实验1
任务一:
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> template<typename T> void output(const T &c); void test1(); void test2(); void test3(); int main() { std::cout << "测试1: \n"; test1(); std::cout << "\n测试2: \n"; test2(); std::cout << "\n测试3: \n"; test3(); } template <typename T> void output(const T &c) { for(auto &i : c) std::cout << i << ' '; std::cout << '\n'; } void test1() { using namespace std; string s0{"0123456789"}; cout << "s0 = " << s0 << endl; string s1(s0); reverse(s1.begin(), s1.end()); cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl; string s2(s0.size(), ' '); reverse_copy(s0.begin(), s0.end(), s2.begin()); cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl; } void test2() { using namespace std; vector<int> v0{2, 0, 4, 9}; cout << "v0: "; output(v0); vector<int> v1{v0}; reverse(v1.begin(), v1.end()); cout << "v1: "; output(v1); vector<int> v2{v0}; reverse_copy(v0.begin(), v0.end(), v2.begin()); cout << "v2: "; output(v2); } void test3() { using namespace std; vector<int> v0{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; cout << "v0: "; output(v0); vector<int> v1{v0}; rotate(v1.begin(), v1.begin()+1, v1.end()); cout << "v1: "; output(v1); vector<int> v2{v0}; rotate(v2.begin(), v2.begin()+2, v2.end()); cout << "v2: "; output(v2); vector<int> v3{v0}; rotate(v3.begin(), v3.end()-1, v3.end()); cout << "v3: "; output(v3); vector<int> v4{v0}; rotate(v4.begin(), v4.end()-2, v4.end()); cout << "v4: "; output(v4); }
运行结果截图: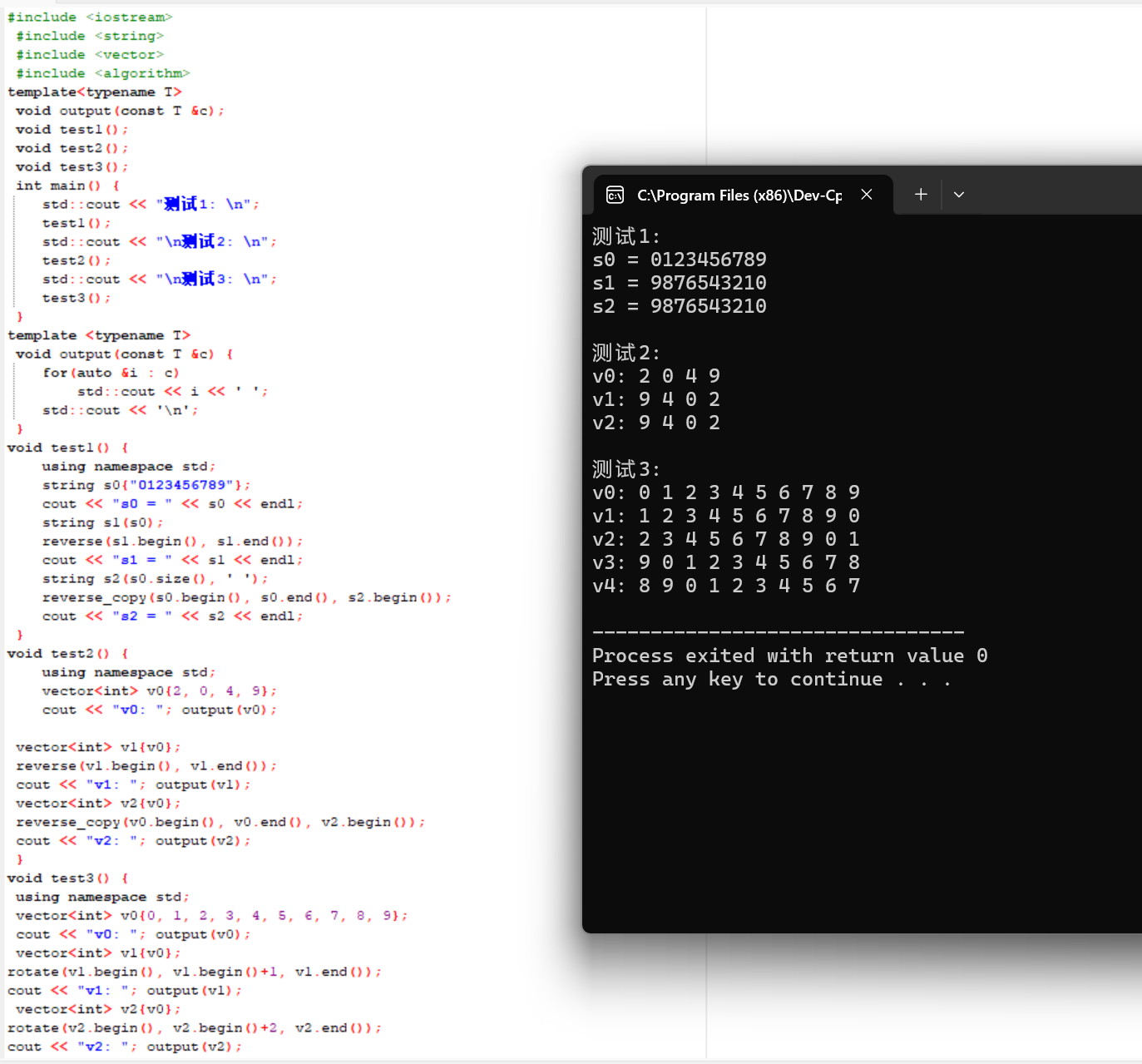
问题1:reverse会改变原始数据,不需要重新分配内存,reverse_copy不会改变原始数据,是将反转结果复制到新的目标范围中,需要重新分配内存
问题2:rotate通过将序列在 middle 处分割并交换前后两部分来实现"循环移位"的效果,三个参数分别代表要旋转范围的开头,旋转后新序列的第一个元素,要旋转范围的末尾
任务2:
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <numeric> #include <iomanip> #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> template<typename T> void output(const T &c); int generate_random_number(); void test1(); void test2(); int main() { std::srand(std::time(0)); std::cout << "测试1: \n"; test1(); std::cout << "\n测试2: \n"; test2(); } template <typename T> void output(const T &c) { for(auto &i: c) std::cout << i << ' '; std::cout << '\n'; } int generate_random_number() { return std::rand() % 101; } void test1() { using namespace std; vector<int> v0(10); generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), generate_random_number); cout << "v0: "; output(v0); vector<int> v1{v0}; sort(v1.begin(), v1.end()); cout << "v1: "; output(v1); vector<int> v2{v0}; sort(v2.begin()+1, v2.end()-1); cout << "v2: "; output(v2); } void test2() { using namespace std; vector<int> v0(10); generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), generate_random_number); cout << "v0: "; output(v0); auto min_iter = min_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); auto max_iter = max_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); cout << "最小值: " << *min_iter << endl; cout << "最大值: " << *max_iter << endl; auto ans = minmax_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); cout << "最小值: " << *(ans.first) << endl; cout << "最大值: " << *(ans.second) << endl; double avg1 = accumulate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), 0.0) / v0.size(); cout << "均值: " << fixed << setprecision(2) << avg1 << endl; sort(v0.begin(), v0.end()); double avg2 = accumulate(v0.begin()+1, v0.end()-1, 0.0) / (v0.size()-2); cout << "去掉最大值、最小值之后,均值: " << avg2 << endl; }
运行结果截图: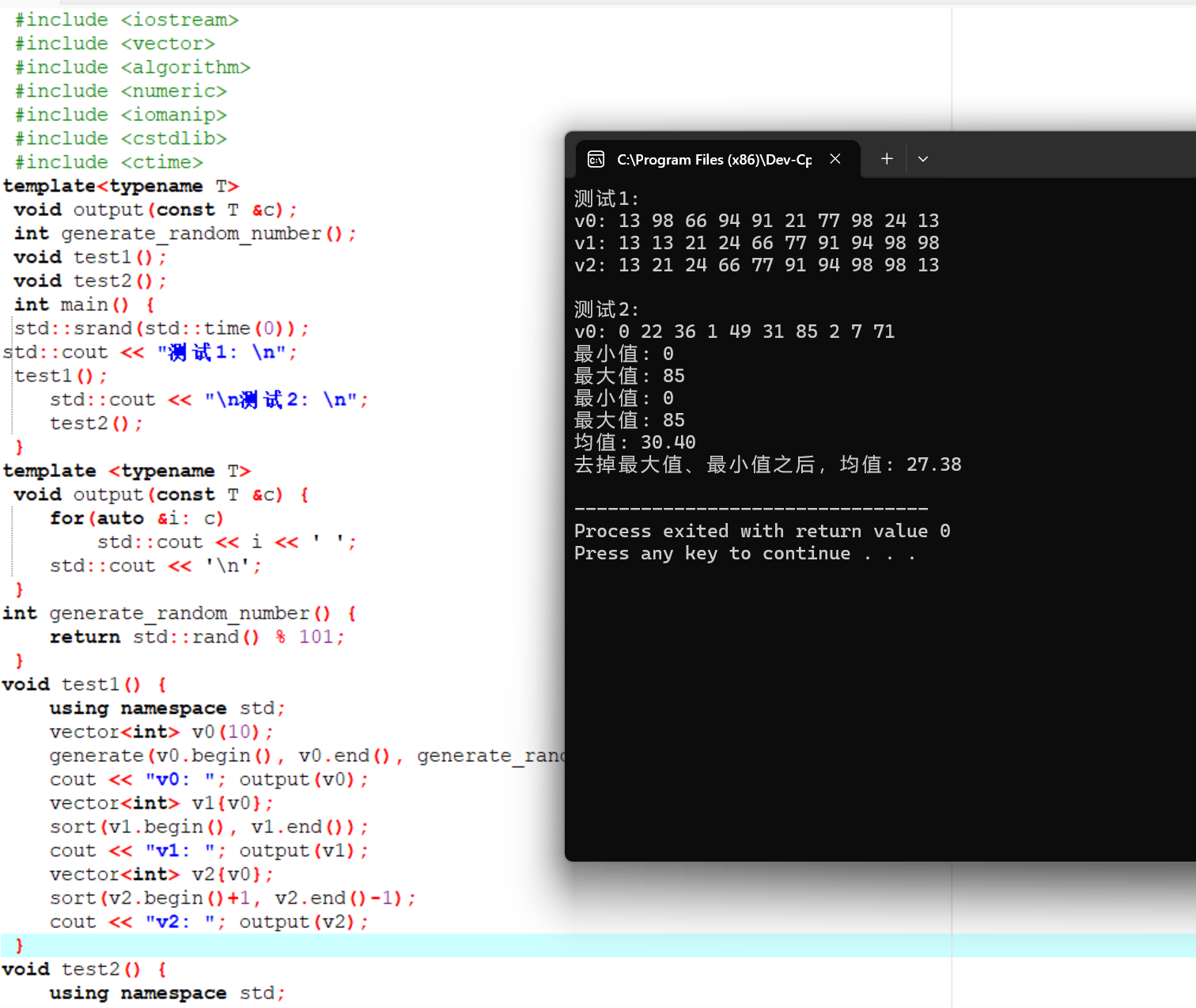
问题1:generate的作用是用提供的函数反复调用来生成新值,并用这些新值覆盖指定范围内的所有元素。
问题2:minmax_element 的主要优势在于 效率,它比分别调用 min_element 和 max_element 要快得多。
问题3:对于简单、一次性、需要捕获上下文的逻辑,使用 Lambda 表达式,对于复杂、可重用、需要测试的逻辑,使用 自定义函数
任务3:
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <cctype> unsigned char func(unsigned char c); void test1(); void test2(); int main() { std::cout << "测试1: 字符串大小写转换\n"; test1(); std::cout << "\n测试2: 字符变换\n"; test2(); } unsigned char func(unsigned char c) { if(c == 'z') return 'a'; if(c == 'Z') return 'A'; if(std::isalpha(c)) return static_cast<unsigned char>(c+1); return c; } void test1() { std::string s1{"Hello World 2049!"}; std::cout << "s1 = " << s1 << '\n'; std::string s2; for(auto c: s1) s2 += std::tolower(c); std::cout << "s2 = " << s2 << '\n'; std::string s3; for(auto c: s1) s3 += std::toupper(c); std::cout << "s3 = " << s3 << '\n'; } void test2() { std::string s1{"I love cosmos!"}; std::cout << "s1 = " << s1 << '\n'; std::string s2(s1.size(), ' '); std::transform(s1.begin(), s1.end(), s2.begin(), func); std::cout << "s2 = " << s2 << '\n'; }
运行结果截图: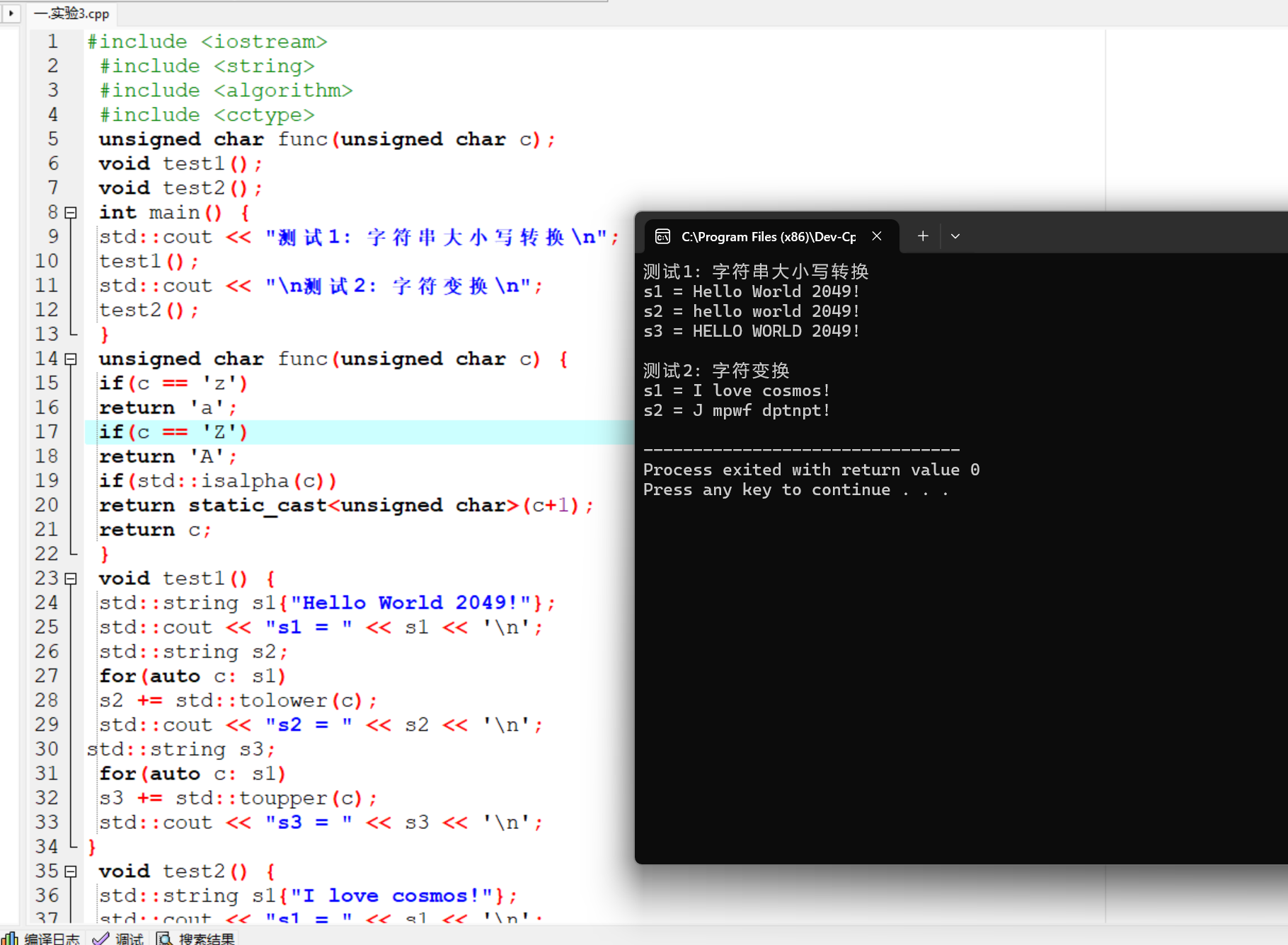
问题1:func的功能是将字母后移一位
问题2:tolower的功能是将大写字母转换为对应的小写字母,toupper的功能是将小写字母转换为对应的大写字母
问题3:第一个参数作用是输入范围的起始位置,第二个参数作用是输入范围的结束位置,第三个参数作用是输出目标的起始位置,第四个参数作用是操作函数,s2.begin()不会改变s1中的数据,改成s1.begin()会改变s1中的数据
任务4:
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> bool is_palindrome(const std::string &s); bool is_palindrome_ignore_case(const std::string &s); int main() { using namespace std; string s; while(cin >> s) { cout << boolalpha << "区分大小写: " << is_palindrome(s) << "\n" << "不区分大小写: " << is_palindrome_ignore_case(s) << "\n\n"; } } bool is_palindrome(const std::string &s) { if (s.empty()) return true; std::string s2(s.size(), ' '); reverse_copy(s.begin(), s.end(), s2.begin()); if(s==s2) return true; else return false; } bool is_palindrome_ignore_case(const std::string &s) { if (s.empty()) return true; std::string s1; for(auto c: s) s1+= std::tolower(c); std::string s2(s1.size(), ' '); reverse_copy(s1.begin(), s1.end(), s2.begin()); if(s1==s2) return true; else return false; }
运行结果截图: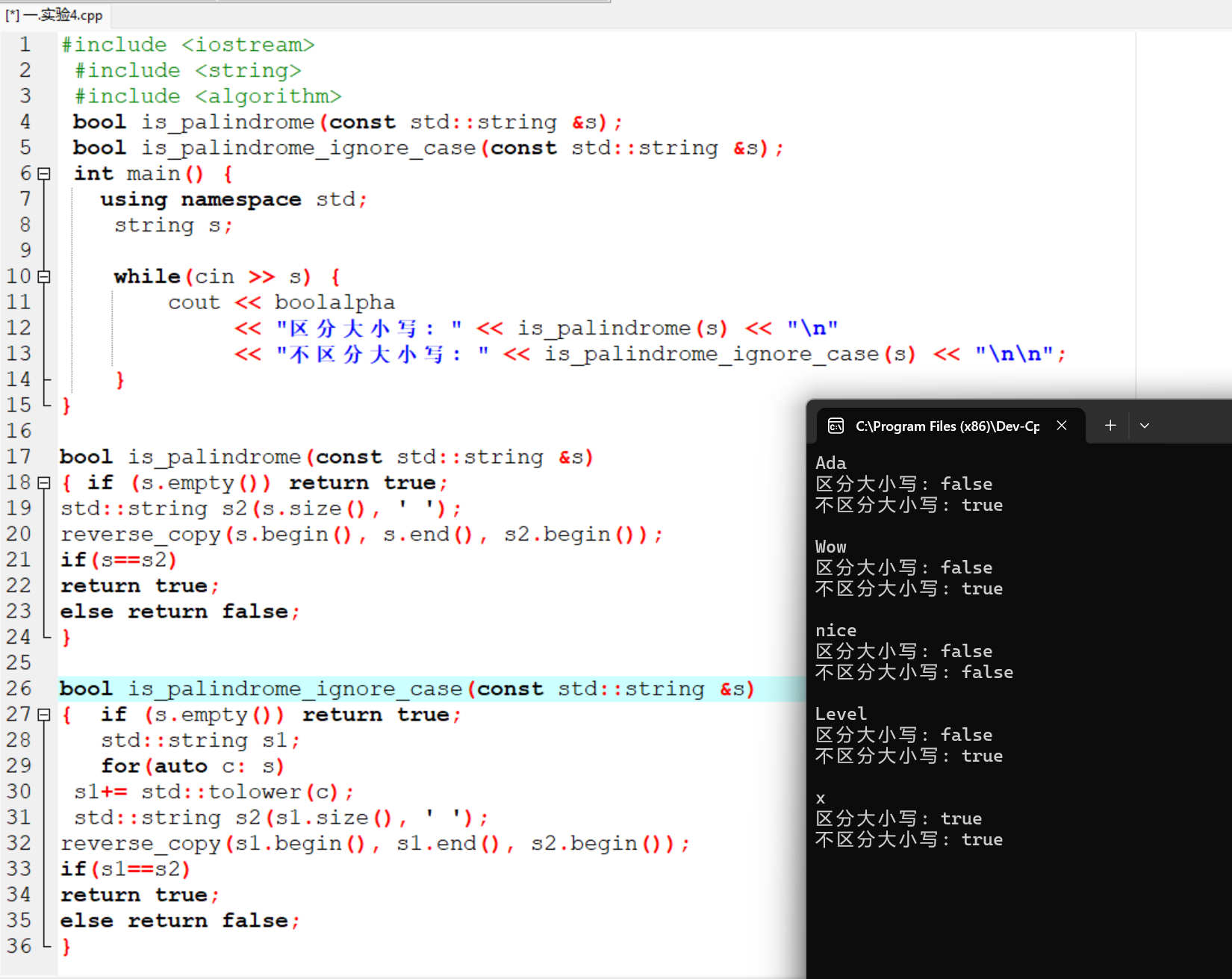
问题回答:将 cin >> s 改为 getline(cin, s)
任务5:
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <algorithm> std::string dec2n(int x, int n = 2); int main() { int x; while(std::cin >> x) { std::cout << "十进制: " << x << '\n' << "二进制: " << dec2n(x) << '\n' << "八进制: " << dec2n(x, 8) << '\n' << "十二进制: " << dec2n(x, 12) << '\n' << "十六进制: " << dec2n(x, 16) << '\n' << "三十二进制: " << dec2n(x, 32) << "\n\n"; } } std::string dec2n(int x, int n) { if (x == 0) { return "0"; } if (n < 2 || n > 36) { return "ERROR"; } std::string result; int num = x; const char digits[] = "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"; while (num > 0) { int remainder = num % n; result += digits[remainder]; num /= n; } std::reverse(result.begin(), result.end()); return result; }
运行结果截图: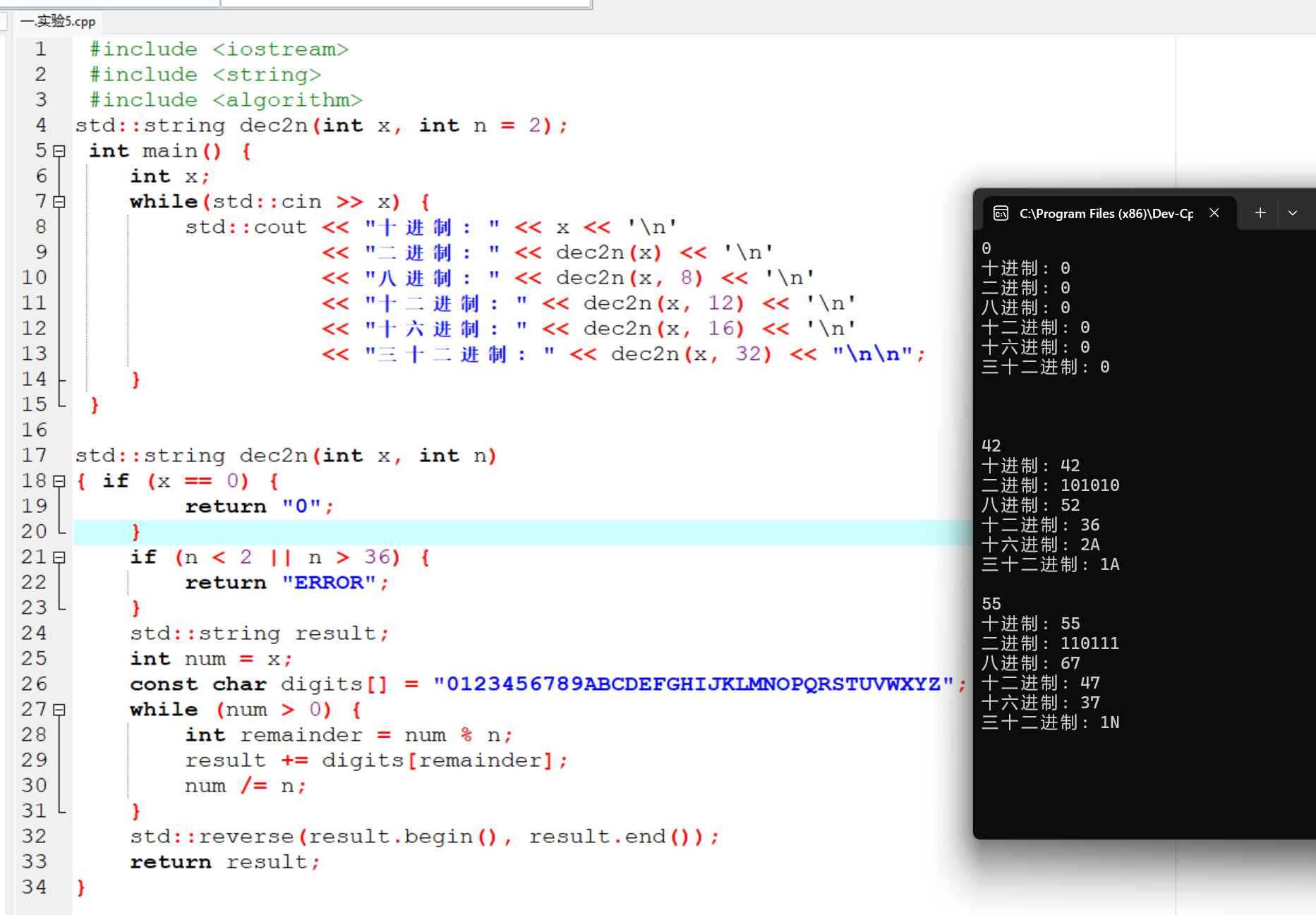
任务6:
#include <iostream> #include <string> int main() { const std::string alphabet0= "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"; std::cout<<" "; for(int i=0;i<26;i++) {std::cout<< alphabet0[i] <<" "; } std::cout << std::endl; std::string alphabet; for(auto c: alphabet0) alphabet+= std::toupper(c); for (int j = 1; j <= 26; j++) { if (j < 10) { std::cout << " "; } std::cout << j<<" "; for (int k = 0; k < 26; k++) { int new_pos = (k + j) % 26; std::cout << alphabet[new_pos]<<" "; } std::cout << std::endl; } return 0; }
运行结果截图: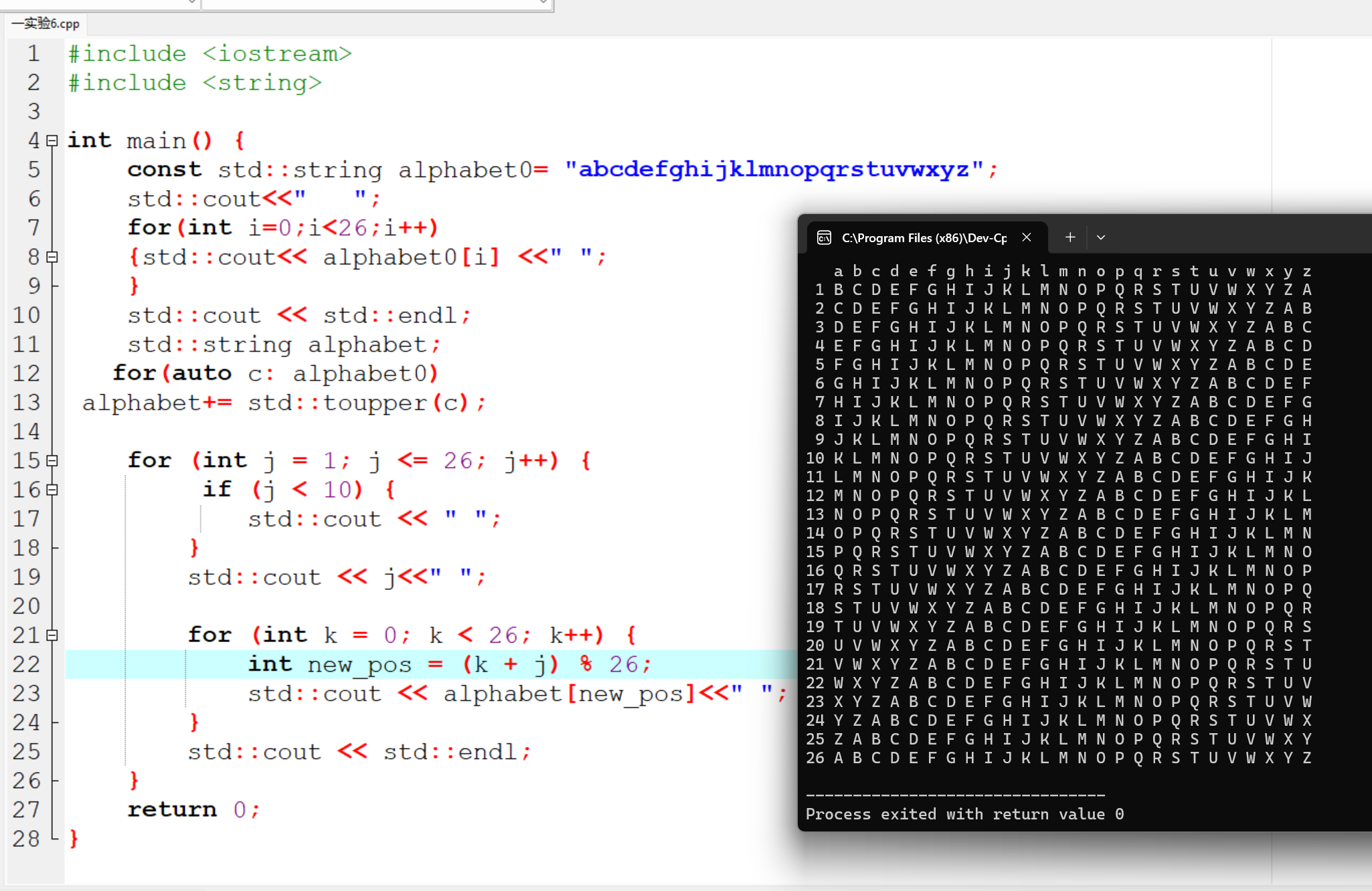
任务7:
#include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> #include <iomanip> int main() { srand(time(0)); int correctCount = 0; const int totalQuestions = 10;for (int i = 1; i <= totalQuestions; i++) { int num1 = rand() % 10 + 1; int num2 = rand() % 10 + 1; int op = rand() % 4; char opChar; int correctAnswer; int userAnswer; switch (op) { case 0: opChar = '+'; correctAnswer = num1 + num2; break; case 1: opChar = '-'; if (num1 < num2) { std::swap(num1, num2); } correctAnswer = num1 - num2; break; case 2: opChar = '*'; correctAnswer = num1 * num2; break; case 3: opChar = '/'; if (num1 % num2 != 0) { do { num2 = rand() % 9 + 1; } while (num1 % num2 != 0); } correctAnswer = num1 / num2; break; } std::cout << num1 << " " << opChar << " " << num2 << " = "; std::cin >> userAnswer; if (userAnswer == correctAnswer) { correctCount++; } } double accuracy = (static_cast<double>(correctCount) / totalQuestions) * 100; std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2); std::cout << "\n正确率:" << accuracy << "%" << std::endl; return 0; }
运行结果截图: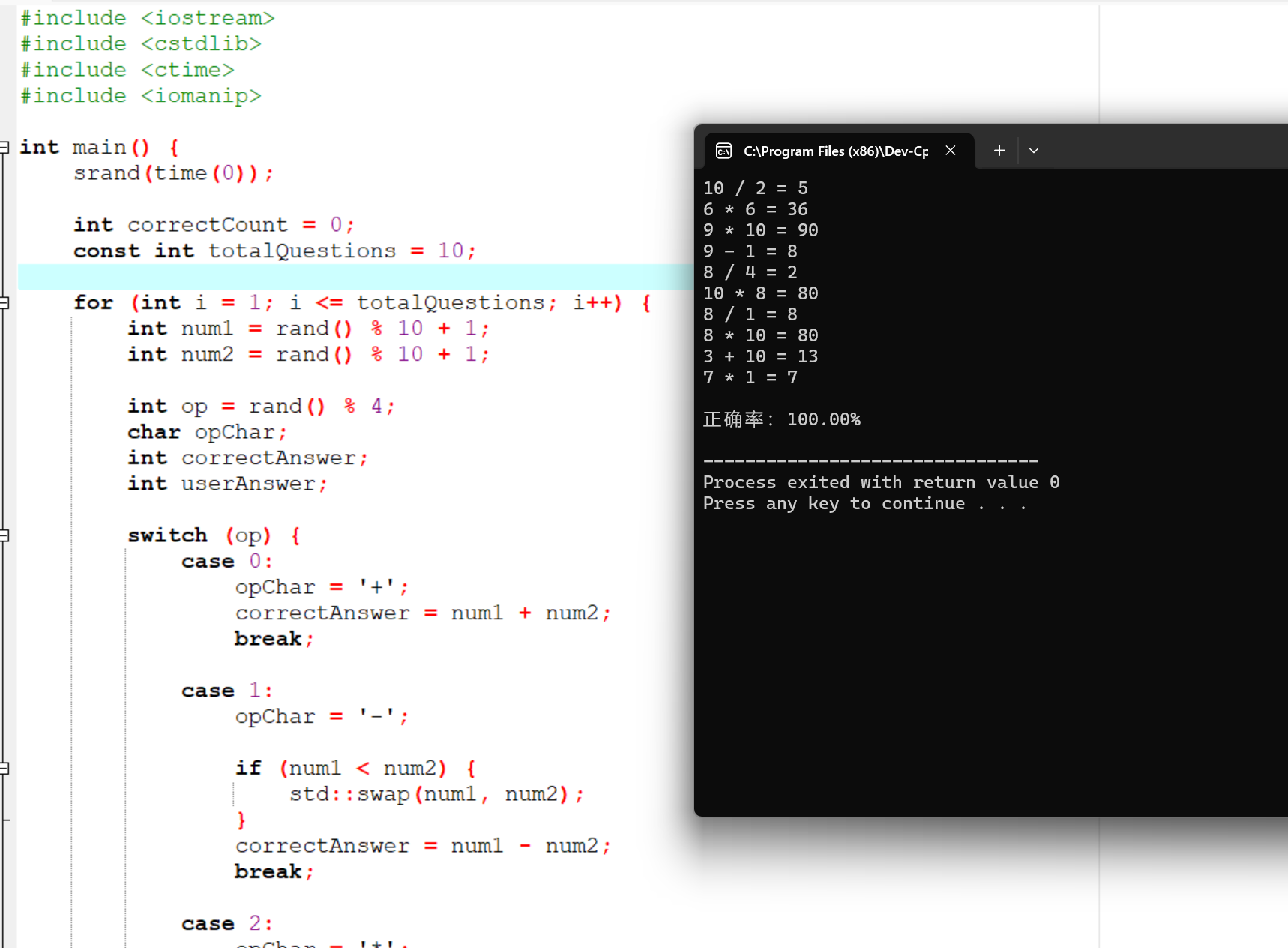



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号