DRAM, SDRAM, DDR
Upcoming versions are expected to have an L4 DRAM cache using embedded or stacked DRAM (see Sections 2.2 and 2.3).
The first letter of SRAM stands for static. The dynamic nature of the circuits in DRAM requires data to be written back after being read—thus the difference between the access time and the cycle time as well as the need to refresh. SRAMs don’t need to refresh, so the access time is very close to the cycle time. SRAMs typically use six transistors per bit to prevent the information from being disturbed when read. SRAM needs only minimal power to retain the charge in standby mode. 4GB就是24G个晶体管。The M1 Max has 10 CPU cores and either 24 or 32 GPU cores depending on the configuration you get. At 57 billion transistors. the M1 Max is the largest CPU Apple has ever made while the M1 Pro has 33.7 billion transistors. Both are made on the same 5-nanometer process as the existing M1.
In earlier times, most desktop and server systems used SRAM chips for their primary, secondary, or tertiary caches. The access times for large, third-level, on-chip caches are typically two to eight times that of a second-level cache. Even so, the L3 access time is usually at least five times faster than a DRAM access.
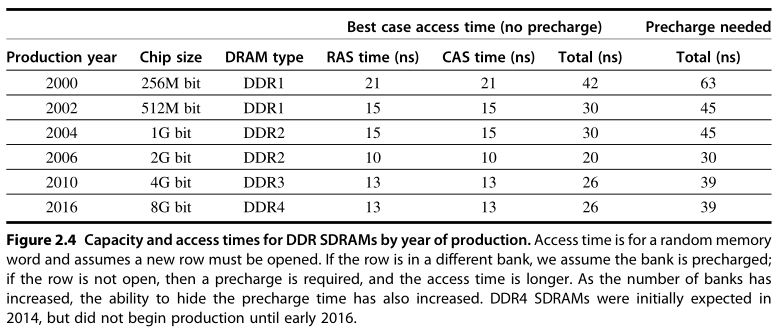
An additional requirement of DRAM derives from the property signified by its first letter, D, for dynamic. To pack more bits per chip, DRAMs use only a single transistor, which effectively acts as a capacitor, to store a bit. This has two implications: first, the sensing wires that detect the charge must be precharged, which sets them “halfway” between a logical 0 and 1, allowing the small charge stored in the cell to cause a 0 or 1 to be detected by the sense amplifiers. On reading, a row is placed into a row buffer, where CAS [column access strobe] signals can select a portion of the row to read out from the DRAM. Because reading a row destroys the information, it must be written back whenthe row is no longer needed. This write back happens in overlapped fashion, but in early DRAMs, it meant that the cycle time before a new row could be read was larger than the time to read a row and access a portion of that row. A strobe or a strobe light is a very bright light which flashes on and off very quickly.
In addition, to prevent loss of information as the charge in a cell leaks away (assuming it is not read or written), each bit must be "refreshed" periodically. Fortunately, all the bits in a row can be refreshed simultaneously just by reading that row and writing it back. Therefore every DRAM in the memory system must access every row within a certain time window, such as 64 ms. DRAM controllers include hardware to refresh the DRAMs periodically.
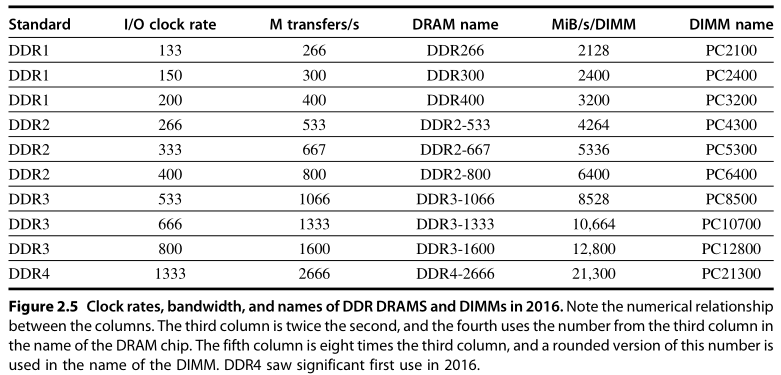
SDRAMs [synchronous DRAM] allowed the addition of a burst transfer mode where multiple transfers can occur without specifying a new column address. Typically, eight or more 16-bit transfers can occur without sending any new addresses by placing the DRAM in burst mode.
六级/考研单词: embed, stack, static, dynamic, data, thereby, differentiate, refreshment, transistor, disturb, standby, desktop, tertiary, derive, signify, parcel, implicit, detect, logic, buffer, portion, overlap, vogue, leak, simultaneous, hardware, burst, multiple




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号