【Python3_基础系列_007】Python3-dict-字典
一、字典-dict
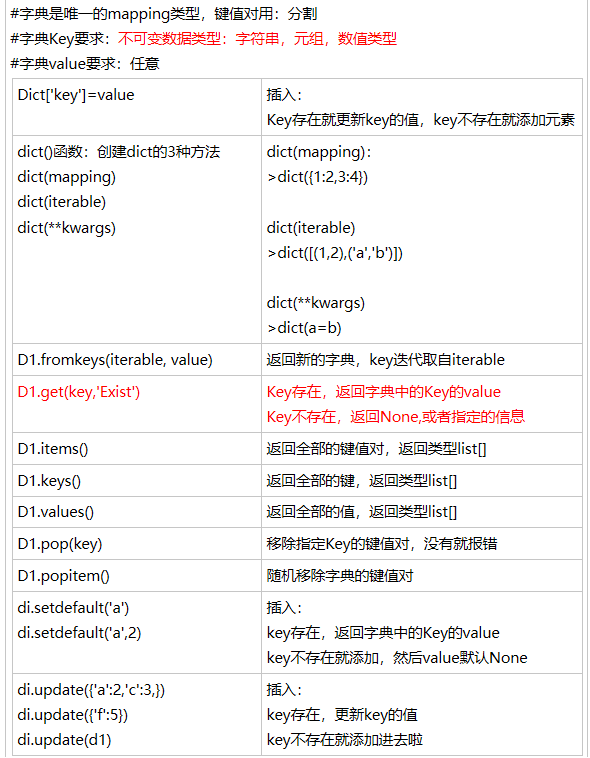
Python字典包含了以下内置方法:
| 序号 | 函数及描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | radiansdict.clear() 删除字典内所有元素 |
| 2 | radiansdict.copy() 返回一个字典的浅复制 |
| 3 | radiansdict.fromkeys() 创建一个新字典,以序列seq中元素做字典的键,val为字典所有键对应的初始值 |
| 4 | radiansdict.get(key, default=None) 返回指定键的值,如果值不在字典中返回default值 |
| 5 | key in dict 如果键在字典dict里返回true,否则返回false |
| 6 | radiansdict.items() 以列表返回可遍历的(键, 值) 元组数组 |
| 7 | radiansdict.keys() 以列表返回一个字典所有的键 |
| 8 | radiansdict.setdefault(key, default=None) 和get()类似, 但如果键不存在于字典中,将会添加键并将值设为default |
| 9 | radiansdict.update(dict2) 把字典dict2的键/值对更新到dict里 |
| 10 | radiansdict.values() 以列表返回字典中的所有值 |
| 11 | pop(key[,default]) 删除字典给定键 key 所对应的值,返回值为被删除的值。key值必须给出。 否则,返回default值。 |
| 12 | popitem() 随机返回并删除字典中的一对键和值(一般删除末尾对)。 |
二、面试题
1.用字典表示学生与数学,语文,英语成绩, 并计算平均分。
dict1 = {"语文":87,"数学":98,"英语":100}
print((dict1.values()))
result = 0;
for i in dict1.values():
result+=i;
print(result/3)
2.单词计数(Wordcount程序)
with open("words.txt",mode='r') as file: lines = file.readlines() result = {} print(lines) for line in lines: line = line.strip().replace('.', '').replace(',', '').replace('*', '').replace('-', '').replace('!', '') ###代码的优化,在分词统计之前先进行信息的过滤,依次是为了:去除2边空格,去除.,*-! 字符。 words = line.split(' ') for word in words: data = word.lower() if data not in result: result.setdefault(data, 1) else: result[data] += 1 print(result)
输出(文档的内容是 import this的内容):
{'the': 6, 'zen': 1, 'of': 3, 'python': 1, 'by': 1, 'tim': 1, 'peters': 1, '': 2, 'beautiful': 1, 'is': 10, 'better': 8, 'than': 8, 'ugly': 1, 'explicit': 1, 'implicit': 1, 'simple': 1, 'complex': 2, 'complicated': 1, 'flat': 1, 'nested': 1, 'sparse': 1, 'dense': 1, 'readability': 1, 'counts': 1, 'special': 2, 'cases': 1, "aren't": 1, 'enough': 1, 'to': 5, 'break': 1, 'rules': 1, 'although': 3, 'practicality': 1, 'beats': 1, 'purity': 1, 'errors': 1, 'should': 2, 'never': 3, 'pass': 1, 'silently': 1, 'unless': 2, 'explicitly': 1, 'silenced': 1, 'in': 1, 'face': 1, 'ambiguity': 1, 'refuse': 1, 'temptation': 1, 'guess': 1, 'there': 1, 'be': 3, 'one': 3, 'and': 1, 'preferably': 1, 'only': 1, 'obvious': 2, 'way': 2, 'do': 2, 'it': 2, 'that': 1, 'may': 2, 'not': 1, 'at': 1, 'first': 1, "you're": 1, 'dutch': 1, 'now': 2, 'often': 1, 'right': 1, 'if': 2, 'implementation': 2, 'hard': 1, 'explain': 2, "it's": 1, 'a': 2, 'bad': 1, 'idea': 3, 'easy': 1, 'good': 1, 'namespaces': 1, 'are': 1, 'honking': 1, 'great': 1, "let's": 1, 'more': 1, 'those': 1}
3.有两个列表 x = [1,2,3,'a','b','c'] y = ['a','b','c'] 找出x列表中在y 中也有的元素
>>> x = [1,2,3,'a','b','c']
>>> y = ['a','b','c']
>>> set (x) & set(y)
{'b', 'c', 'a'}
4.字典有几种插入键值的方法;如何访问这个字典的所有key和values。
dic = {}
dic['name'] = 'budong'
dic.setdefault('age',18)
dic.update({'sex':'male'}) #dict插值有三种方法
dict.keys()
dict.values()
三、dict类解析
>>> help(dict)
Help on class dict in module builtins:
class dict(object)
| dict() -> new empty dictionary
| dict(mapping) -> new dictionary initialized from a mapping object's
| (key, value) pairs
| dict(iterable) -> new dictionary initialized as if via:
| d = {}
| for k, v in iterable:
| d[k] = v
| dict(**kwargs) -> new dictionary initialized with the name=value pairs
| in the keyword argument list. For example: dict(one=1, two=2)
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __contains__(self, key, /)
| True if D has a key k, else False.
|
| __delitem__(self, key, /)
| Delete self[key].
|
| __eq__(self, value, /)
| Return self==value.
|
| __ge__(self, value, /)
| Return self>=value.
|
| __getattribute__(self, name, /)
| Return getattr(self, name).
|
| __getitem__(...)
| x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y]
|
| __gt__(self, value, /)
| Return self>value.
|
| __init__(self, /, *args, **kwargs)
| Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
|
| __iter__(self, /)
| Implement iter(self).
|
| __le__(self, value, /)
| Return self<=value.
|
| __len__(self, /)
| Return len(self).
|
| __lt__(self, value, /)
| Return self<value.
|
| __ne__(self, value, /)
| Return self!=value.
|
| __new__(*args, **kwargs) from builtins.type
| Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature.
|
| __repr__(self, /)
| Return repr(self).
|
| __setitem__(self, key, value, /)
| Set self[key] to value.
|
| __sizeof__(...)
| D.__sizeof__() -> size of D in memory, in bytes
|
| clear(...)
| D.clear() -> None. Remove all items from D.
|
| copy(...)
| D.copy() -> a shallow copy of D
|
| fromkeys(iterable, value=None, /) from builtins.type
| Returns a new dict with keys from iterable and values equal to value.
|
| get(...)
| D.get(k[,d]) -> D[k] if k in D, else d. d defaults to None.
|
| items(...)
| D.items() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's items
|
| keys(...)
| D.keys() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's keys
|
| pop(...)
| D.pop(k[,d]) -> v, remove specified key and return the corresponding value.
| If key is not found, d is returned if given, otherwise KeyError is raised
|
| popitem(...)
| D.popitem() -> (k, v), remove and return some (key, value) pair as a
| 2-tuple; but raise KeyError if D is empty.
|
| setdefault(...)
| D.setdefault(k[,d]) -> D.get(k,d), also set D[k]=d if k not in D
|
| update(...)
| D.update([E, ]**F) -> None. Update D from dict/iterable E and F.
| If E is present and has a .keys() method, then does: for k in E: D[k] = E[k]
| If E is present and lacks a .keys() method, then does: for k, v in E: D[k] = v
| In either case, this is followed by: for k in F: D[k] = F[k]
|
| values(...)
| D.values() -> an object providing a view on D's values
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data and other attributes defined here:
|
| __hash__ = None



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号