(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3)) {
System.out.println("data error");
}
else{
if(a == b || a == c || b == c) {
System.out.print("true ");
}
else {
System.out.print("false ");
}
if(a == b && a == c && b == c) {
System.out.print("true");
}
else {
System.out.print("false");
}
}
}
public void threeDate() {
double a = Math.sqrt((x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2));
double b = Math.sqrt((x1 - x3) * (x1 - x3) + (y1 - y3) * (y1 - y3));
double c = Math.sqrt((x3 - x2) * (x3 - x2) + (y3 - y2) * (y3 - y2));
double C = a + b + c;
double p = C / 2;
double S = Math.sqrt(p * (p - a) * (p - b) * (p - c));
double x = (x1 + x2 + x3) / 3;
double y = (y1 + y2 + y3) / 3;
if(!triangle(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3)) {
System.out.println("data error");
}
else {
System.out.printf(new DecimalFormat("0.0#####").format(C));
System.out.print(" ");
System.out.printf(new DecimalFormat("0.0#####").format(S));
System.out.print(" ");
System.out.printf(new DecimalFormat("0.0#####").format(x));
System.out.print(",");
System.out.printf(new DecimalFormat("0.0#####").format(y));
}
}
public void judgeThreeTriangle() {
double a = Math.sqrt((x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2));
double b = Math.sqrt((x1 - x3) * (x1 - x3) + (y1 - y3) * (y1 - y3));
double c = Math.sqrt((x3 - x2) * (x3 - x2) + (y3 - y2) * (y3 - y2));
double cosa = (b * b + c * c - a * a) / (2 * b * c);
double cosb = (a * a + c * c - b * b) / (2 * a * c);
double cosc = (a * a + b * b - c * c) / (2 * a * b);
if(cosa > 0 && cosb > 0 && cosc > 0){
System.out.println("false false true");
}
else if(cosa == 0 || cosb == 0 || cosc == 0){
System.out.println("false true false");
}
else{
System.out.println("true false false");
}
}
public double triAngleArea(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2, double x3, double y3) {
double a = Math.sqrt((x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2));
double b = Math.sqrt((x1 - x3) * (x1 - x3) + (y1 - y3) * (y1 - y3));
double c = Math.sqrt((x3 - x2) * (x3 - x2) + (y3 - y2) * (y3 - y2));
double C = a + b + c;
double p = C / 2;
double S = Math.abs(Math.sqrt(p * (p - a) * (p - b) * (p - c))/2.0D);
return S;
}
public void five() {
if(superposition(x1, y1, x2, y2)) {
System.out.println("points coincide");
}
else if(!triangle(x3, y3, x4, y4, x5, y5)) {
System.out.println("data error");
}
else{
System.out.println("The point is on the edge of the triangle");
}
}
public void fourPoint() {
double ab,ad,ac,bc,bd,cd;
ab = Math.sqrt((x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2));
ad = Math.sqrt((x1 - x4) * (x1 - x4) + (y1 - y4) * (y1 - y4));
ac = Math.sqrt((x1 - x3) * (x1 - x3) + (y1 - y3) * (y1 - y3));
bc = Math.sqrt((x2 - x3) * (x2 - x3) + (y2 - y3) * (y2 - y3));
bd = Math.sqrt((x2 - x4) * (x2 - x4) + (y2 - y4) * (y2 - y4));
cd = Math.sqrt((x3 - x4) * (x3 - x4) + (y3 - y4) * (y3 - y4));
if(!triangle(x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4)) {
System.out.println("data error");
}
else {
double S = triAngleArea(x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4);
double S1 = triAngleArea(x2,y2,x3,y3,x1,y1);
double S2 = triAngleArea(x2,y2,x4,y4,x1,y1);
double S3 = triAngleArea(x3,y3,x4,y4,x1,y1);
double sumOther = S1 + S2 + S3;
if(ab + ad == bd || ab + ac == bc || ad + ac == cd || superposition(x1, y1, x2, y2) || superposition(x1, y1, x3, y3) || superposition(x1, y1, x4, y4) ){
System.out.println("on the triangle");
}
else if ((S - sumOther) >= -0.000001 && (S - sumOther) <= 0.000001) {
System.out.println("in the triangle");
}
else{
System.out.println("outof the triangle");
}
}
}
}
类图:
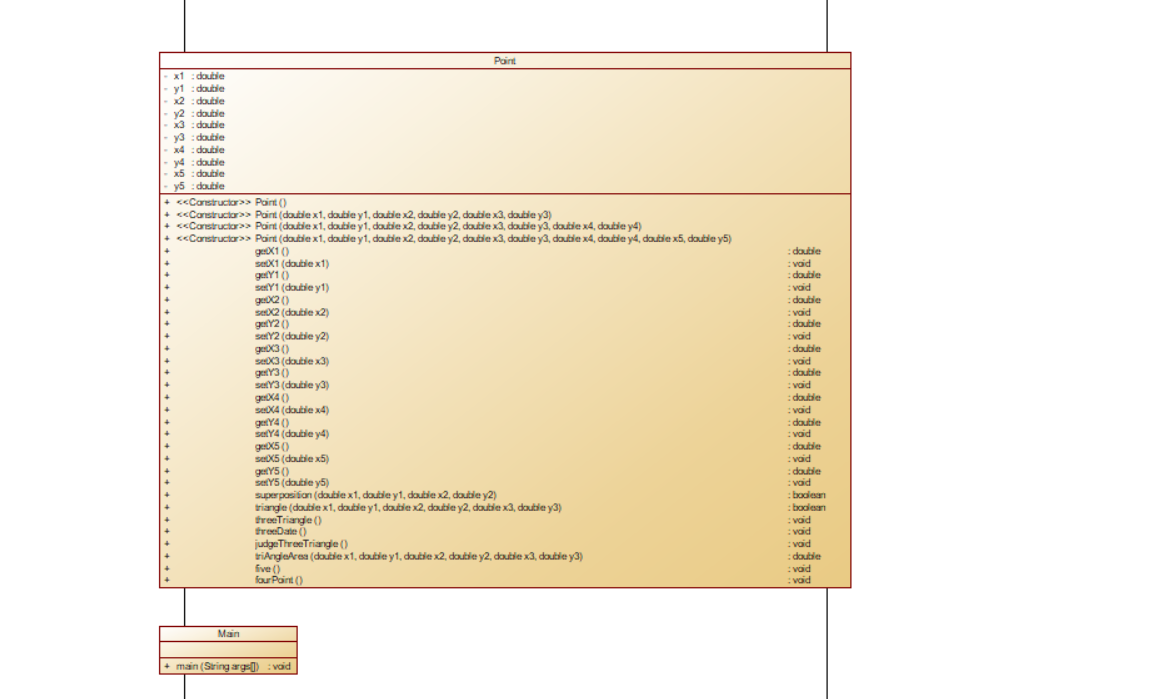
题目分析:本次题目分为两个类,主类和Point类,在Point类中设置10个私有属性,并选择题目中相对应的构造方法来调用方法,在主类一个一个的判断非法和点的数量错误(这里非法错误未对)所以不进行分析了。Point类中的导入import java.text.DecimalFormat,来进行数字的取舍,其余的根据类图来一一编写即可。
采坑心得:本次题目集因为未学习正则表达式导致非法输入都出现了不同的问题,所以写这种对字符串处理的题目一定要先想好正则表达式,对于这道题目来说,除了选项四、五把其他几个选项看清楚,基本都能直接写出,选项5的话使用的是面积法写的。
源码如下:
import java.util.Objects; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String sc = input.nextLine(); String regex1 = "(\\d{19})+\\s+(\\d{8})+\\s+(\\d{2})+\\s+(-?\\d+\\.?\\d{2})"; String regex2 = "\\d{19}"; int flag = 0; Pattern pattern1 = Pattern.compile(regex1); Pattern pattern2 = Pattern.compile(regex2); BankAccount account[] = new BankAccount[8]; account[0] = new BankAccount("中国建设银行","3217000010041315709",10000); account[1] = new BankAccount("中国建设银行","3217000010041315715",10000); account[2] = new BankAccount("中国建设银行","3217000010051320007",10000); account[3] = new BankAccount("中国工商银行","3222081502001312389",10000); account[4] = new BankAccount("中国工商银行","3222081502001312390",10000); account[5] = new BankAccount("中国工商银行","3222081502001312399",10000); account[6] = new BankAccount("中国工商银行","3222081502051320785",10000); account[7] = new BankAccount("中国工商银行","3222081502051320786",10000); Users user[] = new Users[10]; user[0] = new Users("6217000010041315709","杨过"); user[1] = new Users("6217000010041315715","杨过"); user[2] = new Users("6217000010041315718","杨过"); user[3] = new Users("6217000010051320007","郭靖"); user[4] = new Users("6222081502001312389","张无忌"); user[5] = new Users("6222081502001312390","张无忌"); user[6] = new Users("6222081502001312399","张无忌"); user[7] = new Users("6222081502001312400","张无忌"); user[8] = new Users("6222081502051320785","韦小宝"); user[9] = new Users("6222081502051320786","韦小宝"); while(!sc.equals("#")) { Matcher matcher = pattern1.matcher(sc); Matcher matcher2 = pattern2.matcher(sc); if(matcher.find()) { String idCard = matcher.group(1); double passWord = Double.parseDouble(matcher.group(2)); int atmnums = Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(3)); double money = Double.parseDouble(matcher.group(4)); int count = 0; for(int i = 0; i <= 9; i++) { if(Objects.equals(user[i].getIdCard(),idCard)) { int k = i; if(passWord == 88888888){ if(atmnums < 1 || atmnums > 6) { System.out.println("Sorry,the ATM's id is wrong."); break; } if((i <= 3 && atmnums > 4)||(i > 3 && atmnums <= 4)){ System.out.println("Sorry,cross-bank withdrawal is not supported."); break; } else { if(i == 0 || i == 1) { if(Math.abs(money) > account[0].getBalance()) { System.out.println("Sorry,your account balance is insufficient."); break; } else { if(money > 0) { account[0].setBalance(account[0].getBalance() - money); System.out.println(user[k].getName()+"在"+account[0].getbankName()+"的0"+atmnums+"号ATM机上取款¥"+Math.abs(money)+"0"); System.out.println("当前余额为¥"+account[0].getBalance()+"0"); } else { account[0].setBalance(account[0].getBalance() - money); System.out.println(user[k].getName()+"在"+account[0].getbankName()+"的0"+atmnums+"号ATM机上存款¥"+Math.abs(money)+"0"); System.out.println("当前余额为¥"+account[0].getBalance()+"0"); } } break; } else if(i == 2) { if(Math.abs(money) > account[0].getBalance()) { System.out.println("Sorry,your account balance is insufficient."); } else { if(money > 0) { account[1].setBalance(account[1].getBalance() - money); System.out.println(user[k].getName()+"在"+account[1].getbankName()+"的0"+atmnums+"号ATM机上取款¥"+Math.abs(money)+"0"); System.out.println("当前余额为¥"+account[1].getBalance()+"0"); } else { account[0].setBalance(account[1].getBalance() - money); System.out.println(user[k].getName()+"在"+account[1].getbankName()+"的0"+atmnums+"号ATM机上存款¥"+Math.abs(money)+"0"); System.out.println("当前余额为¥"+account[1].getBalance()+"0"); } } break; } else if(i == 3) { if(Math.abs(money) > account[0].getBalance()) { System.out.println("Sorry,your account balance is insufficient."); } else { if(money > 0) { account[2].setBalance(account[2].getBalance() - money); System.out.println(user[k].getName()+"在"+account[2].getbankName()+"的0"+atmnums+"号ATM机上取款¥"+Math.abs(money)+"0"); System.out.println("当前余额为¥"+account[2].getBalance()+"0"); } else { account[2].setBalance(account[2].getBalance() - money); System.out.println(user[k].getName()+"在"+account[2].getbankName()+"的0"+atmnums+"号ATM机上存款¥"+Math.abs(money)+"0"); System.out.println("当前余额为¥"+account[2].getBalance()+"0"); } } break; } else if(i == 4) { if(Math.abs(money) > account[0].getBalance()) { System.out.println("Sorry,your account balance is insufficient."); } else { if(money > 0) { account[3].setBalance(account[3].getBalance() - money); System.out.println(user[k].getName()+"在"+account[3].getbankName()+"的0"+atmnums+"号ATM机上取款¥"+Math.abs(money)+"0"); System.out.println("当前余额为¥"+account[3].getBalance()+"0"); } else { account[3].setBalance(account[3].getBalance() - money); System.out.println(user[k].getName()+"在"+account[3].getbankName()+"的0"+atmnums+"号ATM机上存款¥"+Math.abs(money)+"0"); System.out.println("当前余额为¥"+account[3].getBalance()+"0"); } } break; } else if(i == 5) { if(Math.abs(money) > account[0].getBalance()) { System.out.println("Sorry,your account balance is insufficient."); } else { if(money > 0) { account[4].setBalance(account[4].getBalance() - money); System.out.println(user[k].getName()+"在"+account[4].getbankName()+"的0"+atmnums+"号ATM机上取款¥"+Math.abs(money)+"0"); System.out.println("当前余额为¥"+account[4].getBalance()+"0"); } else { account[4].setBalance(account[4].getBalance() - money); System.out.println(user[k].getName()+"在"+account[4].getbankName()+"的0"+atmnums+"号ATM机上存款¥"+Math.abs(money)+"0"); System.out.println("当前余额为¥"+account[4].getBalance()+"0"); } } break; } else if(i == 6 || i == 7) { if(Math.abs(money) > account[0].getBalance()) { System.out.println("Sorry,your account balance is insufficient."); } else { if(money > 0) { account[5].setBalance(account[5].getBalance() - money); System.out.println(user[k].getName()+"在"+account[5].getbankName()+"的0"+atmnums+"号ATM机上取款¥"+Math.abs(money)+"0"); System.out.println("当前余额为¥"+account[5].getBalance()+"0"); } else { account[5].setBalance(account[5].getBalance() - money); System.out.println(user[k].getName()+"在"+account[5].getbankName()+"的0"+atmnums+"号ATM机上存款¥"+Math.abs(money)+"0"); System.out.println("当前余额为¥"+account[5].getBalance()+"0"); } } break; } else if (i == 8) { if(Math.abs(money) > account[0].getBalance()) { System.out.println("Sorry,your account balance is insufficient."); } else { if(money > 0) { account[6].setBalance(account[6].getBalance() - money); System.out.println(user[k].getName()+"在"+account[6].getbankName()+"的0"+atmnums+"号ATM机上取款¥"+Math.abs(money)+"0"); System.out.println("当前余额为¥"+account[6].getBalance()+"0"); } else { account[6].setBalance(account[6].getBalance() - money); System.out.println(user[k].getName()+"在"+account[6].getbankName()+"的0"+atmnums+"号ATM机上存款¥"+Math.abs(money)+"0"); System.out.println("当前余额为¥"+account[6].getBalance()+"0"); } } break; } else if (i == 9) { if(Math.abs(money) > account[0].getBalance()) { System.out.println("Sorry,your account balance is insufficient."); } else { if(money > 0) { account[7].setBalance(account[7].getBalance() - money); System.out.println(user[k].getName()+"在"+account[7].getbankName()+"的0"+atmnums+"号ATM机上取款¥"+Math.abs(money)+"0"); System.out.println("当前余额为¥"+account[7].getBalance()+"0"); } else { account[7].setBalance(account[7].getBalance() - money); System.out.println(user[k].getName()+"在"+account[7].getbankName()+"的0"+atmnums+"号ATM机上存款¥"+Math.abs(money)+"0"); System.out.println("当前余额为¥"+account[7].getBalance()+"0"); } } break; } } } else { System.out.println("Sorry,your password is wrong."); break; } } else { count++; } } if(count == 10) { System.out.println("Sorry,this card does not exist."); break; } } else { if(matcher2.find()) { String idCard = matcher2.group(0); int count = 0; for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { if(Objects.equals(user[i].getIdCard(),idCard)) { if(i == 0 || i == 1) { System.out.println("¥"+account[0].getBalance()+"0"); } else if(i == 2) { System.out.println("¥"+account[1].getBalance()+"0"); } else if(i == 3) { System.out.println("¥"+account[2].getBalance()+"0"); } else if(i == 4) { System.out.println("¥"+account[3].getBalance()+"0"); } else if(i == 5) { System.out.println("¥"+account[4].getBalance()+"0"); } else if(i == 6 || i == 7) { System.out.println("¥"+account[5].getBalance()+"0"); } else if(i == 8) { System.out.println("¥"+account[6].getBalance()+"0"); } else if(i == 9) { System.out.println("¥"+account[7].getBalance()+"0"); } } else { count++; } } if(count == 10) { System.out.println("Sorry,this card does not exist."); } } } sc = input.nextLine(); } } } class BankAccount{ private String bankName; private String bankAccountId; private double balance; public BankAccount() { super(); } public BankAccount(String bankName, String bankAccountId, double balance) { super(); this.bankName = bankName; this.bankAccountId = bankAccountId; this.balance = balance; } public String getbankName() { return bankName; } public void setbankName(String bankName) { this.bankName = bankName; } public String getBankAccountId() { return bankAccountId; } public void setBankAccountId(String bankAccountId) { this.bankAccountId = bankAccountId; } public double getBalance() { return balance; } public void setBalance(double balance) { this.balance = balance; } } class Users{ private String idCard; private String name; public Users() { super(); } public Users(String idCard, String name) { super(); this.idCard = idCard; this.name = name; } public String getIdCard() { return idCard; } public void setIdCard(String idCard) { this.idCard = idCard; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
类图如下:
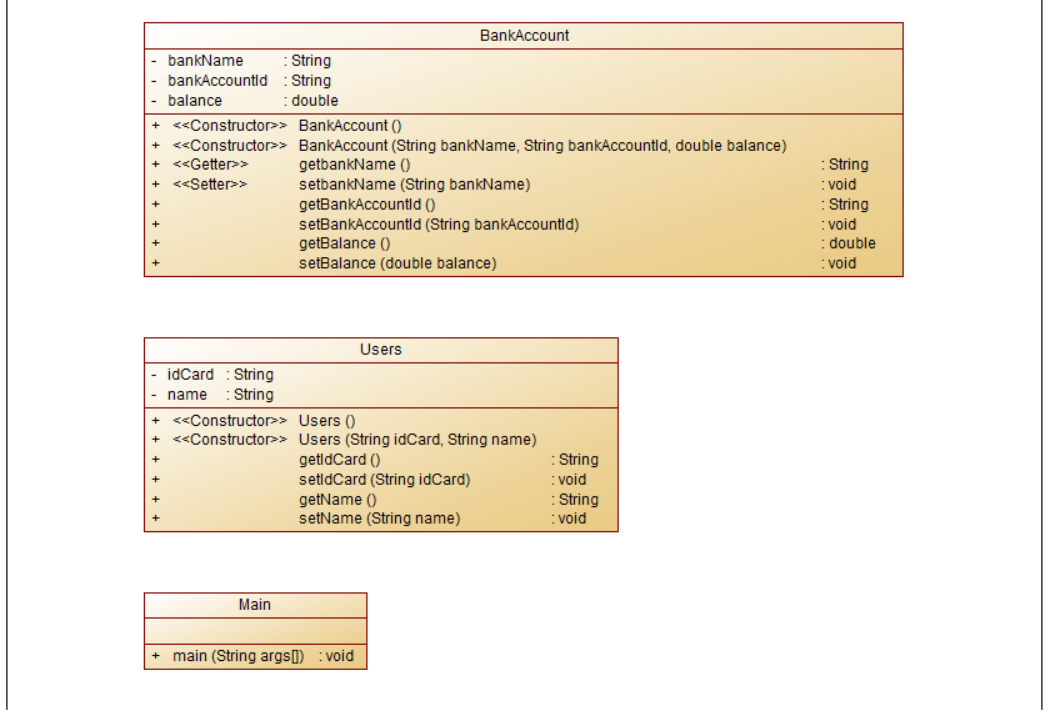
题目分析:本题包括主类共有三个类,其中Users为用户类,BankAccount为银行类,在用户类中有两个私有属性,idCard为身份证号码,name为名字,然后为两个属性的getset方法,在BankAccount类中有三个私有属
性以及三个属性的getset方法和一个存钱取钱的的方法,加上主类,三个类共同构成一个简易的ATM机,在主类中,首先最大的难度是对于正则表达式的书写,对于刚刚学习正则表达式的我来说是非常有难度的,其次对
于正则表达式的函数应用,更是思考了许久,本题还采用了对象数组的方法,便于多个对象的创建,并且根据一项一项的用if-else来判断正常的流程。对于该题还有一个难点在于最终的输出形式,一定要看清楚,当时我
写的时候有点粗心,导致很多结果错误,最终在不断的测试中找到了。
采坑心得:本道题的难度并不是很大,只要按照流程一步一步的走下来,本题有个最坑的地方是,因为当时思维没有转过来,没有使用c语言的输出形式,导致输出的小数不对,并且有一些地方要加钱的符号,这些东西
让当时的我寻找错误寻找了许久。
题目集5总结:本次题目集主要还是利用正则表达式对于字符串的处理来判断非法的输入,不仅如此,也加强了我们对于正则表达式的理解和领悟,总体来说本次题目集的难度比之上一次来说更小一点。
第六次题目集:
源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner; import java.text.DecimalFormat; import java.util.Arrays; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String sc = input.nextLine(); String m=sc.replace(":",","); String a[] = m.split(" |,"); if(sc.matches("1:([+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?,[+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?\\s)+[+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?,[+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?")) { if(a.length == 9) { double x1 = Double.parseDouble(a[1]); double y1 = Double.parseDouble(a[2]); double x2 = Double.parseDouble(a[3]); double y2 = Double.parseDouble(a[4]); double x3 = Double.parseDouble(a[5]); double y3 = Double.parseDouble(a[6]); double x4 = Double.parseDouble(a[7]); double y4 = Double.parseDouble(a[8]); Points fourPoint = new Points(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4); fourPoint.outPutParallelogram(); } else { System.out.print("wrong number of points"); } } else if(sc.matches("2:([+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?,[+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?\\s)+[+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?,[+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?")){ if(a.length == 9) { double x1 = Double.parseDouble(a[1]); double y1 = Double.parseDouble(a[2]); double x2 = Double.parseDouble(a[3]); double y2 = Double.parseDouble(a[4]); double x3 = Double.parseDouble(a[5]); double y3 = Double.parseDouble(a[6]); double x4 = Double.parseDouble(a[7]); double y4 = Double.parseDouble(a[8]); Points fourPoint = new Points(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4); fourPoint.outPutThreeJudge(); } else { System.out.print("wrong number of points"); } } else if(sc.matches("3:([+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?,[+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?\\s)+[+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?,[+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?")) { if(a.length == 9) { double x1 = Double.parseDouble(a[1]); double y1 = Double.parseDouble(a[2]); double x2 = Double.parseDouble(a[3]); double y2 = Double.parseDouble(a[4]); double x3 = Double.parseDouble(a[5]); double y3 = Double.parseDouble(a[6]); double x4 = Double.parseDouble(a[7]); double y4 = Double.parseDouble(a[8]); Points fourPoint = new Points(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4); fourPoint.outPutBump(); } else { System.out.print("wrong number of points"); } } else if(sc.matches("4:([+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?,[+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?\\s)+[+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?,[+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?,[+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?,[+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?")){ if (a.length == 13){ double x1 = Double.parseDouble(a[1]); double y1 = Double.parseDouble(a[2]); double x2 = Double.parseDouble(a[3]); double y2 = Double.parseDouble(a[4]); double x3 = Double.parseDouble(a[5]); double y3 = Double.parseDouble(a[6]); double x4 = Double.parseDouble(a[7]); double y4 = Double.parseDouble(a[8]); double x5 = Double.parseDouble(a[9]); double y5 = Double.parseDouble(a[10]); double x6 = Double.parseDouble(a[11]); double y6 = Double.parseDouble(a[12]); Points sixPoint = new Points(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4,x5,y5,x6,y6); System.out.println("not a quadrilateral or triangle"); } else { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); } } else if(sc.matches("5:([+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?,[+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?\\s)+[+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?,[+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?,[+-]?[\\d]+(.[\\d]*)?")) { if (a.length == 11) { double x1 = Double.parseDouble(a[1]); double y1 = Double.parseDouble(a[2]); double x2 = Double.parseDouble(a[3]); double y2 = Double.parseDouble(a[4]); double x3 = Double.parseDouble(a[5]); double y3 = Double.parseDouble(a[6]); double x4 = Double.parseDouble(a[7]); double y4 = Double.parseDouble(a[8]); double x5 = Double.parseDouble(a[9]); double y5 = Double.parseDouble(a[10]); Points fivePoint = new Points(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4,x5,y5); System.out.println("not a quadrilateral or triangle"); } else { System.out.print("wrong number of points"); } } else { System.out.print("Wrong Format"); } } } class Point{ double x; double y; public Point() { super(); } public Point(double x, double y) { super(); this.x = x; this.y = y; } public double getX() { return x; } public void setX(double x) { this.x = x; } public double getY() { return y; } public void setY(double y) { this.y = y; } } class Points extends Point{ private double x1; private double y1; private double x2; private double y2; private double x3; private double y3; private double x4; private double y4; private double x5; private double y5; private double x6; private double y6; public Points() { super(); } public Points(double x1, double y1) { super(); this.x1 = x1; this.y1 = y1; } public Points(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2, double x3, double y3, double x4, double y4) { super(); this.x1 = x1; this.y1 = y1; this.x2 = x2; this.y2 = y2; this.x3 = x3; this.y3 = y3; this.x4 = x4; this.y4 = y4; } public Points(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2, double x3, double y3, double x4, double y4, double x5, double y5) { super(); this.x1 = x1; this.y1 = y1; this.x2 = x2; this.y2 = y2; this.x3 = x3; this.y3 = y3; this.x4 = x4; this.y4 = y4; this.x5 = x5; this.y5 = y5; } public Points(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2, double x3, double y3, double x4, double y4, double x5, double y5, double x6, double y6) { super(); this.x1 = x1; this.y1 = y1; this.x2 = x2; this.y2 = y2; this.x3 = x3; this.y3 = y3; this.x4 = x4; this.y4 = y4; this.x5 = x5; this.y5 = y5; this.x6 = x6; this.y6 = y6; } public double getX1() { return x1; } public void setX1(double x1) { this.x1 = x1; } public double getY1() { return y1; } public void setY1(double y1) { this.y1 = y1; } public double getX2() { return x2; } public void setX2(double x2) { this.x2 = x2; } public double getY2() { return y2; } public void setY2(double y2) { this.y2 = y2; } public double getX3() { return x3; } public void setX3(double x3) { this.x3 = x3; } public double getY3() { return y3; } public void setY3(double y3) { this.y3 = y3; } public double getX4() { return x4; } public void setX4(double x4) { this.x4 = x4; } public double getY4() { return y4; } public void setY4(double y4) { this.y4 = y4; } public double getX5() { return x5; } public void setX5(double x5) { this.x5 = x5; } public double getY5() { return y5; } public void setY5(double y5) { this.y5 = y5; } public double getX6() { return x6; } public void setX6(double x6) { this.x6 = x6; } public double getY6() { return y6; } public void setY6(double y6) { this.y6 = y6; } public Point getCross() { double k1 = (y1 - y2) / (x1 - x2); double b1 = y1 - (k1 * x1); double k2 = (y3 - y4) / (x3 - x4); double b2 = y3 - (k2 * x4); double x = (b1 - b2) / (k2 - k1); double y = k1 * x + b1; return new Point(x, y); } public boolean haveCrossPoint() { double k1 = (y1 - y2) / (x1 - x2); double k2 = (y3 - y4) / (x3 - x4); return k1 != k2; } public boolean judgeQuadrangle() { double k1 = (y1 - y2) / (x1 - x2); double b1 = y1 - (k1 * x1); double k2 = (y3 - y4) / (x3 - x4); double b2 = y3 - (k2 * x4); double x = (b1 - b2) / (k2 - k1); double y = k1 * x + b1; if (haveCrossPoint() && haveCrossPoint()) { Point p5 = getCross(); if(p5 == null) { return false; } if (p5.getX() >= Math.min(x1, x2) && p5.getX() <= Math.max(x1, x2) && p5.getY() >= Math.min(y1, y2) && p5.getY() <= Math.max(y1, y2)) { return false; } if (p5.getX() >= Math.min(x3, x4) && p5.getX() <= Math.max(x3, x4) && p5.getY() >= Math.min(y3, y4) && p5.getY() <= Math.max(y3, y4)) { return false; } } return true; } public boolean superposition(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3,double x4,double y4){ if(x1 == x2 && y1 == y2 || x1 == x3 && y1 == y3 || x1 == x4 && y1 == y4 || x2 == x3 && y2 == y3 || x2 == x4 && y2 == y4 || x3 == x4 && y3 == y4){ return true; } else{ return false; } } public void outPutParallelogram() { if(superposition(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4)) { System.out.println("points coincide"); } else { System.out.println(this.judgeQuadrangle()+" "+this.judgeParallelogram()); } } public double Distance(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2){ double distance = 0; distance = Math.sqrt((x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(y1-y2)*(y1-y2)); return distance; } public boolean judgeParallelogram() { boolean a = true; double k1=(y1-y2)/(x1-x2); double k2=(y3-y4)/(x3-x4); if(k1==k2||x1==x2&&x3==x4){ a = true; } else { a = false; } if(judgeQuadrangle() && a == true && Distance(x1,y1,x2,y2) == Distance(x3,y3,x4,y4)){ return true; } else { return false; } } public boolean judgeLozenge(){ if(judgeParallelogram() && Distance(x1,y1,x2,y2) == Distance(x2,y2,x3,y3)){ return true; } else { return false; } } public boolean judgeRectangle(){ double k1 = (y1 - y2) / (x1 - x2); double k2 = (y2 - y3) / (x2 - x3); if(judgeParallelogram() && k1 * k2 == -1 || x1 == x2 && y2 == y3){ return true; } else { return false; } } public boolean judgeSquare(){ if(judgeRectangle() && judgeLozenge()){ return true; } else { return false; } } public void outPutThreeJudge() { if(judgeQuadrangle()) { if(!superposition(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4)) { System.out.println(this.judgeLozenge()+" "+this.judgeRectangle()+" "+ this.judgeSquare()); } else { System.out.println("points coincide"); } } else { System.out.println("not a quadrilateral"); } } public double Cir(){ double c = 0; c = Distance(x1,y1,x2,y2)+Distance(x2,y2,x3,y3)+Distance(x3,y3,x4,y4)+Distance(x1,y1,x4,y4); return c; } public double area(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3){ double c = Distance(x1,y1,x2,y2) + Distance(x1,y1,x3,y3) + Distance(x3,y3,x2,y2); double l = c / 2; double s = Math.sqrt(l * (l - Distance(x1,y1,x2,y2)) * (l-Distance(x1,y1,x3,y3)) * (l-Distance(x3,y3,x2,y2))); return s; } public boolean bump(){ double s1 = area(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3); double s2 = area(x3,y3,x4,y4,x1,y1); double s3 = area(x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4); double s4 = area(x4,y4,x1,y1,x2,y2); double S1 = s1 + s2; double S2 = s3 + s4; if (S1 == S2){ return true; } else { return false; } } public double Area() { if(!bump()) { if((area(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3)+area(x3, y3, x4, y4, x1, y1)) > (area(x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4)+area(x4, y4, x1, y1, x2, y2))){ return area(x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4) + area(x4, y4, x1, y1, x2, y2); } else { return area(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3) + area(x3, y3, x4, y4, x1, y1); } } else { double s1 = area(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3); double s2 = area(x3, y3, x4, y4, x1, y1); return s1 + s2; } } public void outPutBump() { if (judgeQuadrangle()){ System.out.print(bump()+" "); System.out.printf(new DecimalFormat("0.0##").format(Cir())); System.out.printf(" "); System.out.printf(new DecimalFormat("0.0#####").format(Area())); } else { System.out.println("not a quadrilateral"); } } }
类图:
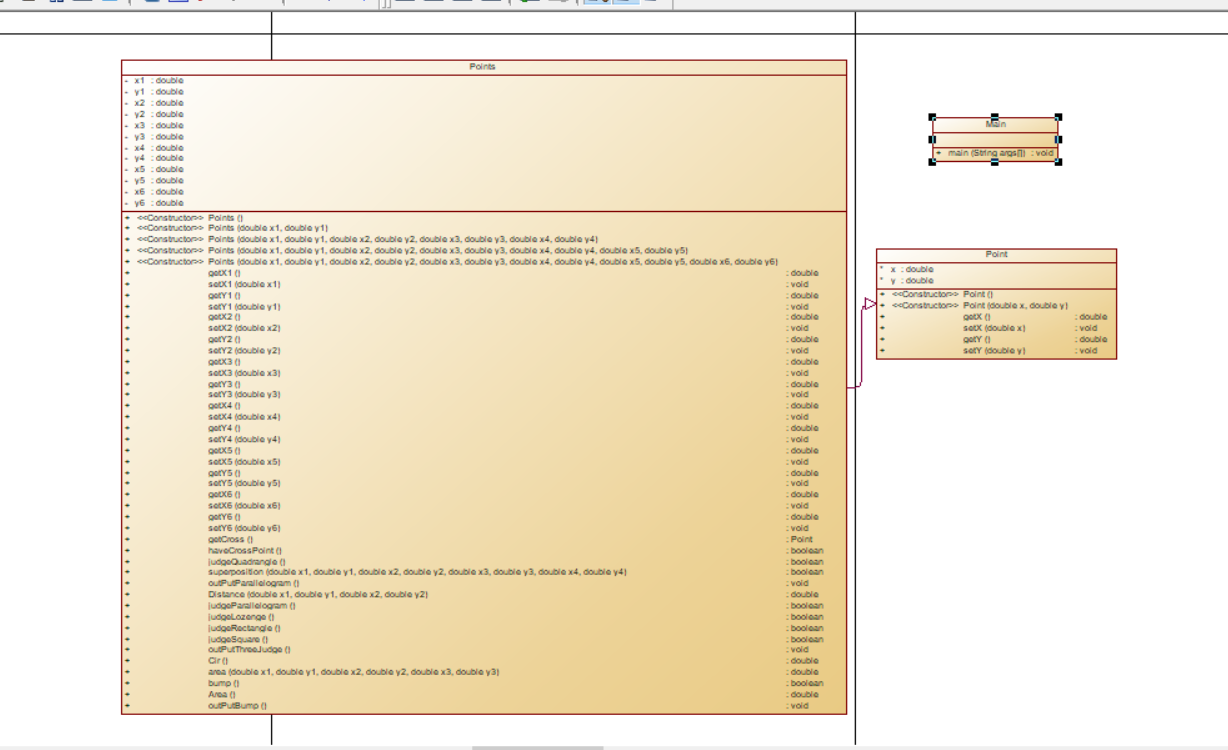
题目分析:本次题目我采用了三个类,分别为Main类,Point类,Points类,其中Point类有两个私有属性x,y,和x,y的构造方法,Points类继承Point类,Points类采用的是多构造方法,一一调用的关系,其中设置了
12个私有属性,和其与题目相关联的几个相应的构造方法(这样使用是为了减少使用引用),其中还有许多的方法,如判断四个点中是否有重合的点,判断是否是四边形的方法,判断是否是平行四边形,判断是否是
菱形,长方形,正方形,凸四边形,凹四边形,并求其周长,面积的方法,其中判断是否是凹凸四边形采用的办法是面积法。
采坑心得:本题的正则表达式一定要思考清楚(我的有问题导致非法错了一半),关于判断是否是四边学的算法,经过和同学交流,最好采用斜率的算法,这样更为简单一点。关于凹凸四边形的面积,首先要进行的是
应用面积法来判断是否是凹凸四边形,判断之后在选择相应的算法来算出四边形的面积。
单向链表:
源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner; interface LinearListInterface { public boolean isEmpty(); public int size(); public E get(int index); public void remove(int index); public void add(int index, E theElement); public void add(E element); public void printList(); } class LList{ private Node<E> head,curr,tail; private int size; public int size(){ return size; } public boolean isEmpty(){ if(size == 0) { return true; } else { return false; } } public E get(int index){ Node<E> p = head; for(int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) { p = p.getNext(); if (i == index) { break; } } return p.getO(); } public void remove(int index) { if (index > size) { return; } Node<E> p = head; for (int i = 0; i < index - 1 && p.getNext() != null; i++) { p = p.getNext(); } if (p.getNext() != null) { p = p.getNext(); size--; } } public void add(int index, E theElement) { if (index > size) { return; } Node<E> p = head; Node<E> f = new Node(); f.setO(theElement); for (int i = 0; i < index - 1 && p.getNext() != null; i++) { p = p.getNext(); if(p.getNext() == null){ p.setNext(f); } } if (p.getNext() != null) { p = p.getNext(); size++; } } public void add(E element) { Node<E> p = head; Node<E> f = new Node(); for (int i = 0;i < size -1 && p.getNext() != null; i++) { p = p.getNext(); if(p.getNext() == null){ p.setNext(f); } } if (p.getNext() != null) { p = p.getNext(); size++; } } public void printList() { Node<E> p = head; while(p.getNext() != null) { System.out.print(p.getNext().getO()); p = p.getNext(); } } } class Node<E>{ private E o; private Node<E> next; public Node() { super(); } public Node(E o, Node<E> next) { super(); this.o = o; this.next = next; } public E getO() { return o; } public void setO(E o) { this.o = o; } public Node<E> getNext() { return next; } public void setNext(Node<E> next) { this.next = next; } } class E{ }
分析:对于链表的学习,从c语言开始我就没怎么学会,导致第一次的单向链表作业,写的很差,其中的一些基本功能都不能完全的实现,以至于大部分都写不出,后来经过老师的讲解,掌握了简单的链表学习,自己
也知道了简易的单向链表要如何实现,至于本题最开始 的时候采用的是使用重构接口的方法,使用泛型分别作出链表的增删改查功能。
采坑心得:首先要先了解到链表是什么东西,在开始考虑每一步界限值,之后在进行代码的编写,其中最主要的是add方法和remove方法。
双向链表:
源码如下
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { DoubleLinkedList<Integer> list = new DoubleLinkedList<>(); list.add(2); list.add(4); list.add(6); list.add(8); list.printList(); list.remove(3); list.printList(); list.add(2,100); list.printList(); System.out.println(list.getFirst()); System.out.println(list.getLast()); } } public class Node<E> { private E data; private Node<E> next; private Node<E> prev; public Node(E data, Node<E> next, Node<E> prev) { super(); this.data = data; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } public Node() { // TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根 } public E getData() { return data; } public void setData(E data) { this.data = data; } public Node<E> getNext() { return next; } public void setNext(Node<E> next) { this.next = next; } public Node<E> getPrev() { return prev; } public void setPrev(Node<E> prev) { this.prev = prev; } } public interface DoubleLinkedListImpl<E> { public boolean isEmpty(); /** * 获取当前链表节点数量 * @return 节点数 */ public int getSize(); /** * 获取链表中第index个位置的节点的data值 * @param index:节点在链表中的位置 * @return:返回该节点的data值 */ public E getData(int index); /** * 删除链表最后一个节点 */ public void remove(); /** *删除链表中第index位置的节点 * @param index:节点在链表中的位置 */ public void remove(int index); /** * 在链表的第index个位置之前插入一个节点,值为theElement,index∈[1,size] * @param index:插入节点在链表中的位置 * @param theElement:新插入节点的data值 */ public void add(int index, E theElement); /** * 在链表尾插入节点,插入节点data值为element * @param element */ public void add(E element); /** * 输出链表 */ public void printList(); /** * 获取第一个节点的data值 * @return */ public E getFirst(); /** * 获取链表最后一个节点的data值 * @return */ public E getLast(); } public class DoubleLinkedList<E> implements DoubleLinkedListImpl<E> { private Node<E> head;//头结点,非第一个节点 private Node<E> curr;//当前节点 private Node<E> tail;//最后一个节点 private int size;//当前链表节点数 public DoubleLinkedList() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub head = new Node<E>(); head.setNext(null); curr = tail = null; this.size = 0; } @Override public boolean isEmpty() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return size == 0; } @Override public int getSize() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return this.size; } @Override public E getData(int index) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(index < 1 || index > this.size) { return null; } curr = head; for(int i = 0; i < index; i ++) { curr = curr.getNext(); } return curr.getData(); } @Override public void remove() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub this.remove(this.size - 1); } @Override public void remove(int index) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(index < 1 || index > this.size) { return ; } curr = head; if(index == 1) { curr = head.getNext(); head.setNext(curr.getNext()); head.getNext().setPrev(null); } else {//找到第index - 1个节点赋给curr for(int i = 1;i < index; i++) { curr = curr.getNext(); } curr.setNext(curr.getNext().getNext()); curr.getNext().setPrev(curr); } if(index == this.size) {//如果删除的是最后一个节点 tail = curr; } this.size --;//整个链表的节点数量-1 } @Override public void add(int index, E theElement) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(index < 1 || index > this.size + 1) { return ; } Node<E> curr = new Node<>(); curr.setData(theElement); curr.setNext(null); if(this.size == 0) { head.setNext(curr); head.setPrev(null); tail = curr; }else if(index == this.size + 1) { curr.setPrev(tail); this.tail.setNext(curr); tail = curr; }else { Node<E> tempNode = head; for(int i = 1; i < index;i++) { tempNode = tempNode.getNext(); } curr.setNext(tempNode.getNext()); curr.setPrev(curr); tempNode.setNext(curr); curr.setPrev(tempNode); } this.size ++; } @Override public void add(E element) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub this.add(this.size + 1,element); } @Override public void printList() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub curr = head.getNext(); for(int i = 1; i <= this.size;i ++) { System.out.print(curr.getData() + " "); curr = curr.getNext(); } System.out.println(""); } @Override public E getFirst() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(this.size != 0) { return head.getNext().getData(); } return null; } @Override public E getLast() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(this.size != 0) { return tail.getData(); } return null; } }
题目分析:首先是经过老师上一次的讲解单向链表,只需在上一次链表的基础上增加一个Prev的属性,作为类型c语言中的指针,双向链表相比于单向链表,多了一个可以指向前一个节点的指针,所以增删上进行修改
即可。
采坑心得:对于双向链表来说,鉴于当时上课的时候老师讲解了单向链表,所以我在老师代码的基础上进行了部分修改,最主要要考虑的是删除和增加的的时候,curr指向下下个节点的时候,要利用curr来使用prev
指向前前个节点。增加的时候,先找到要增加的节点,将curr的setnext指向要增加的节点的setnext,将要增加节点的prev指向curr的prev,将之前的下一个节点的prev指向要增加节点的prev,要增加的节点的setnext
指向之前的下一个节点。
其中考试三道试题:
第一道:
源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); double x1 = input.nextDouble(); double y1 = input.nextDouble(); double x2 = input.nextDouble(); double y2 = input.nextDouble(); String sc = input.next(); if(x1 < 0 || x1 >200 || y1 < 0 || y1 > 200 || x2 < 0 || x2 >200 || y2 < 0 || y2 > 200) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else { Point point1 = new Point(x1, y1); Point point2 = new Point(x2,y2); Line line = new Line(point1,point2,sc); line.display(); } } } class Point{ private double x; private double y; public Point() { super(); } public Point(double x, double y) { super(); this.x = x; this.y = y; } public double getX() { return x; } public void setX(double x) { this.x = x; } public double getY() { return y; } public void setY(double y) { this.y = y; } public void display() { System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n", x,y); } } class Line extends Point{ private Point point1; private Point point2; private String color; public Line() { super(); } public Line(Point point1, Point point2, String color) { super(); this.point1 = point1; this.point2 = point2; this.color = color; } public Point getPoint1() { return point1; } public void setPoint1(Point point1) { this.point1 = point1; } public Point getPoint2() { return point2; } public void setPoint2(Point point2) { this.point2 = point2; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public double getDistance() { double distance = 0; distance = Math.sqrt((point1.getX() - point2.getX()) * (point1.getX() - point2.getX()) + (point1.getY() - point2.getY()) * (point1.getY() - point2.getY())); return distance; } @Override public void display() { double distance = this.getDistance(); System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color); System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); point1.display(); System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); point2.display(); System.out.printf("The line's length is:%.2f", distance); } }
类图:
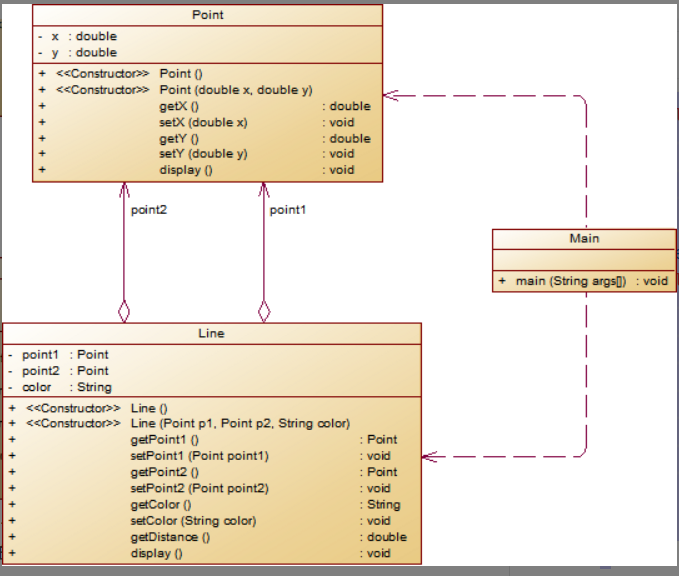
题目分析:本题一共有三个类,主类,点类,线类,其中line类继承点类,并在线类中进行构造方法和getset方法的构建,并进行计算线的长度的方法,以及一个dispaly展示输出的方法,在主类中进行数据的输入和数据
是否合法进行判断并调用line内的display方法。
采坑心得:本题按照给出的类图及提示进行编写,唯一需要注意的是输出格式。
第二题:
源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); double x1 = input.nextDouble(); double y1 = input.nextDouble(); double x2 = input.nextDouble(); double y2 = input.nextDouble(); String sc = input.next(); if(x1 < 0 || x1 >200 || y1 < 0 || y1 > 200 || x2 < 0 || x2 >200 || y2 < 0 || y2 > 200) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else { Point point1 = new Point(x1, y1); Point point2 = new Point(x2,y2); Line line = new Line(point1,point2,sc); Plane plane = new Plane(sc); point1.display(); point2.display(); line.display(); plane.display(); } } } class Point extends Element{ private double x; private double y; public Point() { super(); } public Point(double x, double y) { super(); this.x = x; this.y = y; } public double getX() { return x; } public void setX(double x) { this.x = x; } public double getY() { return y; } public void setY(double y) { this.y = y; } @Override public void display() { System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n", x,y); } } class Line extends Point{ private Point point1; private Point point2; private String color; public Line() { super(); } public Line(Point point1, Point point2, String color) { super(); this.point1 = point1; this.point2 = point2; this.color = color; } public Point getPoint1() { return point1; } public void setPoint1(Point point1) { this.point1 = point1; } public Point getPoint2() { return point2; } public void setPoint2(Point point2) { this.point2 = point2; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public double getDistance() { double distance = 0; distance = Math.sqrt((point1.getX() - point2.getX()) * (point1.getX() - point2.getX()) + (point1.getY() - point2.getY()) * (point1.getY() - point2.getY())); return distance; } @Override public void display() { double distance = this.getDistance(); System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color); System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); point1.display(); System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); point2.display(); System.out.printf("The line's length is:%.2f\n", distance); } } abstract class Element{ public void display() { } } class Plane extends Element{ private String color; public Plane() { super(); } public Plane(String color) { super(); this.color = color; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } @Override public void display() { System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+color); } }
类图:
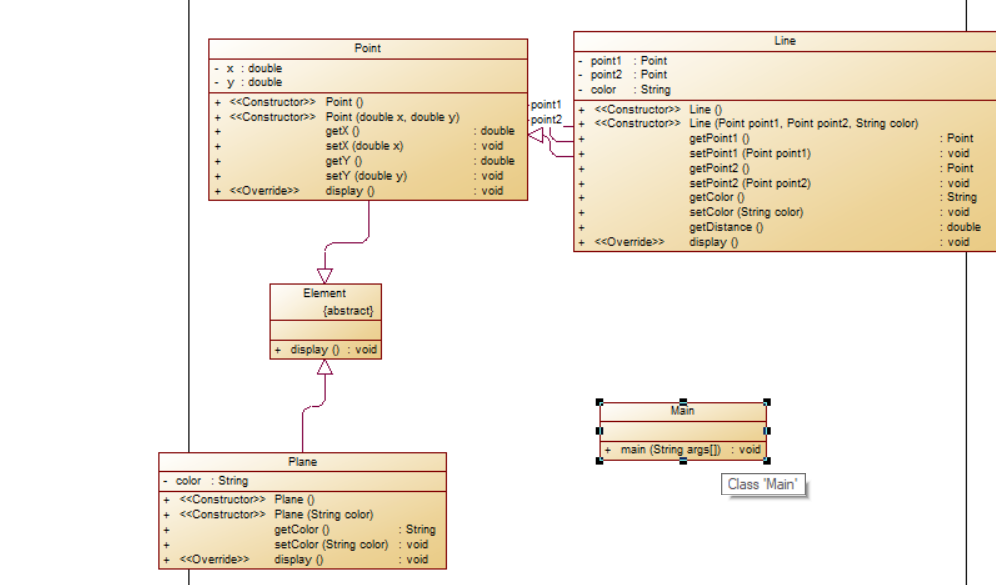
题目分析:本道题可以直接将上面的一题直接拿来使用,并增加 一个抽象类,在此基础上最后增加一个plane类,来获取面的颜色,整体的难度并不是很大。
采坑心得:本题与上一题类似,只是增加了一个抽象类,其余按照提示编写即可。
第三题:
源码如下:
import java.lang.reflect.Array; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int choice = input.nextInt(); GeometryObject list = new GeometryObject(); while(choice != 0) { switch(choice) { case 1://insert Point object into list double x1 = input.nextDouble(); double y1 = input.nextDouble(); if(x1 < 0 || x1 >200 || y1 < 0 || y1 > 200) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else { Point point1 = new Point(x1,y1); list.add(point1); } break; case 2://insert Line object into list double x2 = input.nextDouble(); double y2 = input.nextDouble(); double x3 = input.nextDouble(); double y3 = input.nextDouble(); String sc = input.next(); if(x3 < 0 || x3 >200 || y3 < 0 || y3 > 200 || x2 < 0 || x2 >200 || y2 < 0 || y2 > 200) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else { Point point2 = new Point(x2,y2); Point point3 = new Point(x3,y3); Line line = new Line(point2,point3,sc); list.add(line); } break; case 3://insert Plane object into list String sc1 = input.next(); break; case 4://delete index - 1 object from l list.remove(choice = input.nextInt()); } } for(int i = 0;i<list.getArraylist().size();i++) { list.getArraylist().get(i).display(); } } } class Point extends Element{ private double x; private double y; public Point() { super(); } public Point(double x, double y) { super(); this.x = x; this.y = y; } public double getX() { return x; } public void setX(double x) { this.x = x; } public double getY() { return y; } public void setY(double y) { this.y = y; } @Override public void display() { System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n", x,y); } } class Line extends Point{ private Point point1; private Point point2; private String color; public Line() { super(); } public Line(Point point1, Point point2, String color) { super(); this.point1 = point1; this.point2 = point2; this.color = color; } public Point getPoint1() { return point1; } public void setPoint1(Point point1) { this.point1 = point1; } public Point getPoint2() { return point2; } public void setPoint2(Point point2) { this.point2 = point2; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public double getDistance() { double distance = 0; distance = Math.sqrt((point1.getX() - point2.getX()) * (point1.getX() - point2.getX()) + (point1.getY() - point2.getY()) * (point1.getY() - point2.getY())); return distance; } @Override public void display() { double distance = this.getDistance(); System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color); System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); point1.display(); System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); point2.display(); System.out.printf("The line's length is:%.2f\n", distance); } } abstract class Element{ public void display() { } } class Plane extends Element{ private String color; public Plane() { super(); } public Plane(String color) { super(); this.color = color; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } @Override public void display() { System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+color); } } class GeometryObject{ private ArrayList<Element> arraylist = new ArrayList<>(); public GeometryObject() { super(); } public void add(Element element) { arraylist.add(element); } public void remove(int index) { arraylist.remove(index-1); } public ArrayList<Element> getArraylist() { return arraylist; } }
类图:
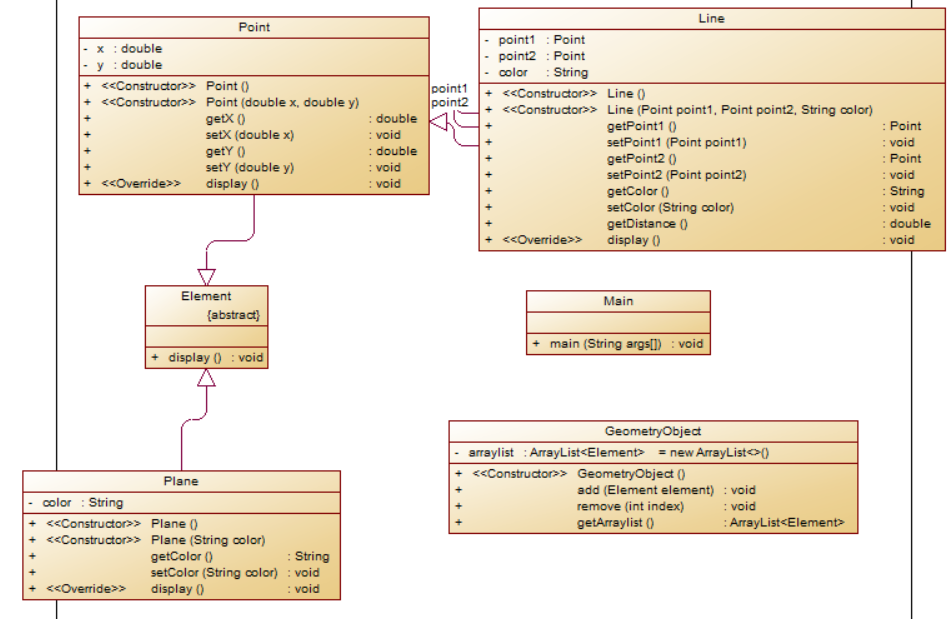
题目分析:在第二题的基础上增加一个容器类,并在这个类里面创建增加减少对象的方法,其余与第二题没有什么差异,在主类中给出的while循环进行补充即可。
采坑心得:本题要合适的利用Arrlist自带的增加和删减容器和会调用容器里面的函数的方法。
改进建议:
对于第四次题目集的作业,因其仅需实现一个功能,就是对输入字符串进行判断,所以均需将非法判断改为正则表达式判断,活着单独写一个方法,每次使用时每次都判断。
对于第五次题目集第五次作业:对于ATM机的处理,本题大部分东西都写在主函数中,可以适当将主函数里面的东西写到类中,看起来更加美观。
对于第六次题目集第二次作业:该题要将正则表达式进行修改,同时将未完成的代码进行补充。
对于期中考试的作业:这三道题目因为类图都以给出,只需按照类图进行正常编写即可。
总结:通过这几次题目集的练习,从最初对java的简单认知到现在对java有了一定的认知,逐渐接触到了越来越难的题目,其中的核心算法也越来越难,最近的非法输入也均需要用正则表达式来判断,对于正则表达式的训练需要加强,对于类与类之间关系连接已经逐渐的掌握,对于之前未了解的知识也逐渐的掌握了,这几次的pta作业正在变难,当时相对应的我的编程能力也在逐渐变强。除此之外,我对于困难的算法老是无法独立思考,需要更进一步的提高独立的思考能力,对于接下来的java学习更加不能松懈,需要不断的接受新知识来扩充自己,增强自己的能力。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号