【Python3_进阶系列_005】Python3-反射基础
一、反射基础
反射可以动态获取对象的方法或者实例,方便开发的过程。python中的反射我们需要了解如下用法:
__import__
getattr
setattr
hasattr
delattr
二、__import__()
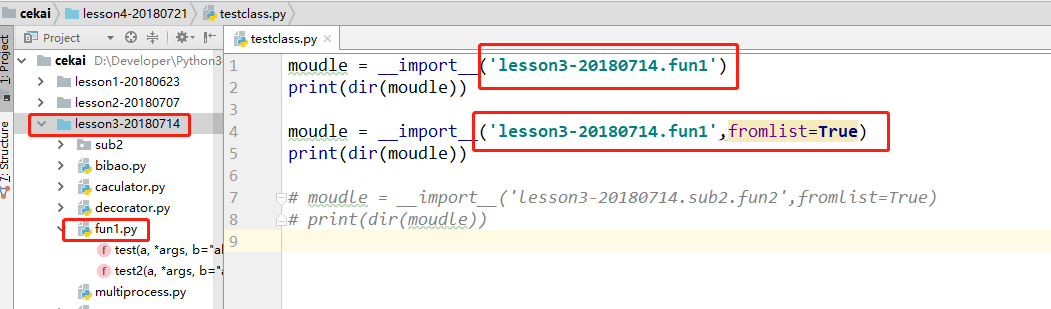
输出:
['__doc__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__path__', '__spec__', 'fun1']
['__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'test', 'test2']
可以看出参数 fromlist的区别,没有fromlist导入是x.y中x的模块,如果有x.y,导入的是y的模块
说明:
1. 函数功能用于动态的导入模块,主要用于反射或者延迟加载模块。
2. __import__(module)相当于import module
先定义两个模块mian.py和index.py,两个文件在同一目录下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
#index.pyprint ('index')def sayHello(): print('hello index')def sayHelloZhCn(): print('你好 index') |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
#mian.pyprint ('main')index = __import__('index')dir(index)index.sayHello()index.sayHelloZhCn() |
执行main.py,可以证实动态加载了index.py,__import__返回的模块也是index模块
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
C:\Users\Admin\Documents\Python3\importtest>python main.pymainindexhello index你好 index |
3. __import__(package.module)相当于from package import name,如果fromlist不传入值,则返回package对应的模块,如果fromlist传入值,则返回package.module对应的模块。
先定义archives包,其中包含user和role两个模块:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
#__index__.pyprint ('archives.__index__')def sayHello(): print('hello archives') |
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
#user.pyprint ('user')def sayHello(): print('hello user') |
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
#role.pyprint ('role')def sayHello(): print('hello role') |
结构如下:
修改mian.py:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
#main.pyprint ('main')archives = __import__('archives')archives.sayHello()archives.user |
执行main.py,可以证实动态加载了archives包,__import__返回的模块也是archives模块
C:\Users\Admin\Documents\Python3\importtest>python main.py
main
archives.__index__
hello archives
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "main.py", line 5, in <module>
archives.user
AttributeError: module 'archives' has no attribute 'user'
修改mian.py:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
#main.pyprint ('main')archives = __import__('archives.user')archives.sayHello()print(archives.user) |
执行main.py,可以证实动态加载了archives包的user模块,__import__返回的模块也是archives模块
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
C:\Users\Admin\Documents\Python3\importtest>python main.pymainarchives.__index__userhello archives<module 'archives.user' from 'C:\\Users\\Admin\\Documents\\Python3\\importtest\\archives\\user.py'> |
修改mian.py:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
#main.pyprint ('main')archives = __import__('archives.user',fromlist = ('user',))archives.sayHello()print(archives) |
执行main.py,可以证实动态加载了archives包的user模块,__import__返回的模块是user模块
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
C:\Users\Admin\Documents\Python3\importtest>python main.pymainarchives.__index__userhello user<module 'archives.user' from 'C:\\Users\\Admin\\Documents\\Python3\\importtest\\archives\\user.py'> |
4. level参数,指定是使用绝对导入还是相对导入。 0(默认值)表示只执行绝对导入。
三、其他方法
getattr -------------
getattr(obj,"name")获取obj中是否有第二个参数
setattr--------------
setattr(obj,"name","laowang")设置obj中name为laowang
hasattr------------
hasattr(obj,"func"):检查obj中是否存在func成员,当找到第二个参数时返回true,否则返回false
delattr-----------delattr(obj,'attr1')
删除对象的属性
实例1:首先定义一个简单的工厂:
#factorymethod.py
class Pay(): def __init__(self,channel,money): self.channel = channel self.money = money def pay(self): print("收到大猫金融支付金额{0}".format(self.money)) class WeChat(): def __init__(self,money): self.money = money def pay(self): print("收到微信支付金额{0}".format(self.money)) class AliPay(): def __init__(self,money): self.money = money def pay(self): print("收到支付宝支付金额{0}".format(self.money)) class BigCatFactory(): def create(self): return
实例2:通过反射访问方法
module =input("请选择模块:") class__ = input("请选择类:") money = input("请输入参数:") # # module = __import__(module) ##获取模块:import factroymethod object = getattr(module, class__)(money) ##获取指定的类,并且需要初始化传参:object = Alipy(money) object.pay() ##object.pay() 输出: 请选择模块:factorymethod 请选择类:AliPay 请输入参数:12.34 收到支付宝支付金额12.34
实例3:
class Foo(object): def __init__(self): self.name = "laozhang" def func(self): return "hello python" obj = Foo() #getattr(obj,"name")判断obj中是否有第二个参数 #如果第二个只是属性,则返回属性值,如果是方法名,则返回方法的内存地址,如果第二个参数没有在对象中找到,程序崩溃 # res = getattr(obj,"name1") #程序崩溃 # res = getattr(obj,"name") #返回属性值 并同时可省略r = res() res = getattr(obj,"func") #res为func的内存地址 r = res() print(r) # hasattr(obj,"func"):检查obj中是否存在func成员,当找到第二个参数时返回true,否则返回false res = hasattr(obj,"func") print(res) print(obj.name) #查看之前obj的name #setattr(obj,"name","laowang")设置obj中name为laowang res = setattr(obj,"name","laowang") print(obj.name) #当设置的值不存在时,会自动添加到实例对象中 #setattr需要三个参数: x,y,z ==> x.y =z #相当于obj.age = 10 setattr(obj,"age","10") print("name=%s,age=%s"%(obj.name,obj.age)) #laowang 10 #删除对象的属性 delattr(obj,"age") #print("name=%s,age=%s"%(obj.name,obj.age)) #程序崩溃 输出: hello python True laozhang laowang name=laowang,age=10
反射机制
先看看我对Java中反射机制的通俗理解:反射之中包含了一个“反”的概念,所以要想解释反射就必须先从“正”开始解释,一般而言,当用户使用一个类的时候,应该先知道这个类,而后通过这个类产生实例化对象,但是“反”指的是通过对象找到类。
而对于Python,如果我们需要动态导入模块,并且动态地访问对象中的属性和方法,怎么做?请看下面的代码。
s = "lib.test.commons"
m1 = __import__(s) # 这样仅仅动态导入了lib模块
m2 = __import__(s, fromlist = True) # fromlist = True,这样才能按路径动态导入commons模块
inp_func = input("请输入要执行的函数:")
f = getattr(m2, inp_func)() # 加"()"动态执行函数
由上述可见,反射就是:
- 通过字符串的形式,动态导入模块;
- 利用字符串的形式,在对象(模块)中操作(查找/获取/删除/添加)成员,是一种基于字符串的事件驱动!
反射机制内置函数
hasattr(obj,name)
判断一个对象obj里面是否有name属性或者name方法,返回bool值,有name特性返回True, 否则返回False。
需要注意的是name要用引号包起来。
class test():
name="xiaohua"
def run(self):
return "HelloWord"
>>> t=test()
>>> hasattr(t, "name") #判断对象有name属性
True
>>> hasattr(t, "run") #判断对象有run方法
True
getattr(obj,name[,default])
获取对象obj的属性或者方法,如果存在就打印出来,如果不存在,则打印出默认值,默认值可选。
需要注意的是,如果是返回的对象的方法,返回的是方法的内存地址,如果需要运行这个方法,可以在后面添加一对括号。
class test():
name="xiaohua"
def run(self):
return "HelloWord"
>>> t=test()
>>> getattr(t, "name") #获取name属性,存在就打印出来。
'xiaohua'
>>> getattr(t, "run") #获取run方法,存在就打印出方法的内存地址。
<bound method test.run of <__main__.test instance at 0x0269C878>>
>>> getattr(t, "run")() #获取run方法,后面加"()"可以将这个方法运行。
'HelloWord'
>>> getattr(t, "age") #获取一个不存在的属性。
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AttributeError: test instance has no attribute 'age'
>>> getattr(t, "age","18") #若属性不存在,返回一个默认值。
'18'
setattr(obj,name,values)
给对象obj的属性赋值,若属性不存在,先创建再赋值。
class test():
name="xiaohua"
def run(self):
return "HelloWord"
>>> t=test()
>>> hasattr(t, "age") #判断属性是否存在
False
>>> setattr(t, "age", "18") #属性不存在就创建之,且赋值,但没有返回值
>>> hasattr(t, "age") #属性存在了
True
delattr(obj,name)
删除对象属性。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号