2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(2)(2 4 5,补3 6 8)
2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(2)(2 4 5,补3 6 8)
1002:烂人方法
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define N 1005
#define mod 998244353
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
string a[] = {"jia","yi","bing","ding","wu","ji","geng","xin","ren","gui","jia","yi","bing","ding","wu","ji","geng","xin","ren","gui","jia","yi","bing","ding","wu","ji","geng","xin","ren","gui","jia","yi","bing","ding","wu","ji","geng","xin","ren","gui","jia","yi","bing","ding","wu","ji","geng","xin","ren","gui","jia","yi","bing","ding","wu","ji","geng","xin","ren","gui","jia","yi","bing","ding","wu","ji","geng","xin","ren","gui"};
//string b[] = {"zi","chou","yin","chen","si","wu","wei","shen","you","xv","hai","zi","chou","yin","chen","si","wu","wei","shen","you","xv","hai","zi","chou","yin","chen","si","wu","wei","shen","you","xv","hai","zi","chou","yin","chen","si","wu","wei","shen","you","xv","hai","zi","chou","yin","chen","si","wu","wei","shen","you","xv","hai","zi","chou","yin","chen","si","wu","wei","shen","you","xv","hai","zi","chou","yin","chen","si","wu","wei","shen","you","xv","hai""zi","chou","yin","chen","si","wu","wei","shen","you","xv","hai","zi","chou","yin","chen","si","wu","wei","shen","you","xv","hai","zi","chou","yin","chen","si","wu","wei","shen","you","xv","hai"};
string b[] = {"zi","chou","yin","mao","chen","si","wu","wei","shen","you","xu","hai","zi","chou","yin","mao","chen","si","wu","wei","shen","you","xu","hai","zi","chou","yin","mao","chen","si","wu","wei","shen","you","xu","hai","zi","chou","yin","mao","chen","si","wu","wei","shen","you","xu","hai","zi","chou","yin","mao","chen","si","wu","wei","shen","you","xu","hai","zi","chou","yin","mao","chen","si","wu","wei","shen","you","xu","hai","zi","chou","yin","mao","chen","si","wu","wei","shen","you","xu","hai"};
void solve()
{
string s;
cin>>s;
int i = 0;
while(1)
{
string c;
c = a[i]+b[i];
//cout<<c;
if(c == s)
{
cout<<1984+i<<"\n";
return;
}
i++;
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
1004:暴力dp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define N 1005
#define mod 998244353
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int f[10005];
void solve()
{
string s1,s2;
cin>>s1>>s2;
int u = 0;
if(s2.size() <= 2)
{
while(!s2.empty())
{
u*=10;
u += s2[0]-'0';
s2.erase(0,1);
}
if(u >= 26)
{
map<char,int>mp;
for(int i = 0;i < s1.size();i++)
{
if(mp[s1[i]]) mp[s1[i]]++;
}
cout<<mp.size()<<"\n";
}
else
{
string s;
while(u--)
{
s+=s1;
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < s.size();i++)
{
f[i] = 1;
for(int j = 0;j < i;j++)
{
if(s[j] < s[i]) {f[i] = max(f[i],f[j]+1);}
}
}
for(int i = 1;i < s.size();i++) ans = max(ans,f[i]);
cout<<ans<<"\n";
}
}
else
{
map<char,int>mp;
for(int i = 0;i < s1.size();i++)
{
if(mp[s1[i]]) mp[s1[i]]++;
}
cout<<mp.size()<<"\n";
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
1005:理性分析
idea:
如果 ( k ) 是奇数,则答案为 0。
先讨论 ( k = 2 ) 的情形,此时有 ( \lceil n/2 \rceil ) 条平行 ( l_0 ) 的直线和 ( \lfloor n/2 \rfloor ) 条垂直 ( l_0 ) 的直线,答案就是二者的积。
对于 ( k > 2 ) 的情形,可以把所有 ( l_i ) 按照 ( i \mod (k/2) ) 分组,此时有 ( n \mod (k/2) ) 组直线有 ( \lfloor n/k \rfloor + 1 ) 条,另外 ( (k/2) - (n \mod (k/2)) ) 组直线有 ( \lfloor n/k \rfloor ) 条。显然垂直的直线都在同一个组内,并且每一个组自身都是一个 ( k = 2 ) 的情形,套用上面的结论即可。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define N 1005
#define mod 998244353
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
void solve()
{
int n,k;
cin>>n>>k;
if(k%2!=0)
{
cout<<0<<"\n";
return ;
}
ll m = k/2;
if(m > n-1)
{
cout<<0<<"\n";
return ;
}
ll q = (n-1)/m;
ll maxj = (q-1)/2;
if(maxj < 0)
{
cout<<0<<"\n";
return ;
}
ll cnt = maxj+1;
ll ans = cnt*n-m*cnt*cnt;
cout<<ans<<"\n";
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
1003:
idea:关键在于找到第三个数字使得(p,0,p,q)能够为答案做出贡献,所以可以用从后往前map来记录一个数字首次出现的位置。再次从前往后遍历,如果p出现了超过两次,那么拿他首次出现位置和目前0的位置比较,如果x[p]<0,那么他就对答案做出贡献,其贡献即为当前>0的数字的后缀和,同时把当前的x[p]标记为inf,那么后面再次遍历到p的时候其则没有贡献
注意:这里的关键从后往前遍历找p首先出现的位置以及从前往后遍历0的位置,如果p只出现一次(后面即使有0,mp[a[i]]也不会再次出现)或者0的位置没有更新,那么p对答案不产生贡献
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define mod 998244353
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e9+7;
int cnt[1000005];
void solve()
{
ll n;
memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt));
cin>>n;
vector<int>a(n+1);//1 1 1 1 0 1 3 1 0 1 2 2 0 2 2 3 5 7 8 9 1 0 2 2 0 0
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) cin>>a[i];
unordered_map<int,int>mp;
int last0 = 0;
vector<int>ans(n+2,0);
for(int i = n;i >= 1;i--)
{
if(a[i] == 0)
{
ans[i] = ans[i+1];
continue;
}
ans[i] = ans[i+1] + (mp[a[i]]==0);
//cnt[a[i]] = i;
mp[a[i]] = i;
}
ll res = 0;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
if(a[i] == 0)
{
last0 = i;
continue;
}
if(mp[a[i]] < last0)
{
res += ans[i+1];
mp[a[i]] = N;
}
}
cout<<res<<"\n";
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
solve();
return 0;
}
1006:博弈论,guess题
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
void solve()
{
ll n,m,k;
cin>>n>>m>>k;
if((n+2*m)%4) cout<<"Alice\n";
else cout<<"Bob\n";
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr),cout.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
solve();
}
}
1008:拓扑,图
ieda:首先每个点只有3种可能的颜色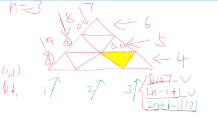
至于怎么推的我也guess了半天,如果某个块出现了直接no即可
如果都成立,那么这个点一定是属于后面的状态(即是最后一次经过的)此时只需要从另外两种颜色向这个颜色连一条边,表示这个点是后面经过的
最后进行拓扑排序,如果存在环,那么则不满足条件
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define N 100005
#define mod 998244353
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define int long long
void solve()
{
int n,k;
cin>>n>>k;
vector<vector<int>>g(3*n+1);
vector<int>in(3*n+1,0);
bool ok = 1;
while(k--)
{
int x,y,z;
cin>>x>>y>>z;
int q = (y+1)/2,p = 2*n-x+1,r = 2*n+x-y/2;
if(!ok) continue;
if(z!=q && z!=p && z!=r)
{
ok = 0;
continue;
}
if(z == q)
{
g[r].push_back(z);
g[p].push_back(z);
}
else if(z == p)
{
g[q].push_back(z);
g[r].push_back(z);
}
else if(z == r)
{
g[q].push_back(z);
g[p].push_back(z);
}
in[z] += 2;
}
if(!ok)
{
cout<<"No\n";
return ;
}
auto tuopu = [&]()
{
queue<int>q;
for(int i = 1;i <= 3*n;i++)
{
if(!in[i])
{
q.push(i);//找到入度为0的点
}
}
while(!q.empty())
{
int now = q.front();
q.pop();
for(auto &i:g[now])
{
if((--in[i]) == 0)
{
q.push(i);
}
}
}
for(int i = 1;i <= 3*n;i++)
{
if(in[i]) return false;
}
return true;
};
if(tuopu()) cout<<"Yes\n";
else cout<<"No\n";
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
solve();
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号