c: two-dimensional array in windows 10 or Ubuntu 20.4
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
/**
* @brief
*
* @param arr
* @param length
* @param key
*/
void removenum(int arr[],int length,int key);
/**
* @brief
*
* @param arr
* @param length
*/
void printnum(int arr[],int length);
/**
* @brief
*
* @param arr
* @param length
*/
void printnum(int arr[],int length)
{
assert(arr!=NULL);
for(int i=0;i<length;i++)
{
printf("%d\n",arr[i]);
}
}
/**
* @brief
*
* @param arr
* @param length
* @param key
*/
void removenum(int arr[],int length,int key)
{
assert(arr!=NULL);
for(int i=0;i<length;i++)
{
if(key==arr[i])
{
for(int j=0;j<length-1;j++)
{
arr[i]=arr[j+1];
}
arr[length-1]=0;
i--;
}
}
}
int arr[12] = { 10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,110,120 };
int(*parr)[12] = &arr;//==int[12]* parr=&arr; *parr指向 int arr[12]的数组。数组里面存储的是12个元素的整形数据。
int* pparr = &arr[0];//==int* pparr[12]= &arr[0],数组元素存储的是指针
void show()
{
printf("sizeof(arr)=%ld\t sizeof(parr)=%ld\n",sizeof(arr),sizeof(parr));//sizeof(arr)=48 sizeof(parr)=8
//特别注意的是:指针和数组,sizeof是不一样,但是访问元素的时候,可以是相同的形式
//sizeof(parr)是指针:占用的内存为8个字节是指针固定占用的内存空间。
//sizeof(arr)是数组:占用的是元素个数总和的空间。
printf("*arr=%d,parr=%d,*pparr=%d,\n",*arr,*(*parr),*parr);
printf("arr=%p\t parr=%p\n",arr,parr);//都是指向数组的首地址
//parr:数组指针指向的是一个数组,准确的说,指向的是一个数组首个元素的地址
printf("*parr=%p\n",*parr);
//parr是一个指针指向的是arr数组,arr数组返回的又是数组元素的手地址,所以*parr返回的是arr数组首个元素的地址
printf("*(*parr)=%d\n",*(*parr));//10
//*(*parr)先解引用parr得到的是第一个元素的地址,在解引用指针就能获取元素的值
printf("parr访问第二个元素地址=%p\n",*parr+2);
printf("arr+1=%p\t parr+1=%p\n",arr+1,parr+1);
//arr指向的是数组的首地址,+1后表示下一个地址
//parr:指针指向的是arr的整个数组,parr+1后指向的就是下一个数组首个元素的地址。
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)
{
}
//遍历
for(int i=0;i<12;i++)
{
printf("第%d个元素的地址=%p\t 第%d个元素的值=%d\n",i,*parr+i,i,*(*parr+i));
}
}
void machar()
{
int a=10;
char* dChar;
dChar=(char *) malloc(10);
strcpy(dChar,"cbg");
strcat(dChar,"B");
printf("dChar=%p\n",dChar);
//*dChar='A';
//strcpy(dChar,'C');
//strcat(dChar,"B");
//dChar[0]='C';
//dChar[1]='b';
//dChar[2]='G';
char* ppf;
ppf=dChar;
printf("dChar=%s\n",dChar);
char *str;
/* 最初的内存分配 */
str = (char *) malloc(15);
strcpy(str, "runoob");
printf("String = %s, Address = %u\n", str, str);
/* 重新分配内存 */
str = (char *) realloc(str, 25);
strcat(str, ".com");
printf("String = %s, Address = %u\n", str, str);
free(str);
free(dChar);
}
int main()
{
printf("geovindu\n");
printf("hello world!");
printf("你好,世界\n");
machar();
int arrdu[4][5]={10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,110,120,130,140,150,160,170,180,190,200};
int arrd[3][4]={10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,110,120};
int (*pp)[4]=arrd;
//printf("%d",(*pp)[0]);
//printf("%d",(*pp)[1]);
//printf("%d",*pp[0]);
//printf("%d",*pp[1]);
//1.
printf("1列的首位元素\n");
for(int k=0;k<3;k++)
{
printf(" %d ",*pp[k]); //列的首位元素
}
printf("\n2第一行的遍历值\n");
for(int k=0;k<3;k++)
{
printf(" %d ",(*pp)[k]); //第一行的遍历值
}
printf("\n3列的首位元素\n");
//3.
for(int k=0;k<3;k++)
{
printf(" %d ",pp[k][0]); //列的首位元素
}
printf("\n4第一行的遍历值\n");
//4 第一行的遍历值
for(int k=0;k<4;k++)
{
printf(" %d ",(*pp)[k]);
}
printf("*((*pp)+1)=%d\n",*((*pp)+1)); //50
printf("*pp[1]=%d\n",*pp[1]); //50
printf("(*pp[1])+1=%d\n",(*pp[1])+1); //51
printf("*(*pp+1)=%d\n",*(*pp+1)); //20
printf("*(*arrd+1)=%d\n",*(*arrd+1)); //50
printf("*arrd[1]=%d\n",*arrd[1]); //50
printf("*arrd[3]=%d\n",*arrd[3]); //50
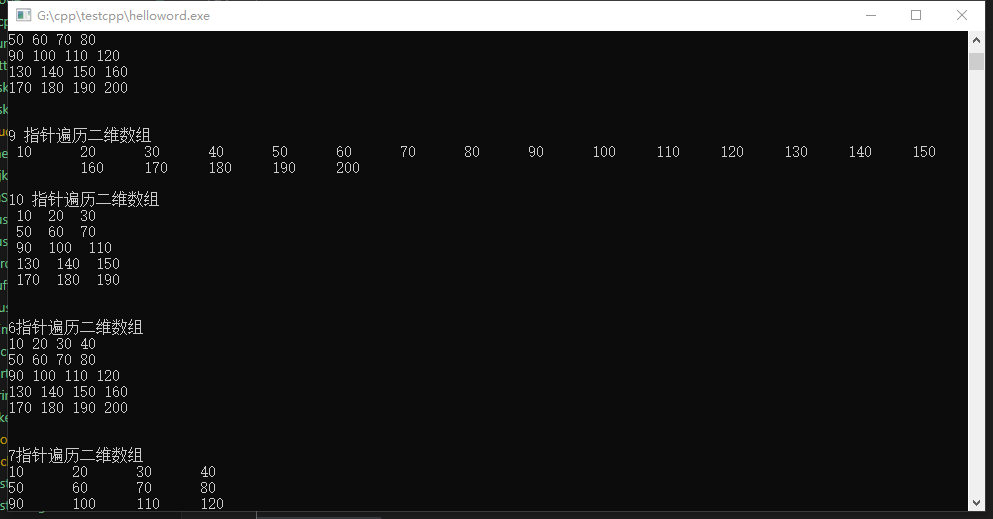
printf("\n6指针遍历二维数组\n");
int *dup;
dup=arrd[0];
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(arrd) / sizeof(int); i++)
{
//printf("%d ",&arrd[i]);
//p = arr[i];
printf("%d ",*dup++);
}
printf("\n7遍历二维数组\n");
//6 遍历二维数组
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
{
for(int k=0;k<4;k++)
{
printf(" %d ",pp[j][k]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n8遍历二维数组\n");
//6 遍历二维数组
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
{
for(int k=0;k<4;k++)
{
printf(" %d ",arrd[j][k]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
show();
char b[]="agbdkfjdkajfkdasjfdkla";
printf("%ld",sizeof(b));
int c=sizeof(b)/sizeof(b[0]);
printf("%d",c);
for (int i = 0; i < c; i++)
{
printf("i=%d,\t b=%c,\b 内存地址=%p\n",i,b[i],&b[i]);
}
int num[5]={1,2,3,4,5};
removenum(num,5,3);
printnum(num,5);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
int arrdu[4][5]={10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,110,120,130,140,150,160,170,180,190,200};
int (*pp)[5]=arrdu;
printf("1列的首位元素\n");
for(int k=0;k<4;k++)
{
printf(" %d ",*pp[k]); //列的首位元素
}
printf("\n2第一行的遍历值\n");
for(int k=0;k<4;k++)
{
printf(" %d ",(*pp)[k]); //第一行的遍历值
}
printf("\n3列的首位元素\n");
//3.
for(int k=0;k<4;k++)
{
printf(" %d ",pp[k][0]); //列的首位元素
}
printf("\n4第一行的遍历值\n");
//4 第一行的遍历值
for(int k=0;k<4;k++)
{
printf(" %d ",(*pp)[k]);
}
printf("\n6指针遍历二维数组\n");
int *dup;
dup=arrdu[0];
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(arrdu) / sizeof(int); i++)
{
//printf("%d ",&arrd[i]);
//p = arr[i];
printf("%d ",*dup++);
}
printf("\n7遍历二维数组\n");
//7 遍历二维数组
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)
{
for(int k=0;k<5;k++)
{
printf(" %d ",pp[j][k]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n8遍历二维数组\n");
//8遍历二维数组
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)
{
for(int k=0;k<5;k++)
{
printf(" %d ",arrdu[j][k]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n9 指针遍历二维数组\n");
int llen=4*5;
for(int i=0;i<20;++i)
{
printf(" %d ",*(*arrdu+i));
}
printf("\n");
printf("\n10 指针遍历二维数组\n");
int *ddpp=*arrdu;
for(int i=0;i<20;++i)
{
printf(" %d ",*(ddpp+i));
}
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
进行二维数组处理进行封装:
/**
* *****************************************************************************
* @file twoDimensional.h
* @brief 二维数组 Pointers and 2-D arrays
* @author geovindu,Geovin Du,涂聚文 (geovindu@163.com)
* ide: vscode c11,c17 windows 10
* @date 2023-10-30
* @copyright geovindu 站在巨人的肩膀上 Standing on the Shoulders of Giants
* matrix => Points to base address of two-dimensional array.
Since array decays to pointer.
*(matrix) => Points to first row of two-dimensional array.
*(matrix + 0) => Points to first row of two-dimensional array.
*(matrix + 1) => Points to second row of two-dimensional array.
**matrix => Points to matrix[0][0]
*(*(matrix + 0)) => Points to matrix[0][0]
*(*(matrix + 0) + 0) => Points to matrix[0][0]
*(*matrix + 1) => Points to matrix[0][1]
*(*(matrix + 0) + 1) => Points to matrix[0][1]
*(*(matrix + 2) + 2) => Points to matrix[2][2]
* *****************************************************************************
*/
#ifndef TWODIMENSIONAL_H_
#define TWODIMENSIONAL_H_
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define BUF_LEN 100 // Length of input buffer
#define COUNT 5 // Initial number of strings
/**
* @brief 输入字符排序
*
*/
void stringInputSort();
/**
* @brief
*
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay(const int** arry,int row,int col);
/**
* @brief
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay1(const** arry,int row,int col);
/**
* @brief
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay0(int arry[10][10],int row,int col);
/**
* @brief OK
*
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param intlength 行列共长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay2(int arry[10][10],int intlength);
/**
* @brief
*
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay3(int** arry,int row,int col);
/**
* @brief Ok
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay4(int** arry,int row,int col);
/**
* @brief OK
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay5(int*** arry,int row,int col);
/**
* @brief ok
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay6(int** arry,int row,int col);
/**
* @brief 释放所有堆内存
* @param ps
* @param n
*
*/
void freeMemoryChar(char **ps,size_t n);
/**
* @brief 释放所有堆内存
* @param ps
* @param n
*
*/
void freeMemoryInt(int **ps,size_t n);
#endif
/**
* *****************************************************************************
* @file twoDimensional.c
* @brief 二维数组 Pointers and 2-D arrays
* @author geovindu,Geovin Du,涂聚文 (geovindu@163.com)
* ide: vscode c11,c17 windows 10
* @date 2023-10-30
* @copyright geovindu 站在巨人的肩膀上 Standing on the Shoulders of Giants
* *****************************************************************************
*/
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include "include/twoDimensional.h"
/**
* @brief 输入字符排序
*
*/
void stringInputSort()
{
char buf[BUF_LEN]; // Input buffer
size_t str_count = 0; // Current string count
size_t capacity = COUNT; // Current maximum number of strings
char **pS = calloc(capacity, sizeof(char*)); // Pointers to strings
char** psTemp = NULL; // Temporary pointer to pointer to char
char* pTemp = NULL; // Temporary pointer to char
size_t str_len = 0; // Length of a string
bool sorted = false; // Indicated when strings are sorted
printf("Enter strings to be sorted, one per line. Press Enter to end:\n");
// Read in all the strings
char *ptr = NULL;
while(true)
{
ptr = fgets(buf, BUF_LEN, stdin);
if(!ptr) // Check for read error
{
printf("Error reading string.\n");
free(pS);
pS = NULL;
return 1;
}
if(*ptr == '\n') break; // Empty line check
if(str_count == capacity)
{
capacity += capacity/4; // Increase capacity by 25%
if(!(psTemp = realloc(pS, capacity))) return 1;
pS = psTemp;
}
str_len = strnlen(buf, BUF_LEN) + 1; //strnlen_s
if(!(pS[str_count] = malloc(str_len))) return 2;
strcpy_s(pS[str_count++], str_len, buf);
}
// Sort the strings in ascending order
while(!sorted)
{
sorted = true;
for(size_t i = 0 ; i < str_count - 1 ; ++i)
{
if(strcmp(pS[i], pS[i + 1]) > 0)
{
sorted = false; // We were out of order so...
pTemp= pS[i]; // swap pointers pS[i]...
pS[i] = pS[i + 1]; // and...
pS[i + 1] = pTemp; // pS[i + 1]
}
}
}
// Output the sorted strings
printf("Your input sorted in ascending sequence is:\n\n");
for(size_t i = 0 ; i < str_count ; ++i)
{
printf("%s", pS[i] );
free(pS[i]); // Release memory for the word
pS[i] = NULL; // Reset the pointer
}
free(pS); // Release the memory for pointers
pS = NULL; // Reset the pointer
}
/**
* @brief 可以
*
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay(const** arry,int row,int col)
{
//在main 中直接使用可以
printf("\n6指针遍历二维数组\n");
int *dup;
//dup= arry[0]; //*(*(arry + 0));//*(arry + 0);//
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) //sizeof(arry) / sizeof(int)
{
dup= arry[i];
for(int j=0;j<col;j++)
{
printf("%d ",*dup++);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay1(const** arry,int row,int col)
{
//在main 中直接使用可以
printf("\n7指针遍历二维数组\n");
int* dup;
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) //sizeof(arry) / sizeof(int)
{
dup=arry[i];//*arry;//
for(int j=0;j<col;j++)
{
// printf ("%d \t", *(dup+i)); //printf("\n"); //显示了第一行
printf ("%d \t", *(dup+j));
}
//printf("%d ",*dup++);
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay0(int arry[10][10],int row,int col)
{
printf("\n14指针遍历二维数组\n");
int *dup;
dup=&arry[0][0];
for (int i=0; i<row; i++){
for (int j=0; j<col; j++){
printf ("%d \t", *(dup+i*col+j));
}
printf("\n");
}
int (*pp)[col]=arry;
printf("\n1列的首位元素\n");
for(int k=0;k<row;k++)
{
printf(" %d ",*pp[k]); //列的首位元素
}
printf("\n");
printf("\n2第一行的遍历值\n");
for(int k=0;k<row;k++)
{
printf(" %d ",(*pp)[k]); //第一行的遍历值
}
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief
*
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param intlength 行列共长度 row*col
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay2(int arry[10][10],int intlength)
{
printf("\n9 指针遍历二维数组\n");
//int llen=4*5;
for(int i=0;i<intlength;++i)
{
printf(" %d\t",*(*arry+i));
}
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief 可以
*
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay3(int** arry,int row,int col)
{
//在main 中直接使用可以
printf("\n10 指针遍历二维数组\n");
int *ddpp;//=*arry;
for(int i=0;i<row;++i)
{
ddpp=*(arry+i);
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
printf(" %d ",*(ddpp+j));
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief Ok
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay4(int** arry,int row,int col)
{
printf("\n11 指针遍历二维数组\n");
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
printf("%d ", arry[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief ok
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay6(int** arry,int row,int col)
{
printf("\n13 指针遍历二维数组\n");
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
//printf("Address of %d th array %u \n",i , *(arry + i));
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
printf("%d ", *( *(arry + i) + j));
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief OK
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay5(int*** arry,int row,int col)
{
printf("\n12 指针遍历二维数组\n");
for (int i = 0; i <row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <col; j++)
{
printf("%d ", *arry[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief 释放所有堆内存
* @param ps
* @param n
*
*/
void freeMemoryChar(char **ps,size_t n)
{
for(size_t i=0;i<n;n++)
{
free(ps[i]);
ps[i]=NULL;
}
free(ps);
ps=NULL;
}
/**
* @brief 释放所有堆内存
* @param ps
* @param n
*
*/
void freeMemoryInt(int **ps,size_t n)
{
for(size_t i=0;i<n;n++)
{
free(ps[i]);
ps[i]=NULL;
}
free(ps);
ps=NULL;
}
调用:
windows10:
int main()
{
printf("hello c world \n");
printf("你好,中国\n");
// stringInputSort();
int arrdu[5][4]={
{10,20,30,40},
{50,60,70,80},
{90,100,110,120},
{130,140,150,160},
{170,180,190,200}
};
// 4 列
int dum=4;
//5 行
int dun=5;
for(int i = 0; i <dun ; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < dum; j++) {
printf("%d ", arrdu[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n\n");
for(int i = 0; i <dun ; i++)
{
printf("Address of %d th array %u \n",i , *(arrdu + i));
for(int j = 0; j <dum ; j++)
{
printf("arr[%d][%d]=%d\n", i, j, *( *(arrdu + i) + j) );
}
printf("\n\n");
}
int* ptr = malloc((dum * dun) * sizeof(int));
/* Putting 1 to 12 in the 1D array in a sequence */
for (int i = 0; i < dun * dum; i++)
ptr[i] = i + 1;
//int** pe;
//pe=arrdu;
/**/
//分配内存
int** pe = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int)*dum);
for(int i=0; i<dun; i++)
{
pe[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*dum);
}
//初始化内存
//memset(*pe, 0, sizeof(int)*dum*dun);
//2分配内存
int*** arr2 = malloc(dum * sizeof(int**));
for (int i = 0; i < dun; i++)
arr2[i] = malloc(dun * sizeof(int*));
// Initialising each element of the
// pointer array with the address of
// element present in the other array
for (int i = 0; i <dun; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <dum ; j++) {
arr2[i][j] = &arrdu[i][j];
}
}
printf("The values are\n");
for (int i = 0; i <dun ; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <dum ; j++) {
printf("%d ", *arr2[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//strcpy(pe,arrdu);
for (int i = 0; i <dun ; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <dum ; j++)
{
pe[i][j]= arrdu[i][j];
//ptr[i][j]=arrdu[i][j];
//strcpy(pe[i][j],arrdu[i][j]);
printf("%d\n",arrdu[i][j]);
}
}
printf("PE The values are\n");
for (int i = 0; i < dun; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <dum ; j++) {
printf("%d ", pe[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
pointDisplay0(arrdu,dun,dum); //ok
pointDisplay4(pe,dun,dum); //ok
pointDisplay5(arr2,dun,dum); //ok
pointDisplay6(pe,dun,dum); //ok
pointDisplay2(arrdu,dum*dun); //ok
pointDisplay3(pe,dun,dum);
pointDisplay(pe,dun,dum); //12
pointDisplay1(pe,dun,dum); //12
//释放资源
free(pe);
free(arr2);
pe=NULL;
arr2=NULL;
system("pause");// linux 无效 ,只win 下有效
return 0;
}
windows or Ubuntu:
printf("hello c world, \n");
printf("你好,中国\n");
//setlocale(LC_ALL,"CN");
//int arrdu[5][4]={10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,110,120,130,140,150,160,170,180,190,200};
int arrdu[5][4]={
{10,20,30,40},
{50,60,70,80},
{90,100,110,120},
{130,140,150,160},
{170,180,190,200}
};
//5 行
int dun=5;
// 4 列
int dum=4;
for(int i = 0; i <dun ; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < dum; j++) {
printf("%d ", arrdu[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n\n");
for(int i = 0; i <dun ; i++)
{
printf("Address of %d th array %u \n",i , *(arrdu + i));
for(int j = 0; j <dum ; j++)
{
printf("arr[%d][%d]=%d\n", i, j, *( *(arrdu + i) + j) );
}
printf("\n\n");
}
int* ptr = malloc((dum * dun) * sizeof(int));
/* Putting 1 to 12 in the 1D array in a sequence */
for (int i = 0; i < dun * dum; i++)
ptr[i] = i + 1;
//int** pe;
//pe=arrdu;
/**/
//分配内存
// int** pe = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int)*dum);
// for(int i=0; i<dun; i++)
//{
//pe[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*dum);
//}
//分配内存
//int** pe = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int)*dum);
int** pe =malloc(dum * sizeof(int**));// (int**)malloc(sizeof(int)*dum);
for(int i=0; i<dun; i++)
{
pe[i] =malloc(dun * sizeof(int*));// (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*dun); //dum
}
//初始化内存
//memset(*pe, 0, sizeof(int)*dum*dun);
//2分配内存
int*** arr2 = malloc(dum * sizeof(int**));
for (int i = 0; i < dun; i++)
arr2[i] = malloc(dun * sizeof(int*));
// Initialising each element of the
// pointer array with the address of
// element present in the other array
for (int i = 0; i <dun; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <dum ; j++) {
arr2[i][j] = &arrdu[i][j];
}
}
printf("The values are\n");
for (int i = 0; i <dun ; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <dum ; j++) {
printf("%d ", *arr2[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//strcpy(pe,arrdu);
for (int i = 0; i <dun ; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <dum ; j++)
{
pe[i][j]= arrdu[i][j];
//ptr[i][j]=arrdu[i][j];
//strcpy(pe[i][j],arrdu[i][j]);
printf("%d\n",arrdu[i][j]);
}
}
printf("PE The values are\n");
for (int i = 0; i < dun; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <dum ; j++) {
printf("%d ", pe[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
pointDisplay0(arrdu,dun,dum); //ok
pointDisplay4(pe,dun,dum); //ok
pointDisplay5(arr2,dun,dum); //ok
pointDisplay6(pe,dun,dum); //ok
pointDisplay2(arrdu,dum*dun); //ok
pointDisplay3(pe,dun,dum);
pointDisplay(pe,dun,dum); //12
pointDisplay1(pe,dun,dum); //12
修改一下内存分配,就都可以用。
//分配内存
//int** pe = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int)*dum);
int** pe =malloc(dum * sizeof(int**));// (int**)malloc(sizeof(int)*dum);
for(int i=0; i<dun; i++)
{
pe[i] =malloc(dun * sizeof(int*));// (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*dun); //dum
}
调用也可以封装在头文件中:
/**
* *****************************************************************************
* @file pointersHat.c
* @brief Understand pointers to your hat size - if you dare
* @author geovindu,Geovin Du,涂聚文 (geovindu@163.com)
* ide: vscode c11,c17 windows 10
* @date 2023-10-31
* @copyright geovindu站在巨人的肩膀上 Standing on the Shoulders of Giants
* *****************************************************************************
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "include/pointersHat.h"
#include "include/typeGame.h"
#include "include/twoDimensional.h"
/**
* @brief 显示二维数组指针
*
*/
void displayTwoPoint()
{
int arrdu[5][4]={
{10,20,30,40},
{50,60,70,80},
{90,100,110,120},
{130,140,150,160},
{170,180,190,200}
};
// 4 列
int dum=4;
//5 行
int dun=5;
for(int i = 0; i <dun ; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < dum; j++) {
printf("%d ", arrdu[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n\n");
for(int i = 0; i <dun ; i++)
{
printf("Address of %d th array %u \n",i , *(arrdu + i));
for(int j = 0; j <dum ; j++)
{
printf("arr[%d][%d]=%d\n", i, j, *( *(arrdu + i) + j) );
}
printf("\n\n");
}
int* ptr = malloc((dum * dun) * sizeof(int));
/* Putting 1 to 12 in the 1D array in a sequence */
for (int i = 0; i < dun * dum; i++)
ptr[i] = i + 1;
//int** pe;
//pe=arrdu;
/**/
//分配内存
/**
*
*
window
int** pe = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int)*dum);
for(int i=0; i<dun; i++)
{
pe[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*dum);
}
*/
//windows Ubuntu 都可以用
int** pe =malloc(dum * sizeof(int**));
for(int i=0; i<dun; i++)
{
pe[i] =malloc(dun * sizeof(int*));
}
//初始化内存
//memset(*pe, 0, sizeof(int)*dum*dun);
//2分配内存
int*** arr2 = malloc(dum * sizeof(int**));
for (int i = 0; i < dun; i++)
arr2[i] = malloc(dun * sizeof(int*));
// Initialising each element of the
// pointer array with the address of
// element present in the other array
//赋值
for (int i = 0; i <dun; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <dum ; j++) {
arr2[i][j] = &arrdu[i][j];
}
}
printf("The values are\n");
for (int i = 0; i <dun ; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <dum ; j++) {
printf("%d ", *arr2[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//strcpy(pe,arrdu);
//赋值
for (int i = 0; i <dun ; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <dum ; j++)
{
pe[i][j]= arrdu[i][j];
//ptr[i][j]=arrdu[i][j];
//strcpy(pe[i][j],arrdu[i][j]);
printf("%d\n",arrdu[i][j]);
}
}
printf("PE The values are\n");
for (int i = 0; i < dun; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <dum ; j++) {
printf("%d ", pe[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
pointDisplay0(arrdu,dun,dum); //ok
pointDisplay4(pe,dun,dum); //ok
pointDisplay5(arr2,dun,dum); //ok
pointDisplay6(pe,dun,dum); //ok
pointDisplay2(arrdu,dum*dun); //ok
pointDisplay3(pe,dun,dum);//ok
pointDisplay(pe,dun,dum); //ok
pointDisplay1(pe,dun,dum); //ok
//释放资源
free(pe);
free(arr2);
pe=NULL;
arr2=NULL;
}
输出:

/** * ***************************************************************************** * @file geovindu.h * @brief * * @author geovindu,Geovin Du,涂聚文 (geovindu@163.com) * ide: vscode c11,c17 windows 10 * @date 2023-11-01 * @copyright geovindu 站在巨人的肩膀上 Standing on the Shoulders of Giants * ***************************************************************************** */ #ifndef GEOVINDU_H_ #define GEOVINDU_H_ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdbool.h> #include <ctype.h> #include <string.h> #include "CheckTieck.h" #include "TakeNumber.h" #include "Dustring.h" #include "SortAlgorithm.h" #include "KruskalAlgorithm.h" #include "FordFulkersonAlgorithm.h" #include "PrimsAlgorithm.h" #include "HuffmanCoding.h" #include "RecursionFunc.h" #include "duSortType.h" /** * @brief 排队叫号 * */ void QueueDisplay(); /** * @brief 作业 * */ void HomeWork(); /** * @brief 其他 * */ void other(); /** * @brief 1.冒泡排序 * */ void displayBubbleSort(); /** * @brief 2选择排序 * */ void displaySelectionSort(); /** * @brief 3插入排序 * */ void displayInsertionSort(); /** * @brief 4快速排序 * */ void displayQuickSort(); /** * @brief 5合并排序 * */ void displayMergeSort(); /** * @brief 6计数排序 * */ void displayCountingSort(); /** * @brief 7基数排序 * */ void displayRadixsort(); /** * @brief 8桶排序 * */ void displayBucketSort(); /** * @brief 9堆排序 * */ void displayHeapSort(); /** * @brief 10.希尔排序 * */ void displayShellSort(); /** * @brief 11.顺序查找 * */ void displayLinearSearch(); /** * @brief 12.二分搜索 * */ void displayBinarySearch(); /** * @brief 13.kruskal算法,请输入三个数字一行,输完一个数字时,按一个空格分开 * */ void displayKruskalAlgo(); /** * @brief Ford - Fulkerson algorith * */ void displayFordFulkerson(); /** * @brief Dijkstra's Algorithm 迪杰斯特拉算法 最短路径算法 * */ void displayDijkstra(); /** * @brief Prim's Algorithm * */ void displayPrims(); /** * @brief 17.霍夫曼编码 Char | Huffman code * */ void displayHuffmanarr(); #endif
/**
* *****************************************************************************
* @file geovindu.c
* @brief
* @author geovindu,Geovin Du,涂聚文 (geovindu@163.com)
* ide: vscode c11,c17 windows 10
* @date 2023-11-01
* @copyright geovindu 站在巨人的肩膀上 Standing on the Shoulders of Giants
* *****************************************************************************
*/
#include "include/geovindu.h"
/**
* @brief 排队叫号
*
*/
void QueueDisplay()
{
QueueCalling *queue1;
//int iii,nnn;
char select='1';
//int num=1;//顾客序号
num=0; //叫号编号
queue1=QueueInit(); //初始化队列
if(queue1==NULL)
{
printf("创建队列时出错!\n");
getch();
return 0;
}
do{
if(select=='1'||select=='2') //不定这条件,在Ubuntu上此列表会显示两次
{
printf("\n请选择具体操作:\n");
printf("1.新到顾客\n");
printf("2.下一个顾客\n");
printf("0.退出\n") ;
fflush(stdin);
}
select=getchar(); //windows getch() Ubuntu: getchar()
switch(select)
{
case '1':
add(queue1);
printf("\n现在共有%d位顾客在等候!\n",QueueLen(queue1));
break;
case '2':
next(queue1);
printf("\n现在共有%d位顾客在等候!\n",QueueLen(queue1));
break;
case '0':
break;
}
}while(select!='0');
QueueFree(queue1); //释放队列
//getch();
getchar();
//内存分配函数 malloc() 分配并初始化函数 calloc() 重新分配内存函数 realloc 释放内存free()
int *buf1,* buf2, * buf3;
buf1=(int*)malloc(100*sizeof(int));
buf2=(int*)calloc(100,sizeof(int));
buf3=(int*)realloc(buf2,500*sizeof(int));
free(buf1);
free(buf3);
}
/**
* @brief 作业
*
*/
void HomeWork()
{
char *dustr = "GXZXLeaag%^*** 1092367145 &*@654123HUYqianrushi"; //这个不可以用替换函数,需要索引长度大于自身的宽度
char *substr = "109236714533";
char *substr2 = "654123";
char geovindu[100] = "GXZXLeaag%^*** 1092367145 &*@654123HUYqianrushi"; //必须索引值大,否则不可以替换
char *newdig[10];
char *digg;
char *sdu;
char *newdig2[6];
char newstrd[10]={0};//初始化赋值
char *ddu[10]={'\0'};; //初始化赋值
int digitsdu[10] = {0}; // 存储数字出现的次数
for (int i = 0; substr[i] != '\0'; i++) {
if (isdigit(substr[i])) {
digitsdu[substr[i] - '0']++;
}
}
for (int i = 9; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = 0; j < digitsdu[i]; j++) {
char digitChar = i + '0';
strncat(newstrd, &digitChar, 1);
//printf("%c",digitChar);
strncat(ddu, &digitChar, 1);
}
}
char newstrd2[6]={0}; //初始化赋值
char *ddu2[6]={'\0'};//初始化赋值
int digitsdu2[10] = {0}; // 存储数字出现的次数
for (int i = 0; substr2[i] != '\0'; i++) {
if (isdigit(substr2[i])) {
digitsdu2[substr2[i] - '0']++;
}
}
for (int i = 9; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = 0; j < digitsdu2[i]; j++) {
char digitChar = i + '0';
strncat(newstrd2, &digitChar, 1);
//*(newchar+j)=digitChar;
//*(newchar+i)=digitChar;
//printf("%c",digitChar);
//ddu2[i]=digitChar;
strncat(ddu2, &digitChar, 1);
}
}
printf("\n1: %s\n",newstrd);
printf("2: %s\n",ddu);
printf("3: %s\n",newstrd2);
printf("4: %s\n",ddu2);
char *newddd=newstrd;
char *fff;
char *kk;
char dustr11[10] = "1092367145";
char dustr22[6] = "654123";
digg=duStrCmpSortDesc(dustr11,newdig,10);
kk=duStrCmpSortDesc(dustr22,newdig2,6);
char* Olddustr11 = "1092367145";
char* Olddustr22 = "654123";
fff=duReplace(geovindu,Olddustr11,ddu); //ddu
printf("fff1:%s\n",fff);
fff=duReplace(geovindu,Olddustr22,ddu2);
printf("fff2:%s\n",fff);
printf("\nnew:%s\n",digg);
printf("newdig:%s\n",newdig);
printf("newdig2:%s\n",newdig2);
printf("kk:%s\n",kk);
printf("fff3:%s\n",fff);
/*
//查找索引
char *dus =strstr(dustr,substr); //
char *dus2=strstr(dustr,substr2);//
if(dus==NULL)
printf("can't find %s in %s\n",substr,dustr);
else
printf("%s include %s;show the string from start found address:%s\n", dustr,substr,dus);
//起始索引
int index=dus - dustr;
int index2=dus2-dustr;
//结束索引
int endindex=index+strlen(substr);
int endindex2=index2+strlen(substr2);
printf("1092367145 start index:%d,end:%d.\n",index,endindex);
printf("654123 start index:%d,end:%d.\n",index2,endindex2);
*/
//char ch[100] = "GXZXLeaag%^*** 1092367145 &*@654123HUYqianrushi";
char duresult[100]; // 存储处理后的结果
char gx[]="GXZX";
char *dup;
char *gxdup;
char newstr[100];
char *des;
dup=fff; //fff
char gxz[]="高训中心";
//strcat(newstr, "高训中心");
strncat(newstr,&gxz,8);
//printf("%s/n",gxdup);
int gxlen=strlen("高训中心");
//*(dup+14)='d';
int l=sizeof(geovindu)/sizeof(geovindu[0]);
//倒序显示
//for(int i=l;i>=0;i--)
//{
// printf("%c\n",dup[i]); //
// }
//顺序显示
for(int i=4;i<l;i++)
{
if(dup[i]>='A' && dup[i]<='Z')
{
printf("%c\n",dup[i]);
char sd=dup[i];
strncat(newstr,&sd,1);
}
else if(dup[i]>='a' && dup[i]<='z')
{
printf("%c\n",toupper(dup[i]));
*(dup+i)=toupper(dup[i]);
char sx=toupper(dup[i]);
strncat(newstr,&sx,1);
}
else if(isdigit(dup[i]))
{
printf("數字:%c\n",dup[i]);
char sszi=dup[i];
strncat(newstr,&sszi,1);
}
else
{
//des=newstr;
//des=dup[i];
//strcat(des[1],dup[i]); //strcpy(des, dup[i]);
//memset(des, '\0', sizeof(des));
//strcat(&des,&dup[i]);
//*(des+i) = '*';
//*(des+i+1)=dup[i];
//printf("%c\n",dup[i]);
char qita=dup[i];
strncat(newstr, &qita, 1);
strncat(newstr, &qita, 1);
}
//
}
//gxdup=duReplace(ch,"GXZX","高训中心");
//printf("gx=%s\n",gxdup);
printf("处理后的字符串:= %s\n",newstr);
/*
// (1) 将GXZX前四个字符串中的大写字母转换成“高训中心”
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if (isupper(ch[i])) {
strcat(duresult, "高训中心");
} else {
// (2) 将字符串中其余的小写字母转换成大写字母
char uppercaseChar = toupper(ch[i]);
strncat(duresult, &uppercaseChar, 1);
}
}
// (3) 数字降序排序
int digits[10] = {0}; // 存储数字出现的次数
for (int i = 0; ch[i] != '\0'; i++) {
if (isdigit(ch[i])) {
digits[ch[i] - '0']++;
}
}
for (int i = 9; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = 0; j < digits[i]; j++) {
char digitChar = i + '0';
strncat(duresult, &digitChar, 1);
}
}
// (4) 特殊符号加倍输出
for (int i = 4; ch[i] != '\0'; i++) {
if (!isalpha(ch[i]) && !isdigit(ch[i])) {
strncat(duresult, &ch[i], 1);
strncat(duresult, &ch[i], 1);
}
}
printf("处理后的字符串:%s\n", duresult);
*/
}
/**
* @brief 其他
*
*/
void other()
{
/*
textbackgroud(0);
clrscr();
for(int i=1;i<8;i++)
{
window(10+i*5,5+i,30+i*5,15+i);
textbacktgroud(i);
clrscr();
}
gettch();*/
/*
//char a[10]="1092367145"; //变量名重复赋值,这个编译出问题
char bbdu[10]="1092367145";
char* c[10]={'\0'};
qsort(a,strlen(a),sizeof(a[0]),cmp);
for(int i=0;i<=10;i++)
{
char du=a[i];
printf("%c ",du);
strncat(c, &du, 1);
//c[i]=du;
}
printf("\nc=:%s length=:%d\n",c,strlen(c));
char* charqs[10]={'\0'};//NULL; //
char* reqs;
printf("\n 原串: %s",bbdu);
reqs=duStrCmpSortDesc(bbdu,charqs,10);
printf("\nchar:%s lenght=:%d\n",charqs,strlen(charqs));
printf("\nchar:%s\n",reqs);
*/
/*
//分割字符串 https://githubmota.github.io/2017/12/29/2017-12-29-Linux-C-Split/
//如何找到数字字符串的首位数和末位数索引
char ssss[] = "GXZXLeaag%^*** 1092367145 &*@654123HUYqianrushi";
char delim[] = " ,!";
char *token;
for(token = strtok(ssss, delim); token != NULL; token = strtok(NULL, delim)) {
printf(token);
printf("\n\f");
}
printf("\n");
*/
//先把数字排序处理了
//再处理其他的
//最后替换其他的
//printf("%s",dup);
//*(p+10)="G";
char str1[14] = "涂聚文";
char str2[14] = "google";
char str3[14];
int len ;
/* 复制 str1 到 str3 */
strcpy(str3, str1);
printf("strcpy( str3, str1) : %s\n", str3 );
/* 连接 str1 和 str2 */
strcat( str1, str2);
printf("strcat( str1, str2): %s\n", str1 );
/* 连接后,str1 的总长度 */
len = strlen(str1);
printf("strlen(str1) : %d\n", len );
printf("文件名:%s"__FILE__);
printf("\n当前行号:%d",__LINE__);
printf("\n日期:%s",__DATE__);
printf("\n时间:%s\n",__TIME__);
int res=RecursionFun(20);
printf("res=%d",res);
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief 1.冒泡排序
*
*/
void displayBubbleSort()
{
int i;
int *p;
char str[20];
//1.冒泡排序
int data[12]={60,50,39,27,12,8,45,63,20,2,10,88}; /* 原始数据 */
int lensize=sizeof(data) / sizeof(data [0]);//sizeof(data);
p=BubbleSort(data,lensize);
itoa(lensize, str, 10);
printf("\n1共長度是 %d ",lensize);
printf("\n1冒泡排序的结果为:");
for (i=0;i<lensize;i++)
printf("%3d",p[i]);
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief 2选择排序
*
*/
void displaySelectionSort()
{
int arr[] = { 64, 25, 12, 22, 11,88,28,100 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
SelectionSort(arr, n);
int ii;
printf("2选择排序结果为:");
for(ii = 0; ii < n; ii++)
printf("%d ", arr[ii]);
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief 3插入排序
*
*/
void displayInsertionSort()
{
int ii;
int inarr[] = {25, 23, 28, 16, 18,100,8,99};
// calculating the size of array
int size = sizeof(inarr) / sizeof(inarr[0]);
printf("3插入排序结果为:");
InsertionSort(inarr, size);
for(ii = 0; ii < size; ii++)
printf("%d ", inarr[ii]);
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief 4快速排序
*
*/
void displayQuickSort()
{
int size;
// defining and initializing an array
int qsarr[] = {100,25, 23, 28, 16, 18,8,99,3,20};
printf("4快速排序结果为:");
// calculating the size of array
size = sizeof(qsarr) / sizeof(qsarr[0]);
QuickSort(qsarr, 0, size - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
printf("%d ", qsarr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief 5合并排序
*
*/
void displayMergeSort()
{
printf("5合并排序结果为:");
int mearr[] = { 12, 11, 23, 55, 6, 57,3,100,9 };
int arr_size = sizeof(mearr) / sizeof(mearr[0]);
MergeSort(mearr, 0, arr_size - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < arr_size; i++)
printf("%d ", mearr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief 6计数排序
*
*/
void displayCountingSort()
{
printf("6计数排序结果为:");
int carray[] = {4, 2, 2, 8, 3, 3, 1};
int cn = sizeof(carray) / sizeof(carray[0]);
CountingSort(carray, cn);
for (int i = 0; i < cn; i++)
printf("%d ", carray[i]);
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief 7基数排序
*
*/
void displayRadixsort()
{
printf("7基数排序结果为:");
int rarray[] = {121, 432, 564, 23, 1, 45, 788};
int rn = sizeof(rarray) / sizeof(rarray[0]);
Radixsort(rarray, rn);
for (int i = 0; i < rn; i++)
printf("%d ", rarray[i]);
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief 8桶排序
*
*/
void displayBucketSort()
{
printf("8桶排序结果为:");
int barray[] = {42, 32, 33, 5,52, 37,100, 47, 51};
BucketSort(barray);
int bn = sizeof(barray) / sizeof(barray[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < bn; i++)
printf("%d ", barray[i]);
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief 9堆排序
*
*/
void displayHeapSort()
{
printf("9堆排序结果为:");
int harr[] = {1, 12, 9, 5, 6, 10};
int hn = sizeof(harr) / sizeof(harr[0]);
HeapSort(harr, hn);
for (int i = 0; i < hn; i++)
printf("%d ", harr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief 10.希尔排序
*
*/
void displayShellSort()
{
printf("10.希尔排序结果为:");
int sdata[] = {9, 8, 3, 7, 25, 6, 4, 11,38};
int ssize = sizeof(sdata) / sizeof(sdata[0]);
ShellSort(sdata, ssize);
for (int i = 0; i < ssize; i++)
printf("%d ", sdata[i]);
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief 11.顺序查找
*
*/
void displayLinearSearch()
{
printf("11.顺序查找结果为:");
int lsdata[] = {9, 8, 3, 7, 25, 6, 4, 11,38};
int key=25; //要查找的数字
int lsize = sizeof(lsdata) / sizeof(lsdata[0]);
int result = LinearSearch(lsdata, lsize,key);
(result == -1) ? printf("\nElement not found") : printf("\nElement found at index(数组中的索引号是:): %d\n", result);
}
/**
* @brief 12.二分搜索
*
*/
void displayBinarySearch()
{
printf("\n12.二分搜索结果为:\n");
int bsarray[] = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
int bsize = sizeof(bsarray) / sizeof(bsarray[0]);
int xkey = 8;
int bresult = BinarySearch(bsarray, xkey, 0, bsize - 1);
if (bresult == -1)
printf("Not found");
else
printf("Element is found at index(数组中的索引号是:) %d\n", bresult);
}
/**
* @brief 13.kruskal算法,请输入三个数字一行,输完一个数字时,按一个空格分开
*
*/
void displayKruskalAlgo()
{
printf("\n13.kruskal算法,请输入三个数字一行,输完一个数字时,按一个空格分开:\n");
/*
int ki;
struct edge edges[N], minTree[P - 1];
for (ki = 0; ki < N; ki++) {
scanf("%d %d %d", &edges[ki].initial, &edges[ki].end, &edges[ki].weight);//每行输入3个数字 输入一个数字时,按空格键
}
KruskalMinTree(edges, minTree);
*/
//n = 6;
int KruskalGraph[MAX][MAX];
KruskalGraph[0][0] = 0;
KruskalGraph[0][1] = 4;
KruskalGraph[0][2] = 4;
KruskalGraph[0][3] = 0;
KruskalGraph[0][4] = 0;
KruskalGraph[0][5] = 0;
KruskalGraph[0][6] = 0;
KruskalGraph[1][0] = 4;
KruskalGraph[1][1] = 0;
KruskalGraph[1][2] = 2;
KruskalGraph[1][3] = 0;
KruskalGraph[1][4] = 0;
KruskalGraph[1][5] = 0;
KruskalGraph[1][6] = 0;
KruskalGraph[2][0] = 4;
KruskalGraph[2][1] = 2;
KruskalGraph[2][2] = 0;
KruskalGraph[2][3] = 3;
KruskalGraph[2][4] = 4;
KruskalGraph[2][5] = 0;
KruskalGraph[2][6] = 0;
KruskalGraph[3][0] = 0;
KruskalGraph[3][1] = 0;
KruskalGraph[3][2] = 3;
KruskalGraph[3][3] = 0;
KruskalGraph[3][4] = 3;
KruskalGraph[3][5] = 0;
KruskalGraph[3][6] = 0;
KruskalGraph[4][0] = 0;
KruskalGraph[4][1] = 0;
KruskalGraph[4][2] = 4;
KruskalGraph[4][3] = 3;
KruskalGraph[4][4] = 0;
KruskalGraph[4][5] = 0;
KruskalGraph[4][6] = 0;
KruskalGraph[5][0] = 0;
KruskalGraph[5][1] = 0;
KruskalGraph[5][2] = 2;
KruskalGraph[5][3] = 0;
KruskalGraph[5][4] = 3;
KruskalGraph[5][5] = 0;
KruskalGraph[5][6] = 0;
edge_list spanlist;
edge_list elist;
KruskalAlgo(KruskalGraph,spanlist,spanlist);
}
/**
* @brief Ford - Fulkerson algorith
*
*/
void displayFordFulkerson()
{
printf("\n14 Ford - Fulkerson algorith \n");
int n=10;
int capacity[10][10];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
capacity[i][j] = 0;
}
}
capacity[0][1] = 8;
capacity[0][4] = 3;
capacity[1][2] = 9;
capacity[2][4] = 7;
capacity[2][5] = 2;
capacity[3][5] = 5;
capacity[4][2] = 7;
capacity[4][3] = 4;
int s = 0, t =5;
printf("\nMax Flow: %d\n", FordFulkerson(s, t,capacity));
}
/**
* @brief Dijkstra's Algorithm 迪杰斯特拉算法 最短路径算法
*
*/
void displayDijkstra()
{
int Graph[MAX][MAX], j, u;
int n = 7;
Graph[0][0] = 0;
Graph[0][1] = 0;
Graph[0][2] = 1;
Graph[0][3] = 2;
Graph[0][4] = 0;
Graph[0][5] = 0;
Graph[0][6] = 0;
Graph[1][0] = 0;
Graph[1][1] = 0;
Graph[1][2] = 2;
Graph[1][3] = 0;
Graph[1][4] = 0;
Graph[1][5] = 3;
Graph[1][6] = 0;
Graph[2][0] = 1;
Graph[2][1] = 2;
Graph[2][2] = 0;
Graph[2][3] = 1;
Graph[2][4] = 3;
Graph[2][5] = 0;
Graph[2][6] = 0;
Graph[3][0] = 2;
Graph[3][1] = 0;
Graph[3][2] = 1;
Graph[3][3] = 0;
Graph[3][4] = 0;
Graph[3][5] = 0;
Graph[3][6] = 1;
Graph[4][0] = 0;
Graph[4][1] = 0;
Graph[4][2] = 3;
Graph[4][3] = 0;
Graph[4][4] = 0;
Graph[4][5] = 2;
Graph[4][6] = 0;
Graph[5][0] = 0;
Graph[5][1] = 3;
Graph[5][2] = 0;
Graph[5][3] = 0;
Graph[5][4] = 2;
Graph[5][5] = 0;
Graph[5][6] = 1;
Graph[6][0] = 0;
Graph[6][1] = 0;
Graph[6][2] = 0;
Graph[6][3] = 1;
Graph[6][4] = 0;
Graph[6][5] = 1;
Graph[6][6] = 0;
u = 0;
Dijkstra(Graph, n, u);
}
/**
* @brief Prim's Algorithm
*
*/
void displayPrims()
{
int G[V][V] = {
{0, 9, 75, 0, 0},
{9, 0, 95, 19, 42},
{75, 95, 0, 51, 66},
{0, 19, 51, 0, 31},
{0, 42, 66, 31, 0}};
Prims(G);
}
/**
* @brief 17.霍夫曼编码 Char | Huffman code
*
*/
void displayHuffmanarr()
{
int arr[] = { 64, 25, 12, 22, 11,88,28,100 };
char Huffmanarr[] = {'A', 'B', 'C', 'D'};
int freq[] = {5, 1, 6, 3};
int Huffmansize = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf(" 17.霍夫曼编码 Char | Huffman code ");
printf("\n--------------------\n");
HuffmanCodes(Huffmanarr, freq, Huffmansize);
}
调用:、
/*
* @Author: 涂聚文 geovindu,Geovin Du
* @Date: 2023-09-11 14:07:29
* @LastEditors:
* @LastEditTime: 2023-09-20 14:35:49
* @FilePath: \testcpp\helloword.c
* @Description:
*/
/*****************************************************************//**
* \file helloworld.C
* \brief 业务操作方法
* \IDE: VSCODE c11 安装插件“Doxygen Documentation Generator”,用来生成注释。
安装插件”C/C++ Snippets”,用来生成文件头、代码块分割线等。KoroFileHeader
C/C++ Snippets插件设置 https://devblogs.microsoft.com/cppblog/c11-and-c17-standard-support-arriving-in-msvc/
堆区Heap Area 栈区 Stack Area windows
* \author geovindu,Geovin Du 站在巨人的肩膀上 Standing on the Shoulders of Giants
* \date 2023-09-19
* \copyright
* \namespace
*
***********************************************************************/
#include<string.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<dir.h>
#include<dos.h>
#include<process.h>
#include<dos.h>
#include<bitsmsg.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<dos.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
//#include "include/SortAlgorithm.h"
//#include "include/KruskalAlgorithm.h"
//#include "include/FordFulkersonAlgorithm.h"
//#include "include/PrimsAlgorithm.h"
//#include "include/HuffmanCoding.h"
//#include "include/RecursionFunc.h"
//#include "include/duSortType.h"
//
//#include "include/CheckTieck.h"
//#include "include/TakeNumber.h"
//#include "include/twoDimensional.h"
#include "include/dynamicPrime.h"
#include "include/pointersHat.h"
#include "include/typeGame.h"
#include "include/geovindu.h"
//以文件夹的头文件能“分层”显示,易于维护和管理代码文件
int main(void)
{
printf("hello c world \n");
printf("你好,中国\n");
//注释的函数,可以消除注释就可以执行测试效果
//findWord();
//displayGame();
// stringInputSort();
//displayPrime();
//displayHat();
//二维数组指针
//displayTwoPoint();
//排除等候
// QueueDisplay();
//作业 字符串替换
HomeWork();
//
other();
//1.冒泡排序
displayBubbleSort();
//2选择排序
displaySelectionSort();
//3插入排序
displayInsertionSort();
//4快速排序
displayQuickSort();
//5 合并排序
displayMergeSort();
//6 计数排序
displayCountingSort();
//7. 基数排序
displayRadixsort();
//8 Bucket Sort 桶排序
displayBucketSort();
//9堆排序
displayHeapSort();
//10.希尔排序
displayShellSort();
//11 顺序查找(Linear/Sequential Search),也称为线性查找
displayLinearSearch();
//12 Binary Search 二分搜索
displayBinarySearch();
//13 kruskal算法
displayKruskalAlgo();
//14 Ford - Fulkerson algorith
/**/
displayFordFulkerson();
//15 Dijkstra's Algorithm 迪杰斯特拉算法 最短路径算法
displayDijkstra();
//16 Prim's Algorithm
displayPrims();
//17. Huffman Coding
displayHuffmanarr();
system("pause");// linux 无效 ,只win 下有效
return 0;
}
哲学管理(学)人生, 文学艺术生活, 自动(计算机学)物理(学)工作, 生物(学)化学逆境, 历史(学)测绘(学)时间, 经济(学)数学金钱(理财), 心理(学)医学情绪, 诗词美容情感, 美学建筑(学)家园, 解构建构(分析)整合学习, 智商情商(IQ、EQ)运筹(学)生存.---Geovin Du(涂聚文)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号