[ js ] 手写promise
class Ps { constructor(exector) { // 0执行中 1已完成 2已拒绝 this.state = 0; this.sucValue = null; this.errValue = null; this.sucCallbacks = []; this.errCallbacks = []; // 执行 const resolve = value => { if (this.state === 0) { this.state = 1; this.sucValue = value; this.sucCallbacks.forEach(cb => cb(this.sucValue)); } } const reject = value => { if (this.state === 0) { this.state = 2; this.errValue = value; this.errCallbacks.forEach(cb => cb(this.errValue)); } } try { exector(resolve, reject); } catch (err) { reject(err); } } then(onResolved, onRejected) { // 处理参数 onResolved = typeof onResolved === 'function' ? onResolved : value => value; onRejected = typeof onRejected === 'function' ? onRejected : error => error; // 使用queueMicrotask方法将回调函数放入任务队列,保证异步执行 // 返回promise对象是为了保证使用 .then 之后还能通过 .then 获取值, 如果单纯为了连续使用 .then, 可直接返回this // then() { return this } // 返回的新promise必须要调用 resolve/reject 方法, 否则会导致死锁 // 使用 onResolve/onReject 是为了把结果传递给 用户调用 .then 传递进来的回调函数 // resolve(onResolved(value)) 是为了下一次调用.then可以拿到返回值, 前提是上一次调用.then的回调,有返回值 return new Ps((resolve, reject) => { if (this.state === 1) { // 成功 queueMicrotask(() => { resolve(this.sucValue); }) } else if (this.state === 2) { // 失败 queueMicrotask(() => { reject(this.errValue); }) } else { // 初始化 this.sucCallbacks.push((v) => { queueMicrotask(() => { resolve(onResolved(v)) }); }); this.errCallbacks.push((v) => { queueMicrotask(() => { reject(onRejected(v)) }) }); } }) } // then方法的语法糖 catch(onRejected) { this.then(null, onRejected); } } const ps = new Ps((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => { const num = Math.random() > 0.5 return num > 0.5 ? resolve('success333') : reject('error444'); }, 1000); }) ps.then(res => { console.log('.then print success', res); // 如果这里不返回值, 那么下一个.then就拿不到结果 return 'success1 return to ' + res; }).then(res2 => { console.log('.then print success2', res2); // 如果这里不返回值, 那么下一个.then就拿不到结果 return 'success2 return to ' + res2; }).then(res3 => { console.log('.then print success3', res3); }).catch(err => { console.log('.catch print err', err); })
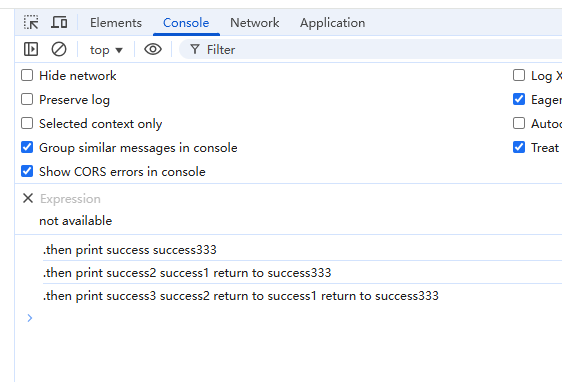
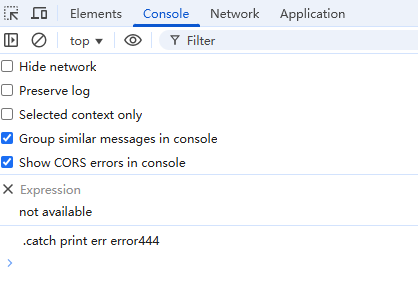
promise设计精妙的地方在于,所有的参数都是函数,所以最简单的理解就是,你给了一个异步函数让promise执行, 然后又给了一会回调让promise执行完成后调用, resolve和reject是promise给你定义的标识符,让用户自己调用,你自己告诉promise你的代码执行完成了,promise再执行你给的回调函数, 形成闭环
真正强大的地方还是 async 和 await 的等待机制
本想把生活活成一首诗, 时而优雅 , 时而豪放 , 结果活成了一首歌 , 时而不靠谱 , 时而不着调



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号