栈
概念
栈(stack)又名堆栈,它是一种运算受限的线性表。限定仅在表尾进行插入和删除操作的线性表。这一端被称为栈顶,相对地,把另一端称为栈底。向一个栈插入新元素又称作进栈、入栈或压栈,它是把新元素放到栈顶元素的上面,使之成为新的栈顶元素;从一个栈删除元素又称作出栈或退栈,它是把栈顶元素删除掉,使其相邻的元素成为新的栈顶元素。
栈是允许在同一端进行插入和删除操作的特殊线性表。允许进行插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶(top),另一端为栈底(bottom);栈底固定,而栈顶浮动;栈中元素个数为零时称为空栈。插入一般称为进栈(PUSH),删除则称为退栈(POP)。栈也称为先进后出表。
用数组实现栈
class ArrayStack { private final int maxSize; private final int[] stack; private int top = -1; public ArrayStack(int maxSize){ this.maxSize = maxSize; stack = new int[maxSize]; } //栈是否满 public boolean isFull(){ return top == maxSize - 1; } //栈是否为空 public boolean isEmpty(){ return top == -1; } //入栈 public void push(int value){ if(isFull()){ System.out.println("栈已满,不能添加数据"); return; } top++; stack[top] = value; } //出栈 public int pop(){ if(isEmpty()){ throw new RuntimeException("栈为空,没有数据"); } int value = stack[top]; top--; return value; } //从栈顶开始显示数据 public void show(){ if(isEmpty()){ System.out.println("栈为空,没有数据"); } for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--){ System.out.printf("stack[%d]=%d\n",i,stack[i]); } } }
测试
ArrayStack stack = new ArrayStack(3); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); boolean flag = true; String result; while (flag){ System.out.println("show: 表示显示栈"); System.out.println("exit: 退出程序"); System.out.println("push: 表示添加数据到栈(入栈)"); System.out.println("pop: 表示从栈取出数据(出栈)"); System.out.println("请输入你的选择"); result = scanner.next(); switch (result) { case "show": stack.show(); break; case "push": System.out.println("请输入一个数"); int value = scanner.nextInt(); stack.push(value); break; case "pop": try { int res = stack.pop(); System.out.printf("出栈的数据是 %d\n", res); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } break; case "exit": scanner.close(); flag = false; break; default: break; } } System.out.println("程序退出~~~");

后进先出
用单向链表实现栈
class StackNode { public int value; public StackNode next; public StackNode(int value) { this.value = value; } @Override public String toString() { return "StackNode{" + "value=" + value + '}'; } }
class LinkedStack { private final StackNode head = new StackNode(0); //链表是否为空 public boolean isEmpty(){ return head.next == null; } //入栈 public void push(int value){ StackNode temp = head; while (temp.next != null){ temp = temp.next; } temp.next = new StackNode(value); } //出栈 public int pop(){ if(isEmpty()){ throw new RuntimeException("栈为空,没有数据"); } StackNode temp = head; while (temp.next.next != null){ temp = temp.next; } int value = temp.next.value; temp.next = null; return value; } //从栈顶开始显示数据 public void show(){ if(isEmpty()){ System.out.println("栈为空,没有数据"); return; } Stack<StackNode> stack = new Stack<>(); StackNode temp = head.next; while (temp != null){ stack.push(temp); temp = temp.next; } while (stack.size() > 0){ System.out.println(stack.pop()); } } }
测试
LinkedStack stack = new LinkedStack(); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); boolean flag = true; String result; while (flag){ System.out.println("show: 表示显示栈"); System.out.println("exit: 退出程序"); System.out.println("push: 表示添加数据到栈(入栈)"); System.out.println("pop: 表示从栈取出数据(出栈)"); System.out.println("请输入你的选择"); result = scanner.next(); switch (result) { case "show": stack.show(); break; case "push": System.out.println("请输入一个数"); int value = scanner.nextInt(); stack.push(value); break; case "pop": try { int res = stack.pop(); System.out.printf("出栈的数据是 %d\n", res); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } break; case "exit": scanner.close(); flag = false; break; default: break; } } System.out.println("程序退出~~~");

用栈实现计算器
只能计算单位数
class ArrayStack2 { private final int maxSize; private final int[] stack; private int top = -1; public ArrayStack2(int maxSize) { this.maxSize = maxSize; stack = new int[maxSize]; } //获取栈顶的值 public int peek() { return stack[top]; } //栈是否满 public boolean isFull(){ return top == maxSize - 1; } //栈是否为空 public boolean isEmpty(){ return top == -1; } //入栈 public void push(int value){ if(isFull()){ System.out.println("栈已满,不能添加数据"); return; } top++; stack[top] = value; } //出栈 public int pop(){ if(isEmpty()){ throw new RuntimeException("栈为空,没有数据"); } int value = stack[top]; top--; return value; } //从栈顶开始显示数据 public void show(){ if(isEmpty()){ System.out.println("栈为空,没有数据"); } for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--){ System.out.printf("stack[%d]=%d\n",i,stack[i]); } } //判断是不是运算符 public boolean isOperator(int val){ return val == '+' || val == '-' || val == '*' || val == '/'; } //返回运算符的优先级,数字越大,则优先级就越高. public int priority(int operator){ if(operator == '*' || operator == '/'){ return 1; }else if(operator == '+' || operator == '-'){ return 0; }else { return -1; } } //计算 public int cal(int num1, int num2, int operator) { int result = 0; switch (operator){ case '+': result = num1 + num2; break; case '-': result = num2 - num1;// 注意顺序 break; case '*': result = num1 * num2; break; case '/': result = num2 / num1; break; default: break; } return result; } }
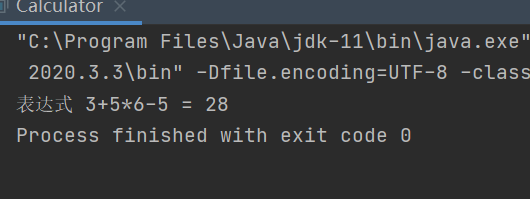
String expression = "3+5*6-5"; //存放数字的栈 ArrayStack2 numStack = new ArrayStack2(10); //存放运算符的栈 ArrayStack2 operatorStack = new ArrayStack2(10); int num1; int num2; int result; char ch ; int index = 0; int operator; do { ch = expression.substring(index, index + 1).charAt(0); //判断是不是运算符 if (operatorStack.isOperator(ch)) { //如果存放运算符的栈是空的,直接将运算符放进去 if (!operatorStack.isEmpty()) { //如果运算符的优先级小于等于栈顶的优先级,就弹出数栈的两个值,符栈的一个值进行运算 //将得到的值放入数栈中,运算符放入符栈 if (operatorStack.priority(ch) <= operatorStack.priority(operatorStack.peek())) { num1 = numStack.pop(); num2 = numStack.pop(); operator = operatorStack.pop(); result = numStack.cal(num1, num2, operator); numStack.push(result); } } operatorStack.push(ch); } else {
//ch现在是字符,对应的埃斯格玛与数字差了48 numStack.push(ch - 48); } index++; } while (index != expression.length()); while (!operatorStack.isEmpty()) { num1 = numStack.pop(); num2 = numStack.pop(); operator = operatorStack.pop(); result = numStack.cal(num1, num2, operator); numStack.push(result); } int result2 = numStack.pop(); System.out.printf("表达式 %s = %d", expression, result2);
计算多位数
使用一个变量来存储是数字的值,如果下一个值是运算符就将这个变量存入数栈中,并清空它的值
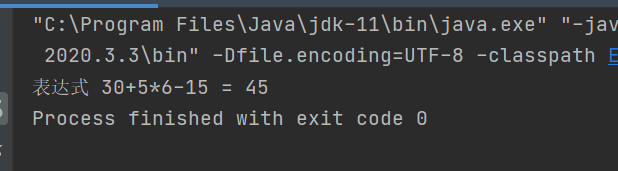
String expression = "30+5*6-15"; //存放数字的栈 ArrayStack2 numStack = new ArrayStack2(10); //存放运算符的栈 ArrayStack2 operatorStack = new ArrayStack2(10); int num1; int num2; int result; char ch ; int index = 0; int operator; String res = ""; do { ch = expression.substring(index, index + 1).charAt(0); //判断是不是运算符 if (operatorStack.isOperator(ch)) { //如果存放运算符的栈是空的,直接将运算符放进去 if (!operatorStack.isEmpty()) { //如果运算符的优先级小于等于栈顶的优先级,就弹出数栈的两个值,符栈的一个值进行运算 //将得到的值放入数栈中,运算符放入符栈 if (operatorStack.priority(ch) <= operatorStack.priority(operatorStack.peek())) { num1 = numStack.pop(); num2 = numStack.pop(); operator = operatorStack.pop(); result = numStack.cal(num1, num2, operator); numStack.push(result); } } operatorStack.push(ch); } else { // numStack.push(ch - 48); res += ch; if(index == expression.length()-1){ numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(res)); } else { //如果下一个是运算符,就将res的值放入数栈中,并将res清空 if(operatorStack.isOperator(expression.substring(index + 1,index + 2).charAt(0))) { numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(res)); res = ""; } } } index++; } while (index != expression.length()); while (!operatorStack.isEmpty()) { num1 = numStack.pop(); num2 = numStack.pop(); operator = operatorStack.pop(); result = numStack.cal(num1, num2, operator); numStack.push(result); } int result2 = numStack.pop(); System.out.printf("表达式 %s = %d", expression, result2);
前缀表达式
前缀表达式是一种没有括号的算术表达式,与中缀表达式不同的是,其将运算符写在前面,操作数写在后面。为纪念其发明者波兰数学家Jan Lukasiewicz,前缀表达式也称为“波兰式”。例如,- 1 + 2 3,它等价于1-(2+3)。
后缀表达式源自于前缀表达式,为了区分前缀和后缀表示,通常将后缀表示称为逆波兰表示;因前缀表示并不常用,所以有时也将后缀表示称为波兰表示。
前缀表达式是一种十分有用的表达式,将中缀表达式转换为前缀表达式后,就可以只依靠出栈、入栈两种简单操作完全解决中缀表达式的全部运算。
中缀表达式
(或中缀记法)是一个通用的算术或逻辑公式表示方法, 操作符是以中缀形式处于操作数的中间(例:3 + 4),中缀表达式是人们常用的算术表示方法。
与前缀或后缀记法不同的是,中缀记法中括号是必需的。计算过程中必须用括号将操作符和对应的操作数括起来,用于指示运算的次序。
后缀表达式
逆波兰式(Reverse Polish notation,RPN,或逆波兰记法),也叫后缀表达式(将运算符写在操作数之后)
作用
实现逆波兰式的算法,难度并不大,但为什么要将看似简单的中缀表达式转换为复杂的逆波兰式?原因就在于这个简单是相对人类的思维结构来说的,对计算机而言中序表达式是非常复杂的结构。相对的,逆波兰式在计算机看来却是比较简单易懂的结构。因为计算机普遍采用的内存结构是栈式结构,它执行先进后出的顺序。
算法实现
首先需要分配2个栈,一个作为临时存储运算符的栈S1(含一个结束符号),一个作为存放结果(逆波兰式)的栈S2(空栈)从中缀式的左端开始取字符,逐序进行如下步骤:
- 若取出的字符是操作数,则分析出完整的运算数,该操作数直接送入S2栈。
- 若取出的字符是运算符,则将该运算符与S1栈栈顶元素比较,如果该运算符(不包括括号运算符)优先级高于S1栈栈顶运算符(包括左括号)优先级,则将该运算符进S1栈,否则,将S1栈的栈顶运算符弹出,送入S2栈中,直至S1栈栈顶运算符(包括左括号)低于(不包括等于)该运算符优先级时停止弹出运算符,最后将该运算符送入S1栈。
- 若取出的字符是“(”,则直接送入S1栈顶。
- 若取出的字符是“)”,则将距离S1栈栈顶最近的“(”之间的运算符,逐个出栈,依次送入S2栈,最后弹出“(”。
- 重复上面的1~4步,直至处理完所有的输入字符。
S2应做一下逆序处理。便可以按照逆波兰式的计算方法计算了!
逆波兰计算器
//将表达式存入集合中 public static List<String> getListString(String suffixExpression) { String[] split = suffixExpression.split(" "); List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); Collections.addAll(list, split); return list; } //计算 public static int calculate(List<String> ls) { Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>(); for (String item : ls){ if (item.matches("\\d+")) { // 匹配的是多位数 // 入栈 stack.push(item); } else { int num1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop()); int num2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop()); int result; switch (item) { case "+": result = num1 + num2; break; case "-": result = num2 - num1; break; case "*": result = num1 * num2; break; case "/": result = num1 / num2; break; default: throw new RuntimeException("运算符有误"); } //把result 入栈 stack.push("" + result); } } return Integer.parseInt(stack.pop()); }
String suffixExpression = "30 4 + 5 * 6 -"; List<String> list = getListString(suffixExpression); System.out.println("list = " + list); int result = calculate(list); System.out.println("result = " + result);

中缀表达式转后缀表达式
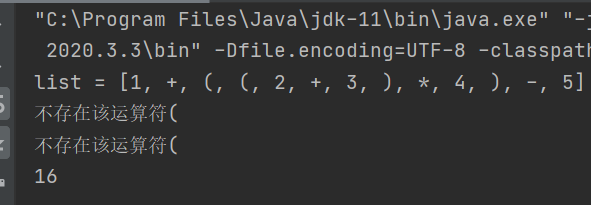
//将中缀表达式存入到集合中 public static List<String> toInfixExpressionList(String s) { List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); int i = 0; char ch; StringBuilder str; do{ //判断是不是运算符 if((ch = s.charAt(i)) < 48 || (ch = s.charAt(i)) > 57){ list.add("" + ch); i++; } else { str = new StringBuilder(); //如果是数字,存入str中,下一位是运算符就结束循环,将str存入集合中 while (i < s.length() && s.charAt(i) >= 48 && (ch = s.charAt(i)) <= 57){ str.append(ch); i++; } list.add(str.toString()); } }while (i < s.length()); return list; } //中缀表达式转后缀表达式,由于s2并不需要弹出数据,最后还需要逆序处理,直接用集合代替 public static List<String> parseSuffixExpressionList(List<String> ls) { Stack<String> s1 = new Stack<>(); List<String> s2 = new ArrayList<>(); for (String item : ls) { if(item.matches("\\d+")) { s2.add(item); } else if (item.equals("(")) { s1.push(item); } else if (item.equals(")")) { while (!s1.peek().equals("(")) { s2.add(s1.pop()); } s1.pop(); } else { while (s1.size() > 0 && Operation.getValue(item) <= Operation.getValue(s1.peek())) { s2.add(s1.pop()); } s1.push(item); } } while (s1.size() > 0){ s2.add(s1.pop()); } return s2; }
class Operation { //写一个方法,返回对应的优先级数字 public static int getValue(String operation) { int result = 0; switch (operation) { case "+": case "-": result = 1; break; case "*": case "/": result = 2; break; default: System.out.println("不存在该运算符" + operation); break; } return result; } }
String expression = "1+((2+3)*4)-5"; List<String> list = toInfixExpressionList(expression); System.out.println("list = " + list); List<String> suffixExpressionList = parseSuffixExpressionList(list); System.out.println(calculate(suffixExpressionList));
完整逆波兰计算器
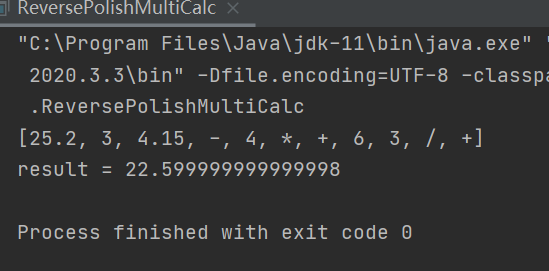
/** * 匹配 + - * / ( ) 运算符 */ static final String SYMBOL = "[+\\-*/()]"; static final String LEFT = "("; static final String RIGHT = ")"; static final String ADD = "+"; static final String MINUS= "-"; static final String TIMES = "*"; static final String DIVISION = "/"; /** * 加減 + - */ static final int LEVEL_01 = 1; /** * 乘除 * / */ static final int LEVEL_02 = 2; /** * 括号优先级最高 */ static final int LEVEL_HIGH = Integer.MAX_VALUE; static Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>(); static List<String> data = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>()); /** * 去除所有空白符 */ public static String replaceAllBlank(String s ){ // \\s+ 匹配任何空白字符,包括空格、制表符、换页符等等, 等价于[ \f\n\r\t\v] return s.replaceAll("\\s+",""); } /** * 判断是不是数字 int double long float */ public static boolean isNumber(String s){ Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("^[-+]?[.\\d]*$"); return pattern.matcher(s).matches(); } /** * 判断是不是运算符 */ public static boolean isSymbol(String s){ return s.matches(SYMBOL); } /** * 匹配运算等级 */ public static int calcLevel(String s){ if("+".equals(s) || "-".equals(s)){ return LEVEL_01; } else if("*".equals(s) || "/".equals(s)){ return LEVEL_02; } return LEVEL_HIGH; } /** * 匹配 */ public static List<String> doMatch (String s) { if(s == null || "".equals(s.trim())) throw new RuntimeException("data is empty"); if(!isNumber(s.charAt(0)+"")) throw new RuntimeException("data illegal,start not with a number"); s = replaceAllBlank(s); String each; int start = 0; for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { if(isSymbol(s.charAt(i)+"")){ each = s.charAt(i)+""; //栈为空,(操作符,或者 操作符优先级大于栈顶优先级 && 操作符优先级不是( )的优先级 及是 ) 不能直接入栈 if(stack.isEmpty() || LEFT.equals(each) || ((calcLevel(each) > calcLevel(stack.peek())) && calcLevel(each) < LEVEL_HIGH)){ stack.push(each); }else if( !stack.isEmpty() && calcLevel(each) <= calcLevel(stack.peek())){ //栈非空,操作符优先级小于等于栈顶优先级时出栈入列,直到栈为空,或者遇到了(,最后操作符入栈 while (!stack.isEmpty() && calcLevel(each) <= calcLevel(stack.peek()) ){ if(calcLevel(stack.peek()) == LEVEL_HIGH){ break; } data.add(stack.pop()); } stack.push(each); }else if(RIGHT.equals(each)){ // ) 操作符,依次出栈入列直到空栈或者遇到了第一个)操作符,此时)出栈 while (!stack.isEmpty()){ calcLevel(stack.peek()); if(LEVEL_HIGH == calcLevel(stack.peek())){ stack.pop(); break; } data.add(stack.pop()); } } start = i ; //前一个运算符的位置 }else if( i == s.length()-1 || isSymbol(s.charAt(i+1)+"") ){ each = start == 0 ? s.substring(start,i+1) : s.substring(start+1,i+1); if(isNumber(each)) { data.add(each); continue; } throw new RuntimeException("data not match number"); } } //如果栈里还有元素,此时元素需要依次出栈入列,可以想象栈里剩下栈顶为/,栈底为+,应该依次出栈入列,可以直接翻转整个stack 添加到队列 Collections.reverse(stack); data.addAll(new ArrayList<>(stack)); System.out.println(data); return data; } /** * 算出结果 */ public static Double doCalc(List<String> list){ double d; if(list == null || list.isEmpty()){ return null; } if (list.size() == 1){ d = Double.parseDouble(list.get(0)); return d; } ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { list1.add(list.get(i)); if(isSymbol(list.get(i))){ Double d1 = doTheMath(list.get(i - 2), list.get(i - 1), list.get(i)); list1.remove(i); list1.remove(i-1); list1.set(i-2,d1+""); list1.addAll(list.subList(i+1,list.size())); break; } } return doCalc(list1); } /** * 运算 */ public static Double doTheMath(String s1,String s2,String symbol){ Double result ; switch (symbol){ case ADD : result = Double.parseDouble(s1) + Double.parseDouble(s2); break; case MINUS : result = Double.parseDouble(s1) - Double.parseDouble(s2); break; case TIMES : result = Double.parseDouble(s1) * Double.parseDouble(s2); break; case DIVISION : result = Double.parseDouble(s1) / Double.parseDouble(s2); break; default : result = null; } return result; }
String math = "25.2 + (3 - 4.15)*4+6/3"; try { double result = doCalc(doMatch(math)); System.out.println("result = " + result); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号