Blog3
一、前言
通过一个学期的学习,我们终于结束了面向对象程序设计这门课,在过去的几周时间内,我们进行了实验、pta以及最后的期末考试,课程虽然结束了,但需要学习和巩固的知识点还有很多,这也是最后一次blog总结。
二、设计与分析
1.电信计费问题
题目要求:
实现一个简单的电信计费程序:
假设南昌市电信分公司针对市内座机用户采用的计费方式:
月租20元,接电话免费,市内拨打电话0.1元/分钟,省内长途0.3元/分钟,国内长途拨打0.6元/分钟。不足一分钟按一分钟计。
南昌市的区号:0791,江西省内各地市区号包括:0790~0799以及0701。
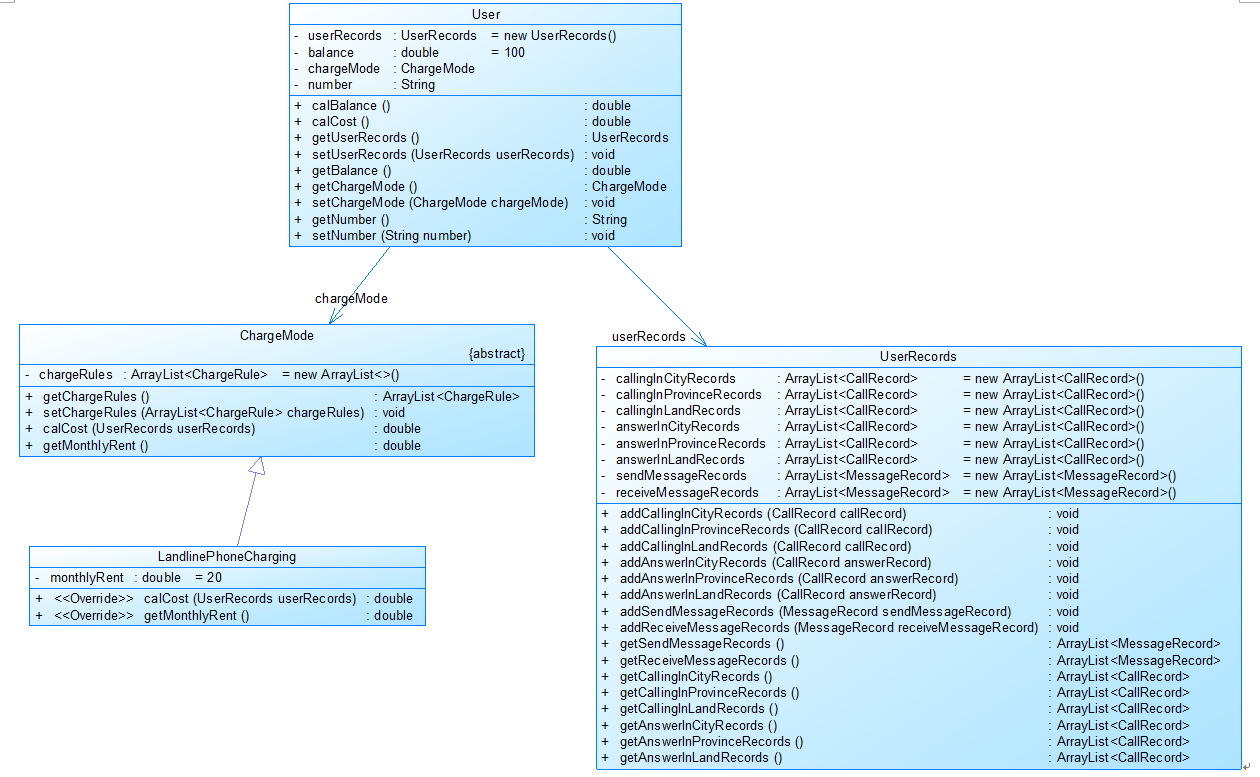
类图如下:
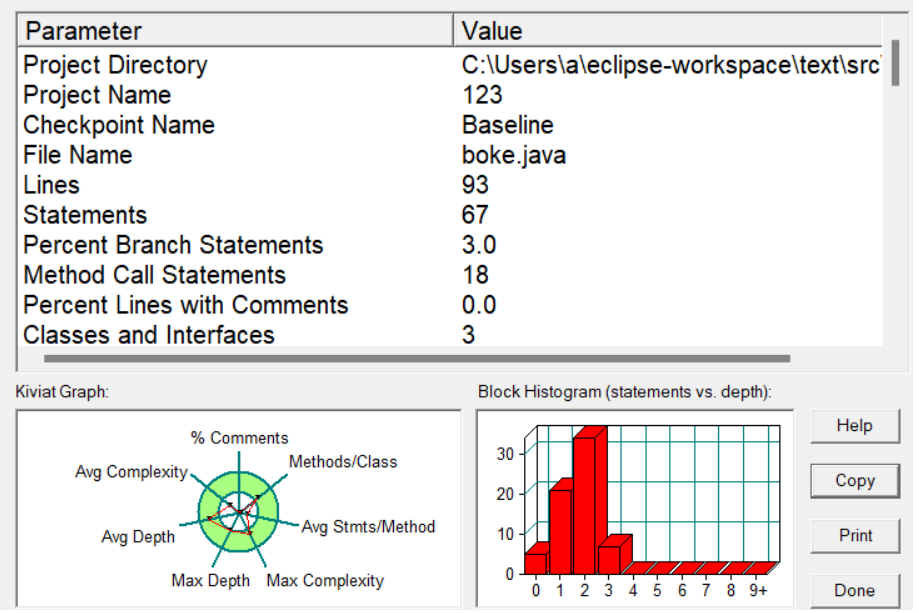
SourceMonitor报表:
部分代码:
class User { private UserRecords userRecords = new UserRecords(); private double balance = 100; private ChargeMode chargeMode; private String number; public void calBalance() { balance = balance - calCost() - chargeMode.getMonthlyRent(); } public double calCost() { return chargeMode.calCost(userRecords) ; } public UserRecords getUserRecords() { return userRecords; } public void setUserRecords(UserRecords userRecords) { this.userRecords = userRecords; } public double getBalance() { return balance; } public ChargeMode getChargeMode() { return chargeMode; } public void setChargeMode(ChargeMode chargeMode) { this.chargeMode = chargeMode; } public String getNumber() { return number; } public void setNumber(String number) { this.number = number; } }
class LandPhoneInLandRule extends CallChargeRule{ @Override public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { long interval; double cost = 0; for(int i = 0; i < callRecords.size(); i++){ interval = callRecords.get(i).getEndTime().getTime() - callRecords.get(i).getStartTime().getTime(); if(interval % 60000 == 0){ interval = interval / 60000; } else { interval = interval / 60000 +1; } cost = cost + interval*0.6; } return cost; } } class LandPhoneInCityRule extends CallChargeRule{ @Override public double calCost(ArrayList<CallRecord> callRecords) { long interval; double cost = 0; for(int i = 0; i < callRecords.size(); i++){ interval = callRecords.get(i).getEndTime().getTime() - callRecords.get(i).getStartTime().getTime(); if(interval % 60000 == 0){ interval = interval / 60000; } else { interval = interval / 60000 +1; } cost = cost + interval*0.1; } return cost; } }
这次的电信计费问题是我认为难度最大的一道题,它是对我们java整体知识框架的考察,实话实说,我并没有把这道题目做出来,可能是因为我对知识和题目的处理还不太熟悉和细致,面对这种复杂的题目,不知道从哪里下手。
题目2:
题目要求:
定义容器Container接口。模拟实现一个容器类层次结构,并进行接口的实现、抽象方法重写和多态机制测试。各容器类实现求表面积、体积的方法。
定义接口Container:
属性:
public static final double pi=3.1415926;
抽象方法:
public abstract double area();
public abstract double volume();
static double sumofArea(Container c[]);
static double sumofVolume(Container c[]);
其中两个静态方法分别计算返回容器数组中所有对象的面积之和、周长之和;
定义Cube类、Cylinder类均实现自Container接口。
Cube类(属性:边长double类型)、Cylinder类(属性:底圆半径、高,double类型)
实验代码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); int n=in.nextInt(); Container[] c = new Container[n]; for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) { String s = in.next(); if(s.equals("cube")) { double d = in.nextDouble(); c[i] = new Cube(d); } else if(s.equals("cylinder")) { double r = in.nextDouble(); double h = in.nextDouble(); c[i] = new Cylinder(r,h); } } System.out.printf("%.2f\n%.2f",Container.sumOfArea(c),Container.sumOfVolume(c)); in.close(); } } interface Container { double pi = 3.1415926; double area(); double volume(); static double sumOfArea(Container[] c) { double sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) { sum += c[i].area(); } return sum; } static double sumOfVolume(Container[] c) { double result = 0; for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) { result += c[i].volume(); } return result; } } class Cube implements Container{ public double d; public Cube(double d2) { this.d = d2; } public double area() { return 6*d*d; } public double volume() { return Math.pow(d, 3); } } class Cylinder implements Container{ public double r,h; public Cylinder(double r2, double h2) { this.r = r2; this.h = h2; } public double area() { return (2*pi*r*h + 2*pi*r*r); } public double volume() { return (pi*r*r*h); } }
这道题目比较简单,就是普通的接口问题,Cube类、Cylinder类均要实现自Container接口,抽象方法分别计算返回容器数组中所有对象的面积之和、周长之和,方法比较简单,只要知道接口的原理再按照题目提示把代码写出即可。
题目3:
题目要求:
现在他要统计班里学生的名单,但是C~K在教务系统中导出班级名单时出了问题,发现会有同学的信息重复,现在他想把重复的同学信息删掉,只保留一个。
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); List<Student> List=new ArrayList<Student>(); int n=in.nextInt(); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { String number = in.next(); String name = in.next(); int age = in.nextInt(); char sex = in.next().charAt(0); Student stu=new Student(number,name,age,sex); if(!List.contains(stu)) { List.add(stu); } } Collections.sort(List); System.out.println(List.size()); Iterator<Student> a = List.iterator(); while(a.hasNext()) { Student next = a.next(); System.out.println(next); } in.close(); } } class Student implements Comparable<Student>{ String idString; String nameString; int ageString; char sexString; public Student(String idString, String nameString, int ageString, char sexString) { super(); this.idString = idString; this.nameString = nameString; this.ageString = ageString; this.sexString = sexString; } public int hashCode() { final int p = 31; int r = 1; r = p * r + ageString; r = p * r + ((idString == null) ? 0 : idString.hashCode()); r = p * r + ((nameString == null) ? 0 : nameString.hashCode()); r = p* r + sexString; return r; } public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) return true; if (obj == null) return false; if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false; Student other = (Student) obj; if (ageString != other.ageString) return false; if (idString == null) { if (other.idString != null) return false; } else if (!idString.equals(other.idString)) return false; if (nameString == null) { if (other.nameString != null) return false; } else if (!nameString.equals(other.nameString)) return false; if (sexString != other.sexString) return false; return true; } public String toString() { return idString + " " + nameString + " " + ageString + " " + sexString ; } public int compareTo(Student o) { return this.idString.compareTo(o.idString); } }
这道题使用了arraylist 等有关列表的方法,题目本身不难,只要小心把每种情况计算进去就行,题目解法也不唯一,可以尝试用多种方法解决该问题。
期末考试:
代码:
import java.util.Scanner; import static java.lang.Math.PI; public class qimo { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); int choice = 0; choice = in.nextInt(); switch (choice) { case 1://Construct Circle Object double a = in.nextDouble(); if(a<=0){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } else { Circle circle = new Circle(a); circle.show(); break; } case 2://Construct Rectangle Object double b = in.nextDouble(); double c = in.nextDouble(); if(b<=0||c<=0){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } else{ Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(b,c); rectangle.show(); break; } case 3://Construct Ball Object double d = in.nextDouble(); if(d<=0){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } else{ Ball ball = new Ball(d); ball.show(); break; } case 4://Construct Box Object double f = in.nextDouble(); double g = in.nextDouble(); double h = in.nextDouble(); if(f<=0||g<=0||h<=0){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } else{ Box box = new Box(f,g,h); box.show(); break; } default: System.out.println("Wrong Format"); break; } } } abstract class AbstractShape{ abstract public double getArea(); abstract public void show(); } class Circle extends AbstractShape{ private double radius; public Circle() { } public Circle(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } public double getArea() { double area; area = PI*radius*radius; return area; } public void show() { System.out.println("Type:Circle,Area:"+String.format("%.2f",getArea())); } public double getRadius() { return radius; } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } } class Rectangle extends AbstractShape{ private double width; private double length; public Rectangle(){ } public Rectangle(double width,double length) { this.width = width; this.length = length; } public double getArea() { double area; area = width*length; return area; } public void show() { System.out.println("Type:Rectangle,Area:"+String.format("%.2f",getArea())); } public double getWidth() { return width; } public void setWidth(double width) { this.width = width; } public double getLength() { return length; } public void setLength(double length) { this.length = length; } } class Box extends Rectangle{ private double height; public Box() { } public Box(double width,double length,double height) { this.setWidth(width); this.setLength(length); this.setHeight(height); } public double getHeight() { return height; } public void setHeight(double height) { this.height = height; } public double getArea() { double area; area = 2*(getWidth()*getLength()+getWidth()*getHeight()+getLength()*getHeight()); return area; } public void show(){ System.out.println("Type:Box,Area:"+String.format("%.2f",getArea())); } } class Ball extends Circle{ public Ball(){ } public Ball(double radius){ this.setRadius(radius); } public double getArea() { double area; area = 4*PI*getRadius()*getRadius(); return area; } public void show(){ System.out.println("Type:Ball,Area:"+String.format("%.2f",getArea())); } }
本次期末考试我只写出了第一题,但是是最后几分钟才想到引用Math里的PI,之前直接用3.14表示Π导致测试点一直通不过,题目本身不难,和期中考试的题目有点类似,不过是继承了两次,但大致的方法还是相同的,保留两位小数需要使用
String.format("%.2f",getArea())
三、踩坑心得
1.对于全局变量和局部变量需要格外注意,不然容易导致结果出错。全局变量就是从定义的位置起,作用域覆盖整个程序范围的变量。而只在特定的过程或函数中可以访问的变量,被称为局部变量。
2.处理父类和子类关系时,要了解继承的关系和逻辑,不然得出的答案可能会出错。
3.处理类里的变量时,因为属性是私有的,所以调用时只能用get()方法处理。
4.处理问题中的计算问题不能想当然,像这次期末考试的Π不能直接用3.14代。
四、改进建议
1.在代码中多标明注释,以便理解和下次修改。
2.有些代码中有一部分功能相同,可以改成方法,使代码更加简洁,也便于下次对代码进行修改。
3.有一些类也可以和其他类一样变成父类的子类,应该尽量减少代码的重复率,提高代码的利用率和可读性。
4.可以尝试使用不同的方法解决同一道题。
五、总结
经过一个学期的JAVA课程学习,现在虽说算不上什么专业的JAVA程序员,但我还是很有收获。了解了这门语言,探索了这门语言,认知了这门语言。我从一个什么都不懂的菜鸟,到现在能够自己编一个简单的程序并使其跑起来,学习JAVA应该是循环渐进,按部就班,脚踏实地的。学JAVA,一定要做到课前预习与课后复习,书上的概念要理解透彻,代码一定要过手;多和同学沟通,互相学习,取长补短。我觉得应该多看别人的总结,多与别人进行交流,但是本学期学习压力较大,可能自己也不是学的很好,我对课程提出的建议就是我认为pta上的题目可以中档难度的题目多一些,而不是太难的题目,这不仅会使我们学习的自信下降,等下一次pta发布又是这道难题的升级版,无从下手,最终陷入恶性循环。其次,我觉得提交的时间应该更加人性化一点,多给些时间也能让学生们的学习压力减轻一些,不会感觉那么压迫,丧失对java学习的兴趣。Java基础课程已经结束,但对于Java知识的学习与提升才刚刚开始。更熟练的使用Java,更好的类关系设计将作为之后学习的目标与方向。相较于Java宏大的知识体系,所学的知识不过风毛菱角,更加丰富的知识还尚未来到。要不断学习,不断探索,虚心学习,勤于练习。






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号