C++实验一
实验结论
2-28
第一种方法使用while

#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main(){ char i; cout<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select one:"<<endl; while(1){ cin>>i; if(i=='A') cout<<"数据已经增加"<<endl; else if(i=='D') cout<<"数据已经删除"<<endl; else if(i=='S') cout<<"数据已经排序"<<endl; else if(i=='Q') break; else cout<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select one:"<<endl; } return 0; }
第二种方法使用do-while

#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main(){ char i; cout<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select one:"<<endl; cin>>i; while(i!='Q'){ switch(i) { case 'A': cout<<"数据已经增加"<<endl; break; case 'D': cout<<"数据已经删除"<<endl; break; case 'S': cout<<"数据已经排序"<<endl; break; default: cout<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select one:"<<endl; } cout<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select one:"<<endl; cin>>i; } return 0; }
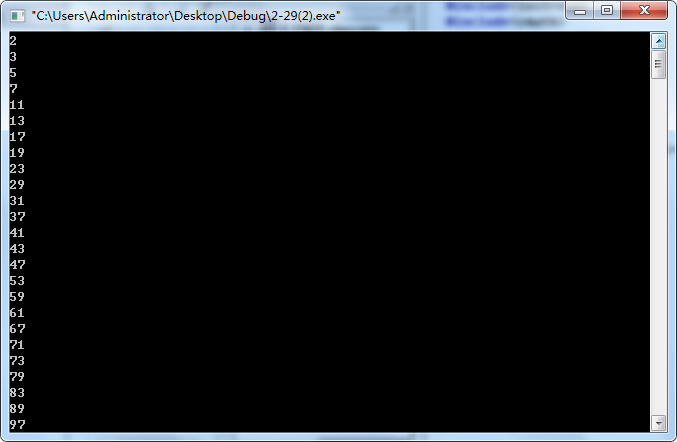
2-29
第一种使用while

#include<iostream> #include<cmath> using namespace std; int main() { int flag,i; int n=2; while(n<=100) {flag=1; for(i=2;i<=sqrt(n);i++) if(n%i==0) {flag=0; break; } if(flag==1) cout<<n<<endl; n++; } return 0; }
用do-while

#include<iostream> #include<cmath> using namespace std; int main() { int flag,i; int n=2; do {flag=1; for(i=2;i<=sqrt(n);i++) if(n%i==0) {flag=0; break; } if(flag==1) cout<<n<<endl; n++; } while(n<=100); return 0; }
使用for

#include<iostream> #include<cmath> using namespace std; int main() { int flag,i,n; for(n=2;n<=100;n++) {flag=1; for(i=2;i<=sqrt(n);i++) if(n%i==0) {flag=0; break; } if(flag==1) cout<<n<<endl; } return 0; }
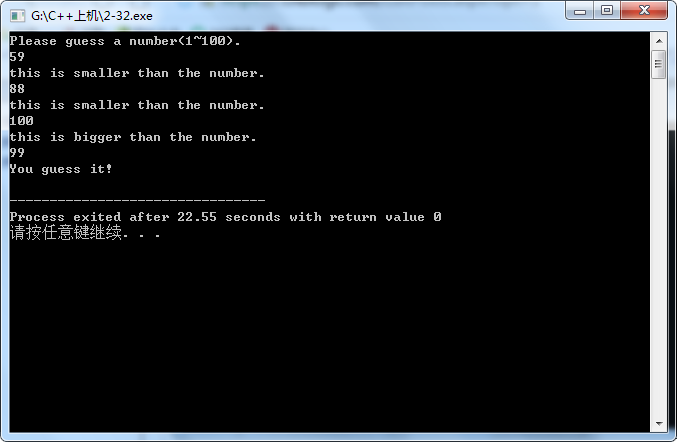
2-32
使用while

#include<iostream> #include<cmath> using namespace std; int main() {int a=99; int b; cout<<"Please guess a number(1~100)."<<endl; cin>>b; while(b!=99) {if(b<a) {cout<<"this is smaller than the number."<<endl; cin>>b; } else {cout<<"this is bigger than the number."<<endl; cin>>b; } } cout<<"You guess it!"<<endl; return 0; }
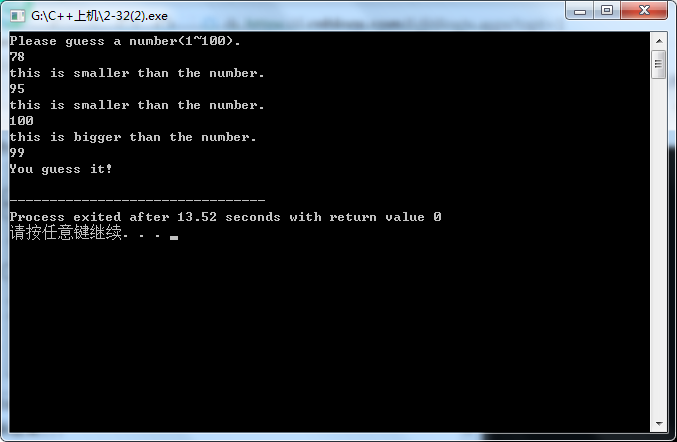
使用do-while

#include<iostream> #include<cmath> using namespace std; int main() {int a=99; int b; cout<<"Please guess a number(1~100)."<<endl; cin>>b; do {if(b<a) {cout<<"this is smaller than the number."<<endl; cin>>b; } else {cout<<"this is bigger than the number."<<endl; cin>>b; } } while(b!=99); cout<<"You guess it!"<<endl; return 0; }
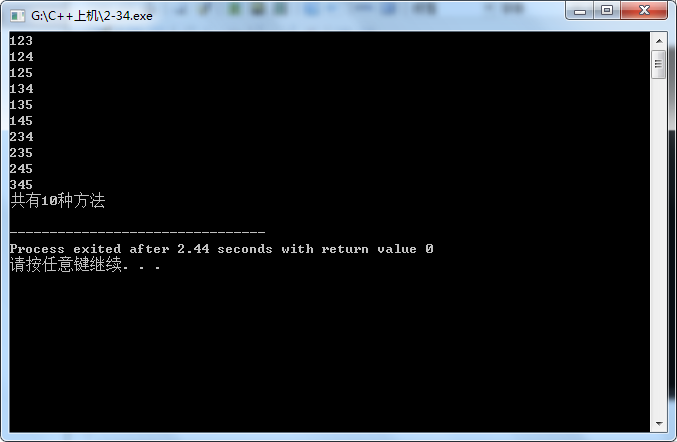
2-34

#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() {int i,j,k,all=0; for(i=1;i<=5;i++) { for(j=i+1;j<=5;j++) { for(k=j+1;k<=5;k++) { all++; cout<<i<<j<<k<<endl;}} } cout<<all<<endl; return 0; }
实验总结与体会
经过这次实验我了解到while、do-while、for三个虽然都是用于循环前三道题的主程序不变但是部分程序是需要更改的,还有需要注意的就是当do-while时放最后时需要跟一个分号。
而且在猜数字时不知道该如何使用随机数。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号