Jingbo Wang-2022-DiverseNaturalSceneAware3DHumanMotionSynthesis-CVPR
# Towards Diverse and Natural Scene-Aware 3D Human Motion Synthesis #paper
1. paper-info
1.1 Metadata
- Author:: [[Jingbo Wang]], [[Yu Rong]], [[Jingyuan Liu]], [[Sijie Yan]], [[Dahua Lin]], [[Bo Dai]]
- 作者机构::
- Keywords:: #HMP
- Journal:: #CVPR
- Date:: [[2022]]
- 状态:: #Done
- 链接:: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/CVPR2022/html/Wang_Towards_Diverse_and_Natural_Scene-Aware_3D_Human_Motion_Synthesis_CVPR_2022_paper.html
- 修改时间:: 2022.11.10
1.2. Abstract
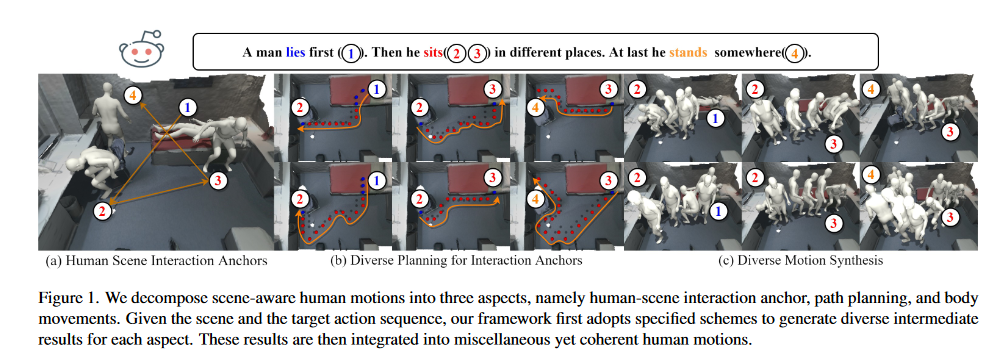
The ability to synthesize long-term human motion sequences in real-world scenes can facilitate numerous applications. Previous approaches for scene-aware motion synthesis are constrained by pre-defined target objects or positions and thus limit the diversity of human-scene interactions for synthesized motions. In this paper, we focus on the problem of synthesizing diverse scene-aware human motions under the guidance of target action sequences. To achieve this, we first decompose the diversity of sceneaware human motions into three aspects, namely interaction diversity (e.g. sitting on different objects with different poses in the given scenes), path diversity (e.g. moving to the target locations following different paths), and the motion diversity (e.g. having various body movements during moving). Based on this factorized scheme, a hierarchical framework is proposed, with each sub-module responsible for modeling one aspect. We assess the effectiveness of our framework on two challenging datasets for scene-aware human motion synthesis. The experiment results show that the proposed framework remarkably outperforms previous methods in terms of diversity and naturalness.
2. Introduction
- 领域:
在真实的场景下合成长序列人体动作 - 之前的方法:
之前的方法主要侧重于对身体运动进行建模未能全面研究场景感知人体运动的内在多样性。 - 作者的方法:
- 作者将该任务的多样性分为3个层次的多样性
diverse human-scene interaction anchors- 对于具有相同运动标签的姿势,将其放置在不同的位置,提高多样性。
- 利用CVAE去推断放置结点的位置。
diverse obstacle-free motion paths- 作者使用一种改进版的A* 算法生成两个点之间的多样化路径--
Neural Mapping
- 作者使用一种改进版的A* 算法生成两个点之间的多样化路径--
diverse body movements- 利用一种基于
Transformer的CVAE网络去生成动作序列。
- 利用一种基于
- 作者将该任务的多样性分为3个层次的多样性
3. Methodology
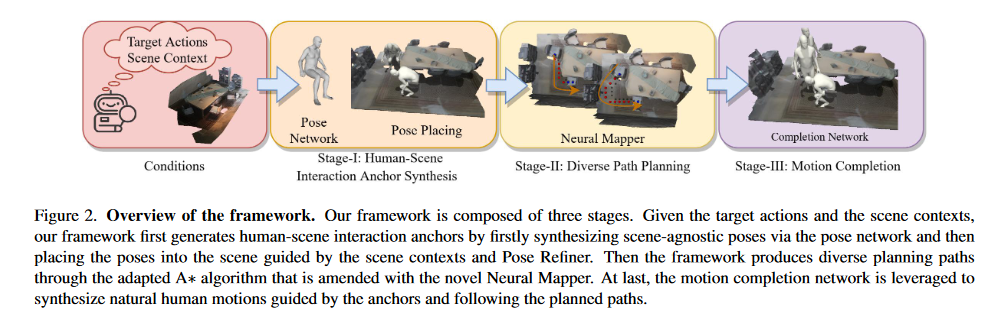
3.1. Overview
triangular mesh\(S=(v^s,f^s)\):表示场景上下文,\(v^s,f^s\)表示点和面
\(A=(a_1,a_2,..,a_N)\):目标行为标签
使用SMPL-X model表示3D human motions :
\(\{P_0,..., P_T\}\)
\(P_i=(t_i, \phi _i, \theta _i)\)
模型根据人体移动内在的特性分为3步骤:
- 生成与场景无关的姿势,并将姿势合理的放在场景当中。
- 根据第一步放置的位置,生成位置与位置之间的路径。
- 在路径的基础上,合成人体动作。
3.2. Human-Scene Interaction Anchor Synthesis
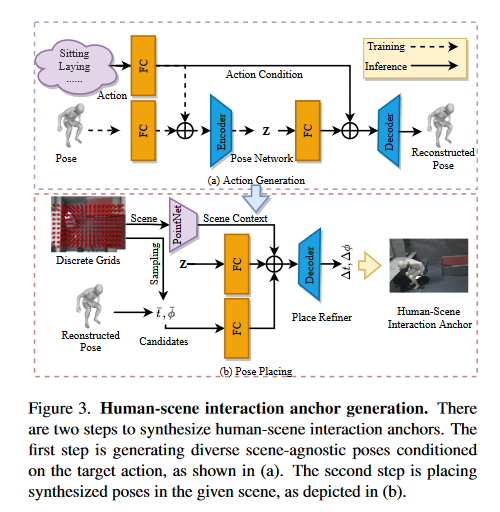
Scene-Agnostic Pose Synthesis
如Fig.3.a所示,使用VAE框架,在给定target action\(a_i\)的情况下合成pose\(\theta_i\) 。首先从先验高斯分布采样一段噪声,将噪声送入一个全连接层,并且将目标行为通过one-hot编码后,也经过一个全连接层;然后将这两个编码后的特征加在一起送入VAE的encoder,模型最后输出的是合成的reconstructed pose\(\theta_i\)。
Scene-Conditioned Anchor Placing
具体分析看论文,理解不到位。
3.3. Diverse Path Planning
作者将A* 算法与关于人类运动多样性的场景感知随机信息相结合。
3.4. Motion Completion
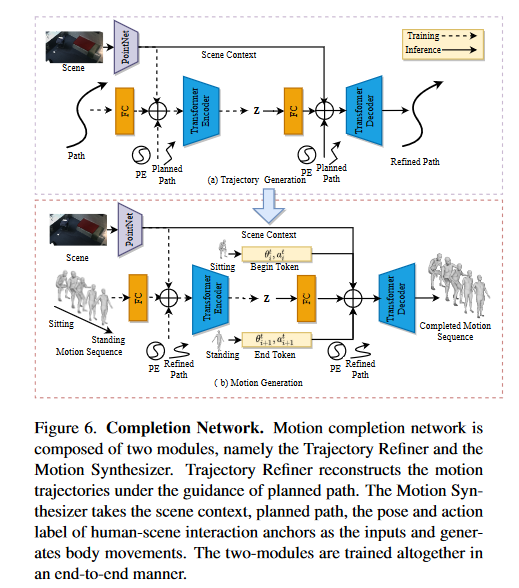
4. 总结
该文章是对StochasticSceneAwareMotionPredictionpaperlink的改进,框架的流程上更流畅,也分为三个步骤,第一步,生成连接点处的人体姿势;第二步,生成连接点之前的多条路径;第三步,根据路径生成人体动作序列。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号