coast
The coast, also known as the coastline or seashore, is defined as the area where land meets the sea or ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the ocean or a lake. Earth has around 620,000 kilometres (390,000 mi 英里) of coastline. Because coasts are constantly changing, a coastline's exact perimeter cannot be determined; this measurement challenge is called the coastline paradox. The term coastal zone is used to refer to a region where interactions of sea and land processes occur. Both the terms coast and coastal are often used to describe a geographic location or region located on a coastline (e.g., New Zealand's West Coast, or the East, West, and Gulf Coast of the United States.)
Coasts are important zones in natural ecosystems, often home to a wide range of biodiversity [bio: 生物], and important zones such as wetlands which are important for bird populations or mangroves [红树] or seagrass which provide nursery habitat for fish or other aquatic species. Some coasts fronts on the open ocean and are called pelagic [远洋的] coast while other coasts are more sheltered coast in a gulf or bay. A shore, on the other hand, may refer to parts of land adjoining any large body of water, including oceans (seashore) and lakes (lake shore).
While there is general agreement in the scientific community regarding the definition of a coast, in the political sphere, the delineation of the extents of a coast differ according to jurisdiction. Government authorities in various countries may define coast differently for economic and social policy reasons. According to the UN atlas, 44% of all people live within 150 km (93 mi) of the sea. Because of their importance in society and high concentration of population, the coast is important for major parts of the global food and economic system. Important human activities happen in port cities, fisheries, and other spaces beaches and seaside resorts which are used for tourism.
delineate: 1) make the borders between two areas very clear; 2) to describe or draw sth carefully
However, the economic importance of coasts makes many of these communities vulnerable to climate change which causes changes in extreme weather and sea level rise and related issues such as coastal erosion, saltwater intrusion and coastal flooding. Other coastal issues, such as marine pollution and debris and marine ecosystem destruction, further complicate the human uses of the coast and threaten coastal ecosystems. International attention to these issues has been captured in Sustainable Development Goal 14 "Life Below Water" which sets goals for international policy focused on preserving coastal ecosystems and supporting more sustainable economic practices for coastal communities.
Tides often determine the range over which sediment is deposited or eroded. Waves erode coastline as they break on shore releasing their energy; the larger the wave the more energy it releases and the more sediment it moves. Sediment deposited by rivers is the dominant influence on the amount of sediment located on a coastline.
Coasts and their adjacent areas on and off shore are an important part of a local ecosystem. The mixture of fresh water [淡水] and salt water (brackish [slightly salty] water) in estuaries [河口湾] provides many nutrients for marine life. Salt marshes and beaches also support a diversity of plants, animals and insects crucial to the food chain.
Coasts, especially those with beaches and warm water, attract tourists often leading to the development of seaside resort communities. In many island nations such as those of the Mediterranean [Medi+terranean: 地中间的(海)], South Pacific and Caribbean, tourism is central to the economy. Coasts offer recreational activities such as swimming, fishing, surfing, boating, and sunbathing.
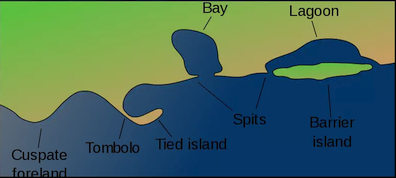
Coastal landforms. The feature shown here as a bay would, in certain (mainly southern) parts of Britain, be called a cove. That between the cuspate foreland and the tombolo is a British bay:
The Coast Guard is a military organization in the US that is in charge of watching for ships in danger and preventing illegal activities in the ocean.
六级/考研单词: paradox, seldom, gulf, unite, ecosystem, nursery, habitat, shelter, bay, shore, sphere, differ, accord, jurisdiction, atlas, globe, vulnerable, issue, erode, intrude, marine, pollute, debris, farther, complicate, sustain, tide, deposit, adjacent, marsh, diverse, insect, surf, militant, illicit


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号