链表
1.链表的定义
/**
* description
*
* @since 2022-03-01
*/
public class ListNode {
public ListNode next;
public int val;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
2.链表的操作
2.1 追加
/**
* description
*
* @since 2022-03-01
*/
public class ListNodeOperation {
// append
public void append(int val) {
if (head == null) {
head = new ListNode(val);
return;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {// 循环结束的条件是cur指向最后一个节点元素
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = new ListNode(val);
}
}
2.2 遍历
/**
* description
*
* @since 2022-03-01
*/
public class ListNodeOperation {
// 遍历
public void print(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.println(cur.val);
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
2.3 删除
/**
* description
*
* @since 2022-03-01
*/
public class ListNodeOperation {
// 删除 双指针实现
public ListNode remove(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);
dummyNode.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummyNode, cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == val) {
pre.next = cur.next;
return dummyNode.next;
}
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummyNode.next;
}
}
2.4 修改
/**
* description
*
* @since 2022-03-01
*/
public class ListNodeOperation {
// 删除
public ListNode set(ListNode head, int oldVal, int newVal) {
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null && cur.val != oldVal) {
cur = cur.next;
}
// 循环结束的条件是cur == null 或者cur.val == oldVal;
if (cur != null) {
cur.val = newVal;
}
return head;
}
}
2.4 查询
/**
* description
*
* @since 2022-03-01
*/
public class ListNodeOperation {
// 查询
public ListNode get(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null && cur.val != val) {
cur = cur.next;
}
// 循环结束的条件是cur == null 或者cur.val == oldVal;
if (cur != null) {
return cur;
}
return null;
}
}
2.5 插入
/**
* description
*
* @since 2022-03-01
*/
public class ListNodeOperation {
// 插入
public ListNode insert(ListNode head, int oldVal, int val) {
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode insertedNode = new ListNode(val);
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null && cur.val != oldVal) {
cur = cur.next;
}
// 循环结束的条件是cur == null 或者cur.val == oldVal;
if (cur != null) {
ListNode tmpNode = cur.next;
cur.next = insertedNode;
insertedNode.next = tmpNode;
}
return head;
}
}
2.6 反转
/**
* description
*
* @since 2022-03-01
*/
public class ListNodeOperation {
// 反转链表reversal,迭代实现
public ListNode reversal(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode preNode = null;
ListNode curNode = head;
while (curNode != null) {
ListNode nextNode = curNode.next; // 1.存储后向节点
curNode.next = preNode; // 2.将当前节点的指针指向前向节点
preNode = curNode; // 3.更新前向节点为当前节点
curNode = nextNode; // 4.更新当前节点为后向节点
}
return preNode;
}
// 反转链表reversal,递归实现
public ListNode reversalWithRecursion(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode last = reversalWithRecursion(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return last;
}
}
2.8 反转前N个节点
private ListNode nextNode = null; // 后向节点
// 反转以head为起点的n个节点,返回新的头节点
public ListNode reverseFirstNNode(ListNode head, int n) {
if (head == null) return head;
if (n == 1) {
// 记录第n + 1个节点
nextNode = head.next;
return head;
}
// 以head.next为起点,需要反转前n-1个节点
ListNode last = reverseFirstNNode(head.next, n - 1);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = nextNode; // 让反转之后的head节点和后面的节点连起来
return last;
}
public ListNode reverseFirstNNode2(ListNode head, int n) {
if (head == null) return head;
// 双指针 + 头插法
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);
dummyNode.next = head;
ListNode g = dummyNode, p = head;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
ListNode removedNode = p.next;
p.next = p.next.next;
removedNode.next = g.next;
g.next = removedNode;
}
return dummNode.next;
}
2.9 反转部分链表节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private ListNode nextNode;
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
// 递归思想
if (left == 1) {
return reverseFirstNNode(head, right);
}
head.next = reverseBetween(head.next, left - 1, right - 1);
return head;
}
private ListNode reverseFirstNNode(ListNode head, int n) {
if (n == 1) {
nextNode = head.next;
return head;
}
ListNode last = reverseFirstNNode(head.next, n - 1);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = nextNode;
return last;
}
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
// 解法2 双指针 + 头插法
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(head.val);
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode g = dummyHead, p = head;
for (int i = 0; i < left; i++) { // 将g指针移动到left的前向节点,p指针移动到left节点
g = g.next;
p = p.next;
}
for (int j = 0; j < right - left; j++) {
ListNode tmpNode = p.next; // 记录p的后向节点
p.next = p.next.next; // 移除p的后向节点
tmpNode.next = g.next; // 从p的头部插入删除的后向节点
g.next = tmpNode; // p的前向节点指向新插入的节点
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
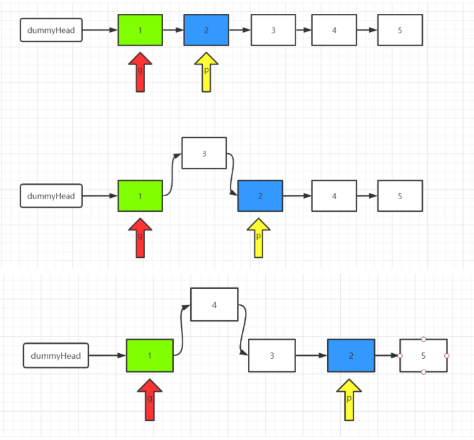
2.7 链表的深拷贝
/**
* description
*
* @since 2022-03-01
*/
public class ListNodeOperation {
public ListNode copy(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);// 创建一个虚拟节点
ListNode curNode = head;
while (curNode != null) {
ListNode tmpNode = new ListNode(curNode.val);
preNode.next = tmpNode;
preNode = tmpNode;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
return dummyNode.next;
}
}
2.8 查询链表的倒数第K个节点
/**
* description
*
* @since 2022-03-01
*/
public class ListNodeOperation {
// 我们可以先遍历得出链表的长度,再查找顺数第N - K个元素,但是这样的时间复杂度是2*O(N)
// 查找倒数第K个节点 时间复杂度O(N)
public ListNode findLastKNode(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (k-- > 0) {
fast = fast.next;
}
while (fast != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
2.9 查找链表的中点
/**
* description
*
* @since 2022-03-01
*/
public class ListNodeOperation {
public ListNode findMiddleNode(ListNode head) {
// 快慢指针实现
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
2.10 合并两个有序链表
/**
* description
*
* @since 2022-03-01
*/
public class ListNodeOperation {
// 两个链表非空
public ListNode mergeTwoNodeList(ListNode node1, ListNode node2) {
// 双指针实现
if (node1 == null) return node2;
if (node2 == null) return node1;
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(-1); // 创建一个虚拟头结点
ListNode cur = dummyNode; // 新链表的移动指针
ListNode cur1 = node1, cur2 = node2;
while (cur1 != null && cur2 != null) {
if (cur1.val < cur2.val) {
cur.next = cur1;
cur1 = cur1.next;
} else {
cur.next = cur2;
cur = cur2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
// 循环终止的条件是cur1、cur2中有一个为null
if (cur1 != null) {
cur.next = cur1;
}
if (cur2 != null) {
cur.next = cur2;
}
return dummyNode.next;
}
}
2.11 合并K个有序链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists.length == 0) return null;
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dummyNode;
PriorityQueue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(lists.length, ((a, b) -> (a.val - b.val))); // 创建一个优先级队列用于存储lists中的头结点
for (ListNode head : lists) {
if (head != null) {
queue.add(head);
}
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ListNode tmp = queue.poll(); // poll出队列中的最小头结点
cur.next = tmp;
if (tmp.next != null) {
queue.add(tmp.next);
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummyNode.next;
}
}
2.12 判断链表是否包含环
public boolean isHasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return null;
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next; // 快指针走两步
slow = slow.next; // 慢指针走一步
if (fast == slow) { // 如果两个指针相遇了则证明有环
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean isHasCycle(ListNode head) { // 时间复杂度O(N),空间复杂度O(N)
if (head == null) return null;
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (set.conatains(cur)) {
return true;
}
set.add(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
2.13 求成环的首个节点
public ListNode findCycleStartNode(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return null;
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next; // 快指针走两步
slow = slow.next; // 慢指针走一步
if (fast == slow) { // 如果两个指针相遇了则证明有环
break;
}
}
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) return null; // 如果fast遇到null则证明没有成环
slow = head; // 此时让慢指针重新回到起点
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}

2.14 求两条链表的相交节点
public ListNode findConnectedNode(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
// 难点是怎么让两个指针同时走到相交点
if (head1 == null || head2 == null) return null;
ListNode cur1 = head1, cur2 = head2;
while (cur1 != cur2) {
// 走到尽头见不到你,于是走过你来时的路,等到相遇时才发现,你也走过我来时的路。
cur1 = cur1 == null ? head2 : cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2 == null ? head1 : cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}
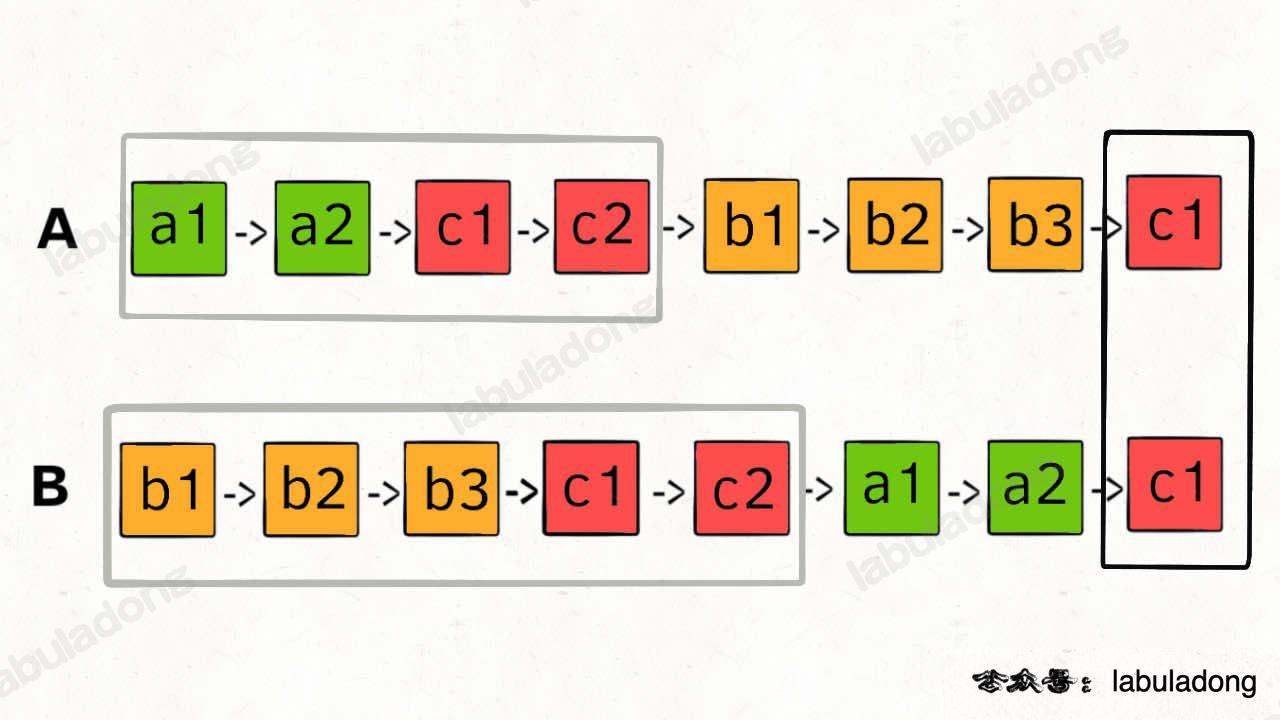
2.15 K个一组反转链表
2.16 判断回文链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
// 解法一:对称-头尾双指针,时间复杂度O(N),空间复杂度O(N)
if (head == null) return false;
ListNode cur = head;
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
while (cur != null) {
res.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.next;
}
return isPalindList(res);
}
private boolean isPalindList(List<Integer> list) {
int i = 0;
int j = list.size() - 1;
while (i < j) {
if (!list.get(i).equals(list.get(j))) {
return false;
}
i++;
j--;
}
return true;
}
public boolean isPalindrome2(ListNode head) {
// 解法二:先找到链表的中间节点,再对后半部分机型反转与前半部分进行比较,时间复杂度O(N),空间复杂度O(1)
if (head == null) return false;
ListNode rightPartNode = findMiddleNode(head);
ListNode right = reverse(rightPartNode);
ListNode left = head;
while (right != null) {
if (right.val != left.val) {
return false;
}
right = right.next;
left = left.next;
}
return true;
}
// 找到待反转的首节点 及中间节点
private ListNode findMiddleNode(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
if (fast != null) {
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
// 反转以head为起点的链表
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return head;
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
3.题目
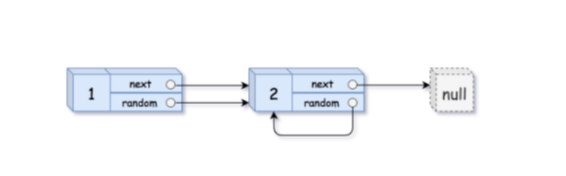
3.1 复杂链表的复制
请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
示例 1:
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:
输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
示例 4:输入:head = []
输出:[]
解释:给定的链表为空(空指针),因此返回 null。提示:
-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000
Node.random 为空(null)或指向链表中的节点。
节点数目不超过 1000 。
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
/**
* 本题难点:在复制链表的过程中构建新链表各节点的 random 引用指向。
*/
public Node copyRandomList1(Node head) {
// 解题思路:使用hashMap来记录原链表节点和新链表节点
if (head == null) return head;
// 1.遍历原链表,创建旧-新节点映射map
Map<Node, Node> recordMap = new HashMap<>();
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
recordMap.put(cur, new Node(cur.val));
cur = cur.next;
}
// 2.遍历原链表,根据原链表的next、random引用关系创建新节点的引用关系
cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
recordMap.get(cur).next = recordMap.get(cur.next);
recordMap.get(cur).random = recordMap.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
// 3.返回新链表的首节点
return recordMap.get(head);
}
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
// 解题思路:拼接+拆分
if (head == null) return head;
// 1.遍历原链表,在原节点后边都加上新节点
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
Node newNode = new Node(cur.val);
newNode.next = cur.next;
cur.next = newNode;
cur = newNode.next;
}
// 2.遍历原链表,连上新节点的random引用
cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.random != null)
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
// 3.拆分链表
cur = head.next;
Node res = head.next;
Node pre = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
pre.next = pre.next.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
pre.next = null;
return res;
}
}
- 链表的拼接与拆分
- 链表的遍历




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号