Python socket
Python socket
所谓套接字(Socket),就是对网络中不同主机上的应用进程之间进行双向通信的端点的抽象。Socket编程是比较底层的应用程序调用,如果实现一个简单的分布式,则可以通过socket进行通信,本篇只是简单的应用Python模拟Server和client进行通信,所以是同一个IP对应不同的端口。
套接字Socket=(IP地址:端口号),套接字的表示方法是点分十进制的lP地址后面写上端口号,中间用冒号或逗号隔开。每一个传输层连接唯一地被通信两端的两个端点(即两个套接字)所确定。例如:如果IP地址是210.37.145.1,而端口号是23,那么得到套接字就是(210.37.145.1:23)
代码实现
Server代码
# This is server side
import socket
# Create Server socket client
server_client = socket.socket()
host = 'localhost'
port = 12345
# Which IP and port to bind for server.
server_client.bind((host, port))
# Server will always listen on this port
server_client.listen()
# keep with listening
try:
while True:
# If we get request, will also get source address ip
c, addr = server_client.accept()
print("Get connection from {}".format(addr))
data = c.recv(1024)
print(data.decode())
# send back to client means that server get the message
c.send("Hi client, this is server!".encode())
except:
print("Stop server!")
Client代码
# To make the socket client to connect with server
import socket
host = 'localhost'
port = 12345
# Bind IP and client port
client_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# start to connect
client_socket.connect((host, port))
data = "hi server!"
# send data to server
client_socket.send(data.encode())
# get result from server
res = client_socket.recv(1024)
print(res.decode())
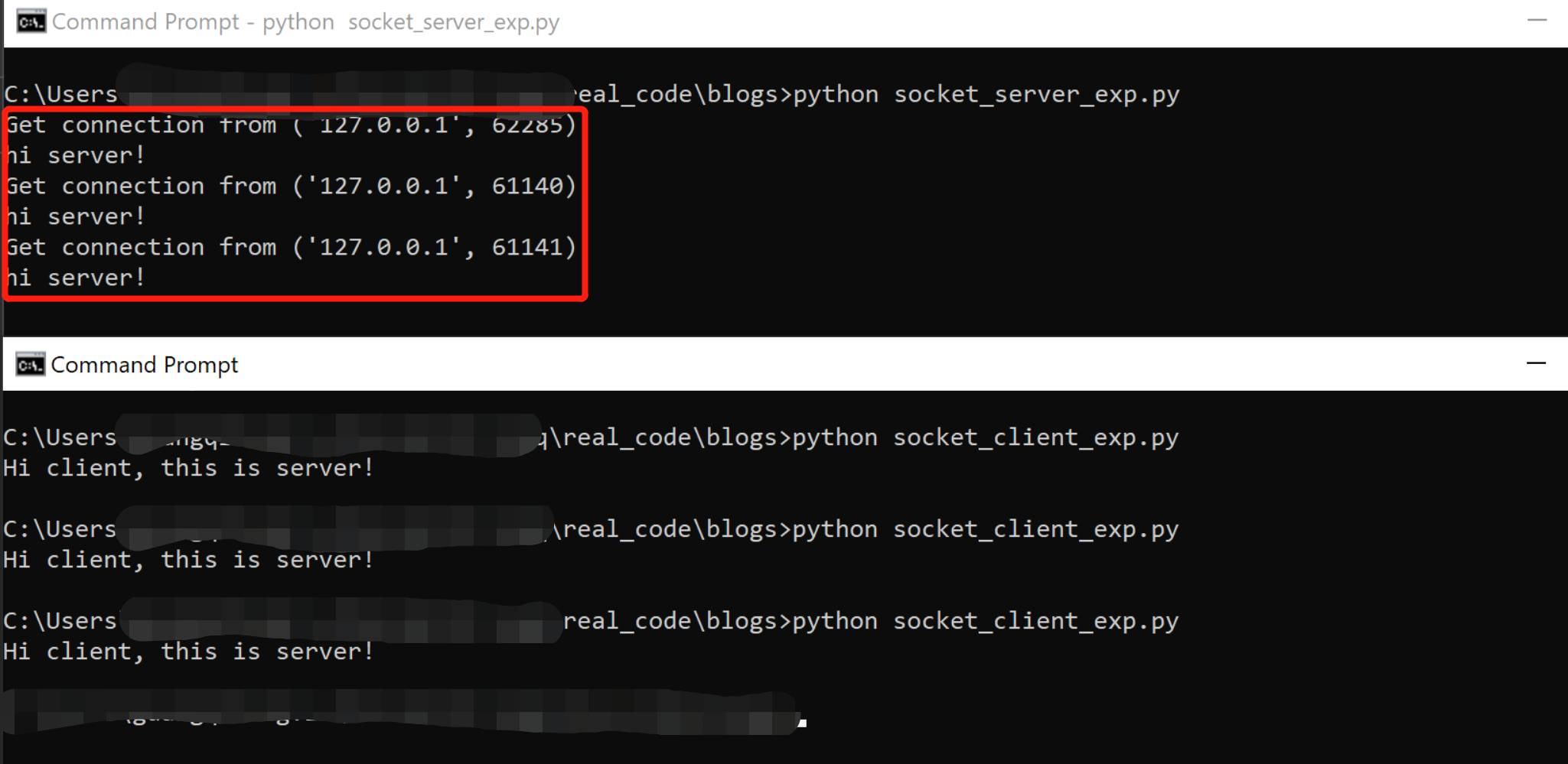
启动结果
因为serer是一个长进程,所以我们可以不断的通过不同的client对server进行调用,所以我们可以看到不同的client port。如果使用不同server,则可以看到不同的IP。
本文来自博客园,作者:{guangqiang.lu},转载请注明原文链接:{https://www.cnblogs.com/guangqianglu/}






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号