象棋图片转FEN字符串详细教程
如把下图
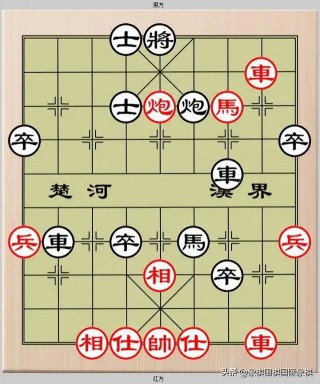
转换成:3ak4/7R1/3aCcN2/p7p/6r2/9/Pr1p1n2P/4B1p2/9/2BAKA1R1
模型21K,Intel N100上训练时间0.969秒,识别时间0.957秒。识别率好像是100%
一、安装软件包
apt install python3-scipy python3-pil
二、建目录data, data\0 a A b B c C k K n N p P r R
识别就是分类。每个目录对应一类,存放属于该类的所有图片。
三、收集和预处理数据
百度搜相似图片。运行prepare.py:

#!/usr/bin/python from common import * from pathlib import Path fn = sys.argv[1] a = slice(fn) fn = Path(fn).stem for i in range(len(a)): cv.imwrite(f'data/{fn}-{i}.png', a[i]) exit() from PIL import Image, ImageDraw img = Image.open(sys.argv[1]) id = ImageDraw.Draw(img) sz = img.size; S,L,T = size(sz[0], sz[1]) for yy in range(10): for xx in range(9): y = T + yy * S x = L + xx * S id.rectangle((x,y,x+S,y+S), outline=(0,255,0,255), width=1) img.show()
如何知道square的大小?图片查看器Gwenview和IfranView显示选择区的大小。或者用OpenCV的演示程序squares.py来高射炮打蚊子。
人工标注数据。文件管理器里按图标查看,把比如红车的改名为首字母为R。按大小排序,改名时列表不会来回乱变。

#!/usr/bin/python from glob import glob from shutil import move s = 'rnbakcp'; s += s.upper() + '0' for c in s: for p in [c + '*.png', c + '*.jpg']: for f in glob(p): move(f, c)
四、训练,运行train.py

from common import * from sklearn.svm import SVC import pickle data_dir = "data" features = []; labels = [] for label in os.listdir(data_dir): label_dir = os.path.join(data_dir, label) if not os.path.isdir(label_dir): continue for img_file in os.listdir(label_dir): img_path = os.path.join(label_dir, img_file) img = cv.imread(img_path) if img is None: continue feature = extract_features(img) if feature is None: continue features.append(feature) labels.append(label) model = SVC(kernel='rbf', C=10, gamma=0.1) model.fit(features, labels) with open("model.pkl", "wb") as f: pickle.dump(model, f)
五,识别
#!/usr/bin/python from common import * import pickle b = [[' '] * 9 for i in range(10)] with open('model.pkl', 'rb') as f: model = pickle.load(f) a = slice(sys.argv[1]) for i in range(len(a)): f = extract_features(a[i]) b[i // 9][i % 9] = model.predict([f])[0] def brd2fen (b): f = '' for y in range(10): n = 0 for x in range(9): c = b[y][x] if c == '0': n += 1 else: if n: f += str(n) f += c; n = 0 if n: f += str(n) if y != 9: f += '/' return f print(brd2fen(b)) for i in range(10): print(b[i])
鄙人的brd2fen是最长的。:-)
五 common.py

import numpy as np import cv2 as cv import pickle import os import sys def size (W, H): S = 68 if W == 640 else 86 # size L = (W - 9 * S) // 2 # left T = (H - 10 * S) // 2 # top return S,L,T def slice (fn): all = [] img = cv.imread(fn); H,W = img.shape[:2] S,L,T = size(W, H) mask = np.zeros((S, S), dtype=bool) HS = S // 2; R = HS - 4 # half S & radius for y in range(S): for x in range(S): # 圆形mask. hypotenuse: 斜边 if np.hypot(x - HS, y - HS) > R: mask[y, x] = True for yy in range(10): for xx in range(9): x = L + xx * S; y = T + yy * S x2 = min(W, x + S); y2 = min(H, y + S) sl = img[y:y2, x:x2]; sl[mask] = 0 all.append(sl) return all def extract_features (img): gray = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) _, bin = cv.threshold(gray, 0, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY + cv.THRESH_OTSU) contours, _ = cv.findContours(bin, cv.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) if len(contours) == 0: return None contour = max(contours, key=cv.contourArea) moments = cv.moments(contour) hu_moments = cv.HuMoments(moments).flatten() # 在阴影或强光条件下,RGB会整体变化,而HSV的色调H和饱和度S相对稳定,更适合颜色识别任务。V是亮度。 hsv = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2HSV) color_features = np.concatenate([ cv.mean(hsv)[:3], cv.meanStdDev(hsv)[1].flatten() ]) return np.concatenate([hu_moments, color_features])
六 其它
circles.py没有用到,但我辛苦地调了参数,愚蠢地用了直径去设置min/max raidus,一并附上。

#!/usr/bin/python import numpy as np import cv2 as cv import sys import os fn = sys.argv[1] img = cv.imread(fn); height, width = img.shape[:2] fn = os.path.basename(fn) circles = cv.HoughCircles( cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY), # 只支持灰度 cv.HOUGH_GRADIENT, # 梯度,not 渐变 1, # 改成2影响很大 60, # Minimum distance between the centers of the detected circles param1=150, # 减小可增加检测到的圆数量 param2=35, # The smaller it is, the more false circles may be detected. minRadius=30, maxRadius=48 ) # 返回shape为(1,n,3)的ndarray if circles is None: exit() circles = np.around(circles).astype(int) mask = np.zeros((96,96), dtype=bool) for y in range(96): for x in range(96): # 以(48,48)为圆心,40为半径的mask. hypotenuse 斜边 if np.hypot(x - 48, y - 48) > 40: mask[y, x] = True for x,y,r in circles[0]: cv.circle(img, (x, y), r, (0, 255, 0), 2) x1 = max(0, x - r); x2 = min(width, x + r) y1 = max(0, y - r); y2 = min(height, y + r) ps = cv.resize(img[y1:y2, x1:x2], (96,96)) ps[mask] = 255 #cv.imwrite(f'tmp/{fn}-{x},{y}.png', ps) from PIL import Image img = Image.fromarray(cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2RGB)) img.show() print(f'{circles.shape[1]} pieces')
七 补充
① train.py和predict.py不用import pickle, common.py import了。
② 在我机器上,用OpenCV显示图像,出来后卡死了,Ctrl-C都不行得kill。PIL的show先在/tmp下存文件再用系统默认图片查看器打开。OpenCV应该是因为我乱改KDE配置坏的事。

这个tough. 死活只能找到31个棋子,带框的炮不行。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号