数据采集第二次作业
作业1
相关代码和结果
点击查看代码
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from bs4 import UnicodeDammit
import urllib.request
import sqlite3
class WeatherDatabase:
def __init__(self):
self.connection = None
self.cursor = None
def initialize_database(self):
self.connection = sqlite3.connect("weather_data.db")
self.cursor = self.connection.cursor()
try:
self.cursor.execute("""
create table weather_records (
city varchar(16),
date varchar(16),
conditions varchar(64),
temperature varchar(32),
primary key (city, date)
)
""")
except:
self.cursor.execute("delete from weather_records")
def finalize_database(self):
self.connection.commit()
self.connection.close()
def add_record(self, city, date, conditions, temp):
try:
self.cursor.execute(
"insert into weather_records values (?,?,?,?)",
(city, date, conditions, temp)
)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Database error: {e}")
def display_records(self):
self.cursor.execute("select * from weather_records")
records = self.cursor.fetchall()
print("%-16s%-16s%-32s%-16s" % ("City", "Date", "Weather", "Temperature"))
for record in records:
print("%-16s%-16s%-32s%-16s" % record)
class WeatherCollector:
def __init__(self):
self.database = WeatherDatabase()
self.request_headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36"
}
self.city_mapping = {
"北京": "101010100",
"上海": "101020100",
"广州": "101280101",
"深圳": "101280601"
}
def fetch_city_weather(self, city_name):
if city_name not in self.city_mapping:
print(f"City code not found for {city_name}")
return
target_url = f"http://www.weather.com.cn/weather/{self.city_mapping[city_name]}.shtml"
try:
request = urllib.request.Request(target_url, headers=self.request_headers)
response = urllib.request.urlopen(request)
webpage_data = response.read()
encoding_detector = UnicodeDammit(webpage_data, ["utf-8", "gbk"])
decoded_content = encoding_detector.unicode_markup
parsed_html = BeautifulSoup(decoded_content, "lxml")
weather_items = parsed_html.select("ul.t.clearfix li")
for item in weather_items:
try:
forecast_date = item.select('h1')[0].text
weather_condition = item.select('p.wea')[0].text
temp_element = item.select('p.tem')[0]
high_temp = temp_element.select('span')
low_temp = temp_element.select('i')[0]
if high_temp:
temperature_range = f"{high_temp[0].text}/{low_temp.text}"
else:
temperature_range = low_temp.text
print(city_name, forecast_date, weather_condition, temperature_range)
self.database.add_record(city_name, forecast_date, weather_condition, temperature_range)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Data parsing error: {e}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Network error: {e}")
def collect_weather_data(self, cities):
self.database.initialize_database()
for city in cities:
self.fetch_city_weather(city)
self.database.finalize_database()
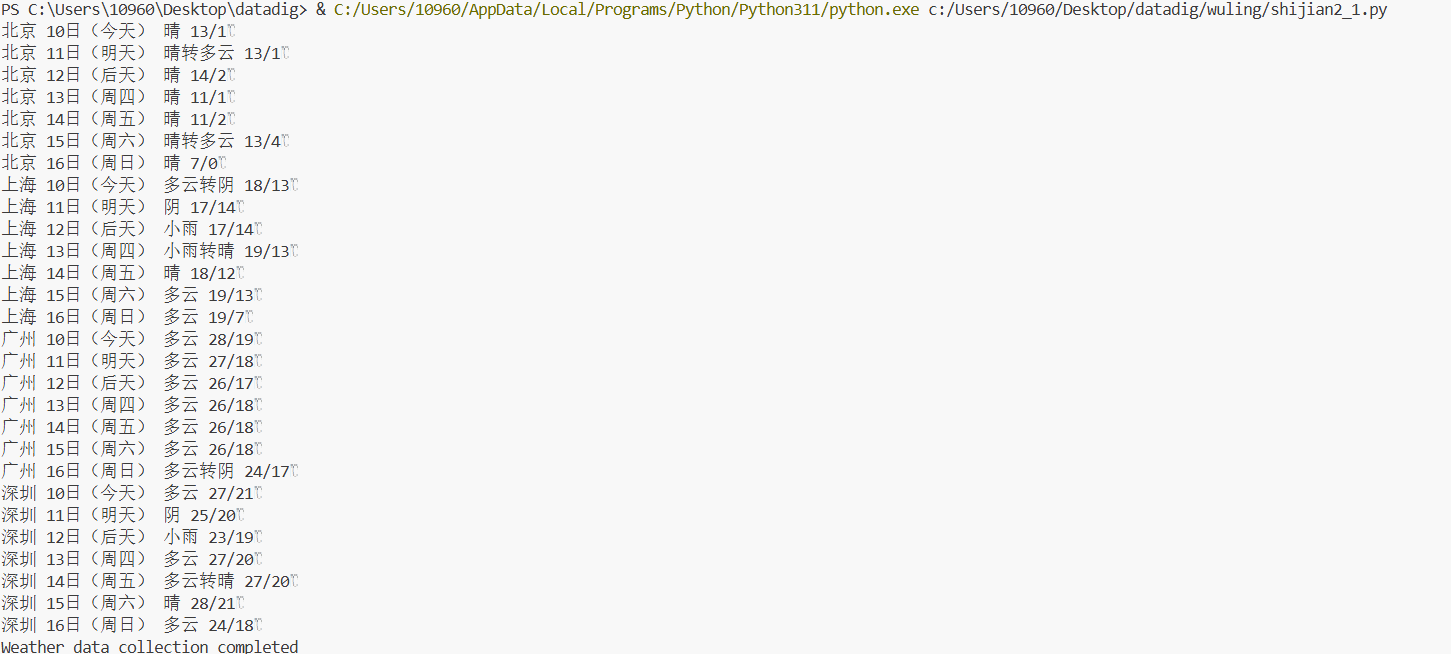
if __name__ == "__main__":
weather_app = WeatherCollector()
weather_app.collect_weather_data(["北京", "上海", "广州", "深圳"])
print("Weather data collection completed")
心得
在解析股票数据时,最大的挑战在于处理网站的反爬机制。通过分析发现,东方财富网的数据是通过动态加载的JSONP格式返回的,需要从复杂的响应文本中提取有效数据。我学会了使用正则表达式匹配JSONP回调函数,然后截取其中的JSON数据。这个过程中深刻体会到,理解网站的数据传输机制比单纯的技术实现更重要。
作业2
相关代码和结果
点击查看代码
import json
import sqlite3
import time
import pandas as pd
import requests
class StockDataCollector:
def __init__(self):
self.headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36',
'Referer': 'https://quote.eastmoney.com/'
}
def format_units(self, number):
"""格式化数字为万/亿单位"""
if number is None:
return "0"
abs_num = abs(number)
if abs_num >= 1e8:
return f"{number/1e8:.2f}亿"
elif abs_num >= 1e4:
return f"{number/1e4:.2f}万"
else:
return f"{number:.2f}"
def init_database(self):
"""初始化数据库"""
conn = sqlite3.connect('stock_market.db')
conn.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS stock_data (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
code TEXT NOT NULL,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
price REAL,
change_rate REAL,
change_amount REAL,
volume REAL,
turnover REAL,
amplitude REAL
)
''')
conn.commit()
conn.close()
def save_stock_data(self, data):
"""保存股票数据"""
conn = sqlite3.connect('stock_market.db')
conn.execute('''
INSERT INTO stock_data (code, name, price, change_rate, change_amount, volume, turnover, amplitude)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
''', data)
conn.commit()
conn.close()
def fetch_stock_info(self, pages=2, delay=1):
"""获取股票信息"""
self.init_database()
all_stocks = []
for page in range(pages):
# 使用原始代码中的URL格式
url = f'https://push2.eastmoney.com/api/qt/clist/get?np=1&fltt=1&invt=2&cb=jQuery&fs=m:0+t:6+f:!2,m:0+t:80+f:!2,m:1+t:2+f:!2,m:1+t:23+f:!2,m:0+t:81+s:262144+f:!2&fields=f12,f13,f14,f1,f2,f4,f3,f152,f5,f6,f7,f15,f18,f16,f17,f10,f8,f9,f23&fid=f3&pn={page+1}&pz=20&po=1&dect=1&ut=fa5fd1943c7b386f172d6893dbfba10b&wbp2u=|0|0|0|web&_={int(time.time()*1000)}'
try:
response = requests.get(url, headers=self.headers)
response.encoding = 'utf-8'
# 处理JSONP响应
text = response.text
start = text.find('(') + 1
end = text.rfind(')')
json_str = text[start:end]
data = json.loads(json_str)
if 'data' in data and 'diff' in data['data']:
stocks = data['data']['diff']
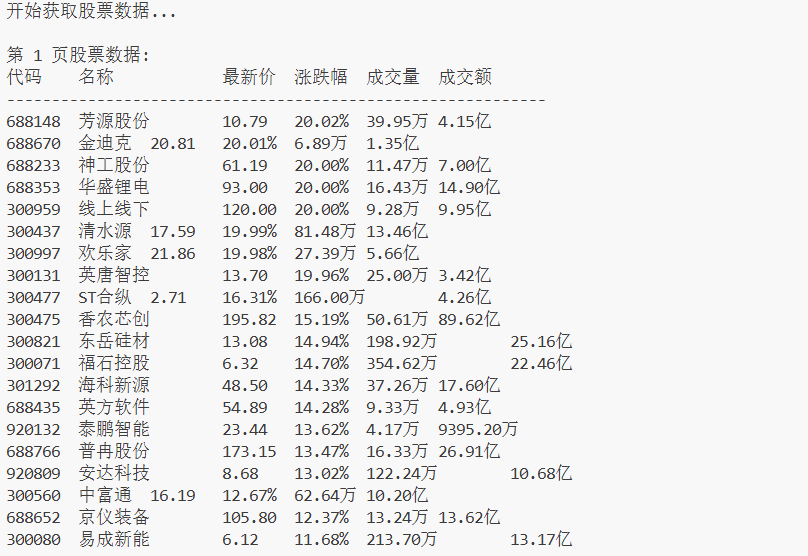
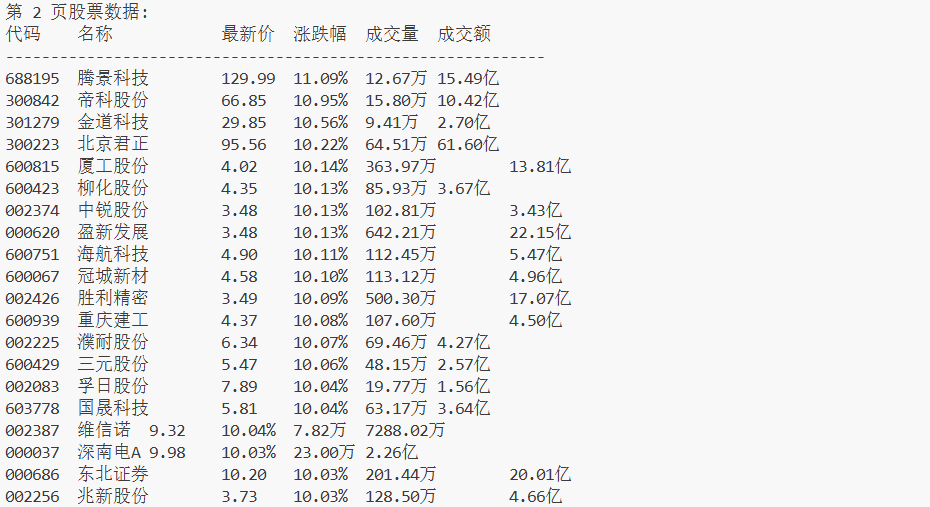
print(f"\n第 {page+1} 页股票数据:")
print("代码\t名称\t\t最新价\t涨跌幅\t成交量\t成交额")
print("-" * 60)
for i, stock in enumerate(stocks):
# 安全地获取字段值
code = stock.get('f12', '')
name = stock.get('f14', '')
price = stock.get('f2', 0) # 最新价
change_rate = stock.get('f3', 0) # 涨跌幅
change_amount = stock.get('f4', 0) # 涨跌额
volume = stock.get('f5', 0) # 成交量
turnover = stock.get('f6', 0) # 成交额
amplitude = stock.get('f7', 0) # 振幅
# 格式化显示
price_str = f"{price/100:.2f}" if price else "0.00"
change_rate_str = f"{change_rate/100:.2f}%" if change_rate else "0.00%"
# 保存到数据库
self.save_stock_data((
code, name, price/100 if price else 0,
change_rate/100 if change_rate else 0,
change_amount/100 if change_amount else 0,
volume, turnover, amplitude/100 if amplitude else 0
))
# 添加到显示列表
all_stocks.append({
'代码': code,
'名称': name,
'最新价': price_str,
'涨跌幅': change_rate_str,
'成交量': self.format_units(volume),
'成交额': self.format_units(turnover)
})
print(f"{code}\t{name[:8]}\t{price_str}\t{change_rate_str}\t{self.format_units(volume)}\t{self.format_units(turnover)}")
time.sleep(delay)
except Exception as e:
print(f"获取第{page+1}页数据时出错: {e}")
continue
return all_stocks
def display_database(self):
"""显示数据库内容"""
conn = sqlite3.connect('stock_market.db')
try:
# 使用pandas读取数据
df = pd.read_sql('SELECT * FROM stock_data', conn)
if len(df) > 0:
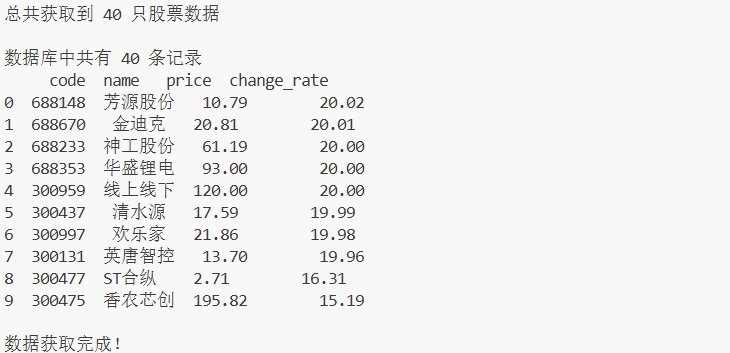
print(f"\n数据库中共有 {len(df)} 条记录")
print(df[['code', 'name', 'price', 'change_rate']].head(10))
else:
print("\n数据库中没有数据")
except Exception as e:
print(f"读取数据库时出错: {e}")
finally:
conn.close()
def main():
collector = StockDataCollector()
print("开始获取股票数据...")
stocks = collector.fetch_stock_info(pages=2, delay=1)
print(f"\n总共获取到 {len(stocks)} 只股票数据")
# 显示数据库内容
collector.display_database()
print("\n数据获取完成!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
心得体会
解析天气预报网站时,主要难点在于HTML结构的复杂性。使用BeautifulSoup解析时,需要准确定位到包含天气信息的特定标签。通过反复调试选择器,我掌握了如何从嵌套的HTML结构中提取目标数据。特别是在处理多城市数据时,发现不同城市页面结构存在细微差异,这让我认识到健壮的解析代码需要兼顾各种可能的情况。
作业3
相关代码和结果
点击查看代码
import requests
import sqlite3
def fetch_university_rankings():
"""获取大学排名数据"""
api_endpoint = "https://www.shanghairanking.cn/api/pub/v1/bcur"
query_params = {"bcur_type": 11, "year": 2021}
browser_headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) "
"AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/17.0 Safari/605.1.15",
"Origin": "https://www.shanghairanking.cn",
"Referer": "https://www.shanghairanking.cn/rankings/bcur/2021"
}
try:
response = requests.get(api_endpoint, params=query_params,
headers=browser_headers, timeout=20)
response.raise_for_status()
json_data = response.json()
university_list = json_data.get("data", {}).get("rankings", [])
return university_list
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as error:
print(f"网络请求异常: {error}")
return []
except ValueError as error:
print(f"JSON解析错误: {error}")
return []
def process_university_data(raw_data):
"""处理大学数据"""
processed_data = []
for university in raw_data:
# 提取必要字段
rank_position = university.get("ranking")
school_name = university.get("univNameCn", "").strip()
location = university.get("province", "").strip()
school_type = university.get("univCategory", "").strip()
total_score = university.get("score", 0)
# 验证必要字段
if not rank_position or not school_name:
continue
processed_data.append((
rank_position,
school_name,
location,
school_type,
total_score
))
return processed_data
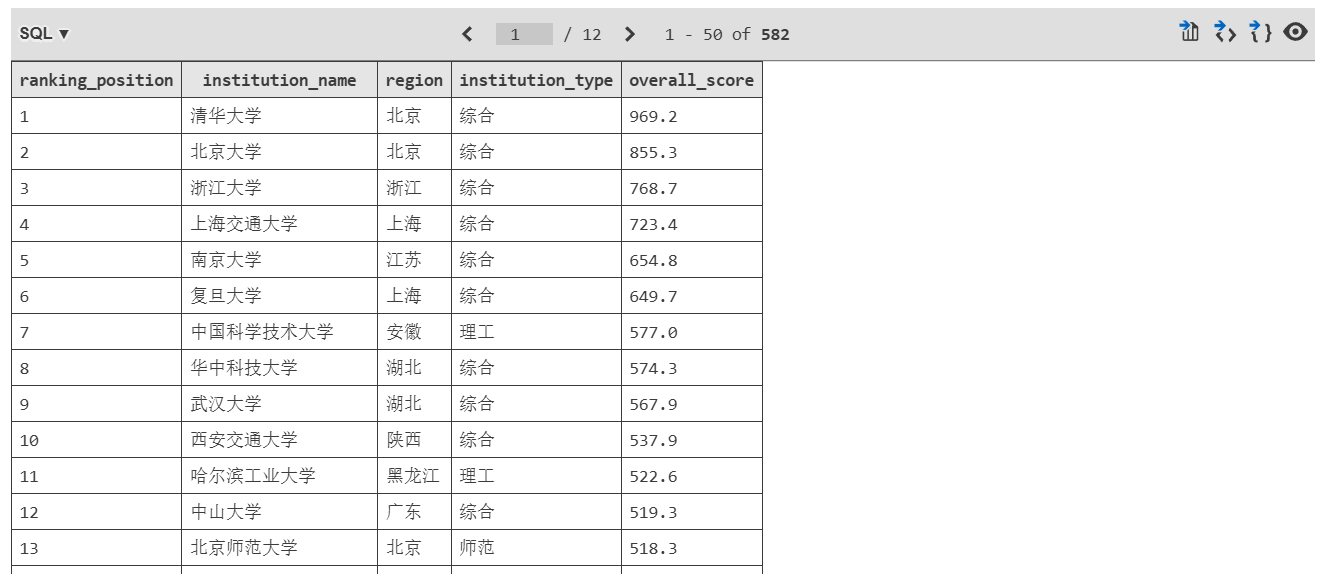
def display_ranking_preview(data_list, preview_count=25):
"""显示排名预览"""
print(f"\n{'='*65}")
print(f"{'位次':<6}{'院校名称':<18}{'所在地':<8}{'类别':<8}{'综合得分':<10}")
print(f"{'-'*65}")
for item in data_list[:preview_count]:
rank, name, province, category, score = item
# 处理长校名显示
display_name = name if len(name) <= 16 else name[:14] + ".."
print(f"{rank:<6}{display_name:<18}{province:<8}{category:<8}{score:<10}")
def setup_database_structure():
"""初始化数据库结构"""
database_connection = sqlite3.connect("academic_rankings.db")
cursor = database_connection.cursor()
cursor.execute("""
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS institution_rankings (
ranking_position INTEGER,
institution_name TEXT NOT NULL,
region TEXT,
institution_type TEXT,
overall_score REAL,
UNIQUE(ranking_position, institution_name)
)
""")
database_connection.commit()
database_connection.close()
print("数据库初始化完成")
def save_to_database(processed_data):
"""保存数据到数据库"""
connection = sqlite3.connect("academic_rankings.db")
db_cursor = connection.cursor()
# 清空现有数据
db_cursor.execute("DELETE FROM institution_rankings")
# 批量插入数据
insertion_count = 0
for data_row in processed_data:
try:
db_cursor.execute("""
INSERT INTO institution_rankings
(ranking_position, institution_name, region, institution_type, overall_score)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
""", data_row)
insertion_count += 1
except sqlite3.IntegrityError:
continue # 忽略重复数据
connection.commit()
connection.close()
return insertion_count
def generate_data_summary(data_count):
"""生成数据统计摘要"""
conn = sqlite3.connect("academic_rankings.db")
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("SELECT COUNT(*) FROM institution_rankings")
actual_count = cur.fetchone()[0]
cur.execute("SELECT MIN(ranking_position), MAX(ranking_position) FROM institution_rankings")
min_rank, max_rank = cur.fetchone()
conn.close()
print(f"\n数据统计摘要:")
print(f"获取数据条数: {data_count}")
print(f"成功入库条数: {actual_count}")
print(f"排名覆盖范围: 第{min_rank}名 - 第{max_rank}名")
def main_execution():
"""主执行流程"""
print("开始获取2021年中国大学主榜排名数据...")
# 初始化数据库
setup_database_structure()
# 获取数据
raw_university_data = fetch_university_rankings()
if not raw_university_data:
print("未能获取到有效数据,程序结束")
return
print(f"成功获取到 {len(raw_university_data)} 所院校数据")
# 处理数据
cleaned_data = process_university_data(raw_university_data)
# 显示预览
display_ranking_preview(cleaned_data)
# 保存到数据库
saved_count = save_to_database(cleaned_data)
# 显示统计信息
generate_data_summary(len(cleaned_data))
print(f"\n数据保存完成!共存储 {saved_count} 条记录到 academic_rankings.db")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main_execution()
心得体会
这次爬虫过程中发现,原始数据文件并非标准JSON格式,直接解析会失败。仔细研究数据结构后才明白,有些字符串实际上是特定值的代号,需要建立映射字典来转换。这次经历让我意识到,爬虫前一定要先摸清数据文件的格式和结构,理解每个字段的含义,不能急于写代码。耐心分析数据源,往往能事半功倍。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号