camera
camera的原意是room. 有比房子还大的照相机。为啥长焦大光圈镜头贵
A camera is an optical instrument used to capture an image. At their most basic, cameras are sealed boxes (the camera body) with a small hole (the aperture) that allow light in to capture an image on a light-sensitive surface (usually photographic film or a digital sensor). Cameras have various mechanisms to control how the light falls onto the light-sensitive surface. Lenses focus the light entering the camera, the size of the aperture can be widened or narrowed to let more or less light into the camera, and a shutter mechanism determines the amount of time the photo-sensitive surface is exposed to the light.
The still image camera is the main instrument in the art of photography and captured images may be reproduced later as a part of the process of photography, digital imaging, photographic printing. The similar artistic fields in the moving image camera domain are film, videography [摄像], and cinematography [电影摄制].
The word camera comes from camera obscura, which means "dark chamber" and is the Latin name of the original device for projecting an image of external reality onto a flat surface. The modern photographic camera evolved from the camera obscura. The functioning of the camera is very similar to the functioning of the human eye. The first permanent photograph was made in 1825 by Joseph Nicéphore Niépce.
The aperture, sometimes called the diaphragm or iris, is the opening through which light enters the camera. Typically located in the lens, this opening can be widened or narrowed to control the amount of light that strikes the film. The aperture is controlled by the movements of overlapping plates or blades that rotate together and apart to shrink and expand the hole at the center. The diameter of the aperture can be set manually, typically by adjusting a dial on the camera body or lens, or automatically based on calculations influenced by an internal light meter. Different apertures of a lens:

The size of the opening is set at standard increments, typically called "f-stops" (but also "f-numbers", "stop numbers", or simply "steps" or "stops"), that usually range from f/1.4 to f/32 in standard increments: 1.4, 2, 2.8, 4, 5.6, 8, 11, 16, 22, and 32. As the numbers increase, each increment (or "stop") halves the amount of light entering the camera. Conversely, the lower the number, the larger the opening, and so the more light that is let into the camera.
The shutter, along with the aperture, is one of two ways to control the amount of light entering the camera. The shutter determines the duration that the light-sensitive surface is exposed to light. The shutter is opened, light enters the camera and exposes the film or sensor to light, and then the shutter closes.
There are two types of mechanical shutters. The leaf-type uses a circular iris diaphragm maintained under spring tension inside or just behind the lens that rapidly opens and closes when the shutter is released. More commonly, a focal-plane shutter is used. This shutter operates close to the film plane and employs metal plates or cloth curtains with an opening that passes across the light-sensitive surface. A focal-plane shutter. In this shutter, the metal shutter blades travel vertically.
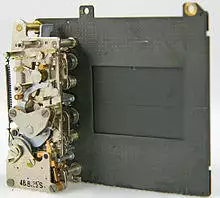
Traditional cameras capture light onto photographic plate or photographic film. Video and digital cameras use an electronic image sensor, usually a charge-coupled device (CCD) or a CMOS sensor to capture images which can be transferred or stored in a memory card or other storage inside the camera for later playback or processing.
The distance range in which objects appear clear and sharp, called depth of field, can be adjusted by many cameras. This allows for a photographer to control which objects appear in focus, and which do not.

六级/考研单词: seal, digit, lens, exposition, reproduce, domain, chamber, evolve, perpetual, overlap, rotate, shrink, diameter, manual, dial, meter, converse, duration, tense, rapid, vertical, electron
- 相机百科 | 国产老相机 (letsfilm.org)
- 国内有哪些公司在做CMOS图像传感器?(zhihu.com)
- CCD/CMOS靶面尺寸规格说明_景通仪器 (sipmv.com)
- 超高清视频制作技术协同中心 (uptcchina.com)
8K的分辨率是7680×4320. 8K HEVC 30FPS视频流码率通常达到100Mbps。未经HEVC高度压缩前的带宽很高:录制介质:基于NVMe M.2的双卡存储。不过可能是RAID 1而不是RAID 0。前者多个备份,后者速度乘2。目前国内有3家厂商制造8K摄像机:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号