链表专题训练
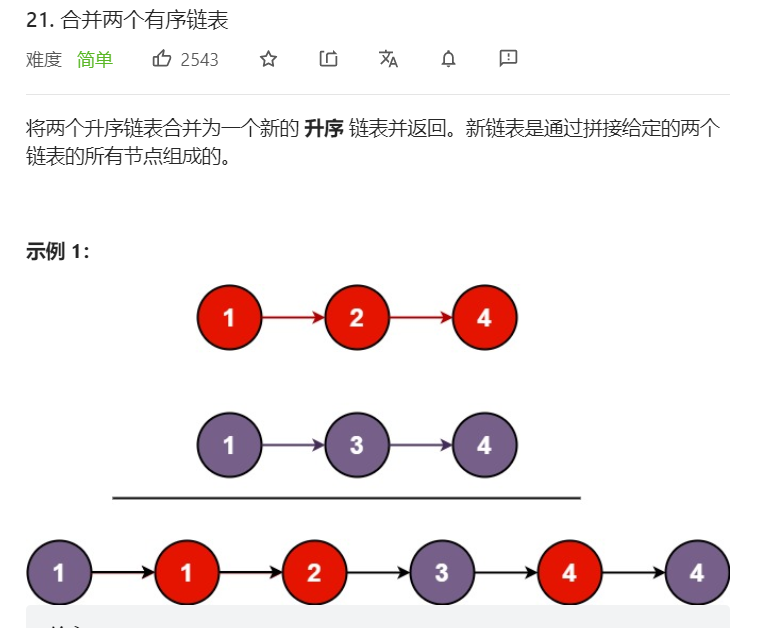
1、合并两个有序链表
递归:判断两个节点值大小并递归下一次,递归出口为当节点为空时
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, list1: Optional[ListNode], list2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not list1:
return list2
if not list2:
return list1
if list1.val<list2.val:
list1.next=self.mergeTwoLists(list1.next,list2)
return list1
if list1.val>list2.val:
list2.next=self.mergeTwoLists(list2.next,list1)
return list2
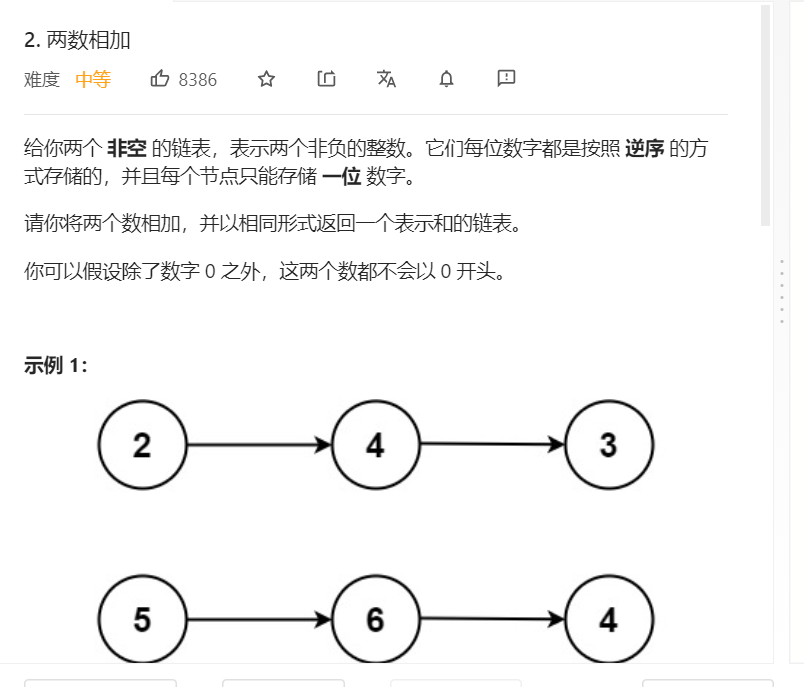
2、两数相加
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
pre=ListNode(0)
cur=pre
a=0
while l1!=None or l2!=None:
x=l1.val if l1 else 0
y=l2.val if l2 else 0
s=x+y+a
a=1 if s>9 else 0
s=s%10
cur.next=ListNode(s)
cur=cur.next
l1=l1.next if l1 else None
l2=l2.next if l2 else None
if a:
cur.next=ListNode(a)
return pre.next
3、回文链表
关i键:有两种解法,第一种创建一个数组复制链表的值然后判断数组是否回文,此种方法消耗O(n)空间;第二种解法用快慢指针,慢指针一次走一步,快指针一次走两步,这样当快指针走到空的的时候慢指针刚好在中间位置
class Solution:
#方法一
def isPalindrome(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
r=[]
h=head
while h!=None:
r.append(h.val)
h=h.next
if r==r[::-1]:
return True
return False
#方法二:快慢指针
def isPalindrome(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
slow=head
fast=head
half_head=self.half(slow,fast)
rev_half=self.reverse(half_head)
h=head
while h!=None and rev_half!=None:
if h.val!=rev_half.val:
return False
h=h.next
rev_half=rev_half.next
return True
def half(self,slow,fast):
try:
while slow.next!=None and fast.next.next!=None:
slow=slow.next
fast=fast.next.next
except:
pass
return slow
def reverse(self,half_head):
h=half_head
p=None
while h!=None:
t=h.next
h.next=p
p=h
h=t
return p

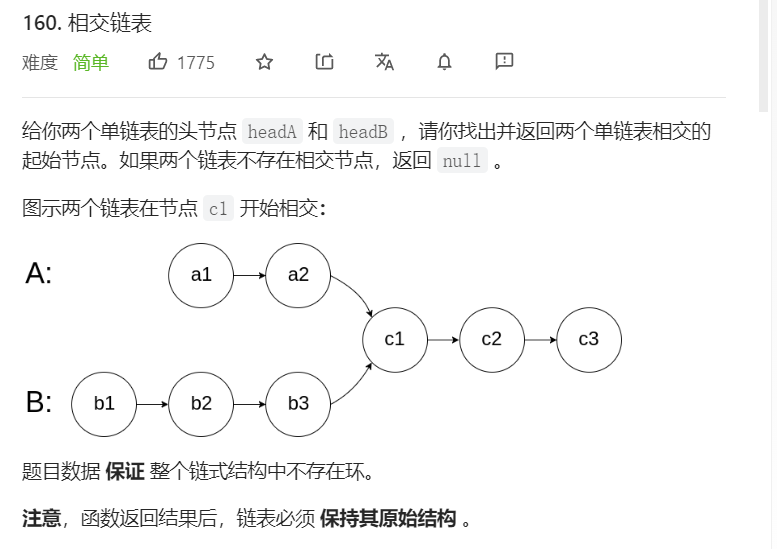
4、相交链表
关键:找交点这种题多涉及循环判断,两个链表存在距离差,距离差在前半部分,后半部分长度相等,则两个链表同时遍历时短距离链表先走到链尾,可以使他再次指向长链表链头,当长链表走到链尾时使他指向短链表链头,这样就可以消除距离差,当两链表节点相同时即找到了交点
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
p1=headA
p2=headB
while p1!=p2: #因为不管是不是None都要循环,所以循环条件是两者是否相等而不是是否为空
p1=p1.next if p1 else headB #一行判断可以提升效率
p2=p2.next if p2 else headA
return p1
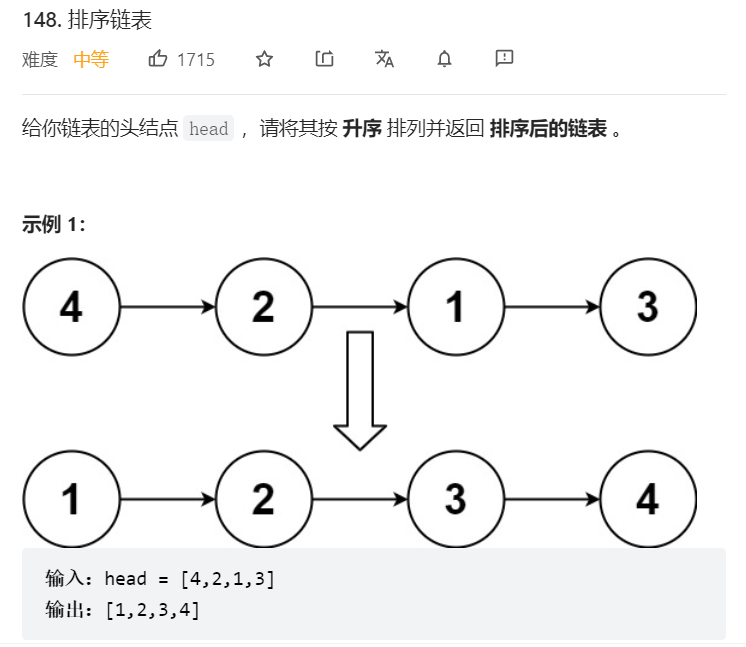
5、排序链表
关键:取值—>排序—>赋值
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head:
return None
r=[]
h=head
while h!=None:
r.append(h.val)
h=h.next
h2=head
for i in sorted(r):
h2.val=i
h2=h2.next
return head
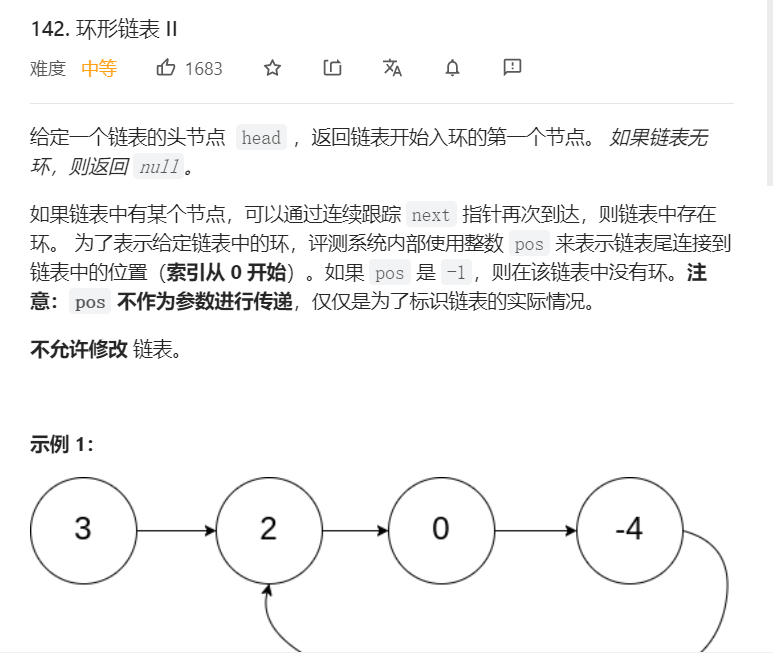
6、环形链表
关键:遍历链表,判断当前链表是否被遍历过
class Solution:
def detectCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
r=set()
h=head
while h!=None:
if h in r:
return h
r.add(h)
h=h.next
return None
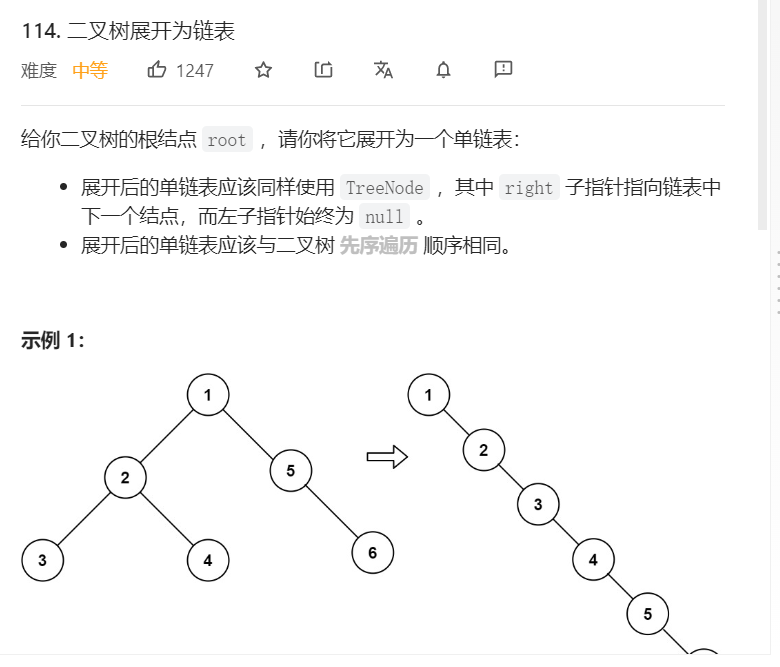
7、二叉树展开为链表
消耗时间和空间
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.r=[]
def flatten(self, root: TreeNode) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead.
"""
if root==None:
return
self.r.append(root.val)
self.flatten(root.left)
self.flatten(root.right)
for i in self.r[1:]:
root.left=None
root.right=TreeNode(i)
root=root.right
8、删除链表倒数第n个结点
关键:设置头节点的细节很重要啊!当需要返回当前链表时一般给当前链表设置一个pre节点的next指向当前head,然后处理完后返回pre.next
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:
l=0
h=head
while h!=None:
l+=1
h=h.next
pre=ListNode(0,head)
h2=pre
for i in range(1,l-n+1): #索引和题目描述一致,从1开始
h2=h2.next
h2.next=h2.next.next
return pre.next


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号