Spring-AOP
什么是 AOP
AOP的本质就是方法拦截,能够在方法执行之前、或者之后,自动执行某些代码。在软件业,AOP为Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期间动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开发中的一个热点,也是Spring框架中的一个重要内容,是函数式编程的一种衍生范型。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
AOP和OOP的关系
AOP:Aspect Oriented Programming:面向切面(方面)编程 (处理横向拦截的任务)
OOP:Object Oriented Programming:面向对象编程 (处理纵向(继承))
AOP和OOP互为补充,AOP不是OOP的替代品
AOP 概念

1)连接点:程序执行过程中的一个点,例如方法的执行或异常的处理。在 Spring AOP 中,一个连接点总是代表一个方法的执行。
2)切入点:匹配连接点的谓词。Advice 与切入点表达式相关联,并在与切入点匹配的任何连接点处运行(例如,执行具有特定名称的方法),即实际被增强的方法,称为切入点。由切入点表达式匹配的连接点的概念是 AOP 的核心,Spring 默认使用 AspectJ 切入点表达式语言。
3)通知(增强)
实际增强的逻辑部分称为通知(增强),有以下类型

底层原理
1)有接口的情况下,使用JDK动态代理
2)没有接口情况,使用 CGLIB 动态代理

环境

aspectjweaver.jar:https://www.eclipse.org/aspectj/downloads.php
aopalliance.jar:https://sourceforge.net/projects/aopalliance/files/aopalliance/1.0/aopalliance.zip/download
execution
execution([权限修饰符] [返回类型] [类全路径] 方法名称 )
示例

AspectJ 注解
前置通知示例
package com.fly.spring5.entity;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Cat {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("=======cat eat=========");
}
}
package com.fly.spring5.entity;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Aspect
public class BeforeAdvice {
@Before(value = "execution(* com.fly.spring5.entity.Cat.eat(..))")
public void before() {
System.out.println("=========before方法========");
}
}
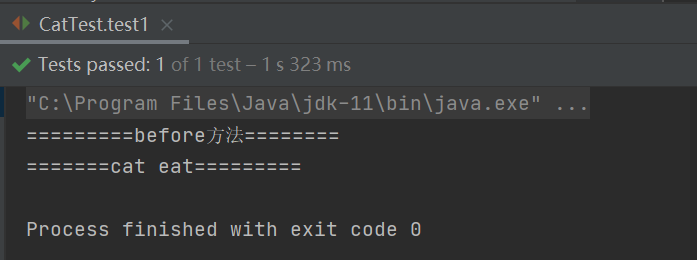
测试
@Test
public void test1() {
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContent.xml");
Cat cat = context.getBean("cat", Cat.class);
cat.eat();
}

其他的通知类似,
切入点抽取
package com.fly.spring5.entity;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Aspect
public class BeforeAdvice {
@Pointcut(value = "execution(* com.fly.spring5.entity.Cat.eat(..))")
public void anyOldTransfer() {
}
@Before(value = "anyOldTransfer()")
public void before() {
System.out.println("=========before方法========");
}
}
增强类优先级
增强类上面添加注解 @Order,数字类型值越小优先级越高(从0开始)。
纯注解开发
使用配置类
package com.fly.spring5.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.fly"})
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class MyConfig {
}
AspectJ 配置文件
package com.fly.spring5.entity;
public class Dog {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("======dog eat=======");
}
}
package com.fly.spring5.entity;
public class DogProxy {
public void before() {
System.out.println("=======DogProxy before======");
}
}
配置文件
<bean id="dog" class="com.fly.spring5.entity.Dog"/>
<bean id="dogProxy" class="com.fly.spring5.entity.DogProxy"/>
<!--配置 aop 增强-->
<aop:config>
<!--切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="p" expression="execution(* com.fly.spring5.entity.Dog.eat(..))"/>
<!--配置切面-->
<aop:aspect ref="dogProxy">
<!--增强作用在具体的方法上-->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="p"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
测试方法
package com.fly.spring5.test;
import com.fly.spring5.entity.Dog;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class DogTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContent.xml");
Dog dog = context.getBean("dog", Dog.class);
dog.eat();
}
}





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号