[LeetCode] 1372. Longest ZigZag Path in a Binary Tree 二叉树中的最长交错路径
You are given the root of a binary tree.
A ZigZag path for a binary tree is defined as follow:
- Choose any node in the binary tree and a direction (right or left).
- If the current direction is right, move to the right child of the current node; otherwise, move to the left child.
- Change the direction from right to left or from left to right.
- Repeat the second and third steps until you can't move in the tree.
Zigzag length is defined as the number of nodes visited - 1. (A single node has a length of 0).
Return the longest ZigZag path contained in that tree.
Example 1:
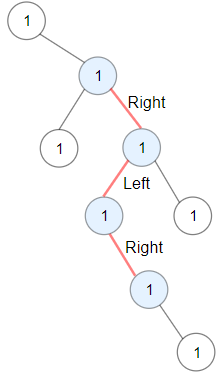
Input: root = [1,null,1,1,1,null,null,1,1,null,1,null,null,null,1]
Output: 3
Explanation: Longest ZigZag path in blue nodes (right -> left -> right).
Example 2:
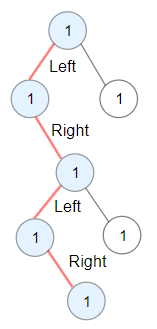
Input: root = [1,1,1,null,1,null,null,1,1,null,1]
Output: 4
Explanation: Longest ZigZag path in blue nodes (left -> right -> left -> right).
Example 3:
Input: root = [1]
Output: 0
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 5 * 104]. 1 <= Node.val <= 100
这道题给了一棵二叉树,说是让找一条最长的‘之’字路线,LeetCode 上关于 ZigZag 的题目还有好几道呢,比如 ZigZag Conversion,Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal,Path In Zigzag Labelled Binary Tree,和 Decrease Elements To Make Array Zigzag,这里的‘之’字路线,对于二叉树来说,就是左右子结点交替变换着,题目中给的例子也有图片展示,应该不难理解。这道题的本质还是一个二叉树的遍历问题,由于是求路径,那么就比较适合使用先序遍历,也就首选递归来解题。如何来写递归呢,难点还是要解决‘之’字遍历的问题,先来分析,若当前结点是其父结点的左子结点,那么只要当前结点的右子结点存在,‘之’字路经长度就可以加1。还有一种情况,若当前结点是其父结点的右子结点,而且当前结点的右子结点也存在,这时候就要以当前结点为起点,重新开始统计‘之’字路经长度,因为题目中并没有说路径必须要以根结点为起点,任意一个结点都可以当作起始结点。
分析到了这里,就可以尝试来写递归来,通过之前的分析,可以知道递归函数需要一些额外的参数,比如当前已经统计的‘之’字路经长度,还有全局的最长路径长度,同时还需要一个变量标记当前‘之’字路经的方向,这里用个整型数变量 dir,其中0表示往左,1表示往右。在主函数中,两个方向分别要调用一次递归函数。在递归函数中,首先判空,然后用当前路径长度 curLen 来更新最终结果 res。然后判断变量 dir,若 dir 为0,则说明目前往左走可以增加路径长度,则对左子结点调用递归函数,为了延长路径,之后应该往右走,所以第二个参数传1,路径长度增加1。同时也要当前结点为路径起点再统计一次,则可以对右子结点调用递归,第二个参数就传0,路径长度重置为1。若 dir 为1,则说明目前往右走可以增加路径长度,则对右子结点调用递归函数,为了延长路径,之后应该往左走,所以第二个参数传0,路径长度增加1。同时也要当前结点为路径起点再统计一次,则可以对左子结点调用递归,第二个参数就传1,路径长度重置为1,参见代码如下:
解法一:
class Solution {
public:
int longestZigZag(TreeNode* root) {
int res = 0;
dfs(root, 0, 0, res);
dfs(root, 1, 0, res);
return res;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* node, int dir, int curLen, int& res) {
if (!node) return;
res = max(res, curLen);
if (dir == 0) {
dfs(node->left, 1, curLen + 1, res);
dfs(node->right, 0, 1, res);
} else {
dfs(node->right, 0, curLen + 1, res);
dfs(node->left, 1, 1, res);
}
}
};
我们再来看一种解法,这种解法的思路是,同时记录当前结点接下来要分别去左边和右边的‘之’字路经长度。这里也是要用递归函数,新建了两个变量 left 和 right,其中 left 表示接下来要去左子结点时当前的路径长度,同理,right 表示接下来要去右子结点时当前的路径长度。在递归函数中,首先判空,然后用 left 和 right 值来更新结果 res。接下来对左子结点调用递归函数,此时因为接下来是往左走的,那么新的 left 就要重置为0,新的 right 值为原来的 left 加1,同理,对右子结点调用递归函数,此时因为接下来是往右走的,那么新的 right 就要重置为0,新的 left 值为原来的 right 加1,参见代码如下:
解法二:
class Solution {
public:
int longestZigZag(TreeNode* root) {
int res = 0, left = 0, right = 0;
dfs(root, left, right, res);
return res;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* node, int left, int right, int& res) {
if (!node) return;
res = max(res, max(left, right));
dfs(node->left, 0, left + 1, res);
dfs(node->right, right + 1, 0, res);
}
};
Github 同步地址:
https://github.com/grandyang/leetcode/issues/1372
类似题目:
Zigzag Grid Traversal With Skip
参考资料:
https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-zigzag-path-in-a-binary-tree




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号