3递归与分治
三递归与分治法及实例
1 Fibonacci数列
- 无穷数列1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34,55,…
public class Fibonacci1 {
public static int fibonacci(int n){
if (n<=1)
return 1;
return fibonacci(n-1)+fibonacci(n-2);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(fibonacci(5));
}
}
2 整数划分问题
题目
- 将正整数n表示成一系列正整数之和:n=m1+m2+...mi;其中mi为正整数,并且1<=m1<=mi<=n;{m1,m2,..mi}为n的一个划分。如果{m1,m2,....mi}中的最大值不超过m,即max{m1,m2,...mi}<=m,则称它属于n的一个m划分
- 正整数n的不同的划分个数称为正整数n的划分数q(n),目标求正整数n的不同划分个数q(n)
- 例如:6的划分:6;5+1;4+2;4+1+1;3+3;3+2+1;3+1+1+1;2+2+2;2+2+1+1;2+1+1+1+1;1+1+1+1+1+1;
思路:根据n和m的关系,考虑以下几种情况:
-
(1)当n=1时,不论m的值为多少(m>0),只有一种划分即{1};
-
(2)当m=1时,不论n的值为多少,只有一种划分即n个1,
-
(3)当n=m时,根据划分中是否包含n,可以分为两种情况:
-
- (a)划分中包含n的情况,只有一个即{n};
- (b)划分中不包含n的情况,这时划分中最大的数字也一定比n小,即n的所有(n-1)划分。 因此 q(n,n) =1 + q(n,m-1);
-
(4)当n<m时,由于划分中不可能出现负数,因此就相当于q(n,n);
-
(5)但n>m时,根据划分中是否包含最大值m,可以分为两种情况:
-
- (a)划分中包含m的情况,即{m, {x1,x2,...xi}}, 其中{x1,x2,... xi} 的和为n-m,因此这情况下为q(n-m,m)
- (b)划分中不包含m的情况,则划分中所有值都比m小,即n的(m-1)划分,个数为q(n,m-1);因此 q(n, m) = q(n-m, m)+q(n,m-1);
结论
- q(n, m) = 1; (n=1 or m=1)
- q(n,m) = q(n, n); (n<m)
- 1+ q(n, m-1); (n=m)
- q(n-m,m)+q(n,m-1); (n>m)
public class ZhenShuHuaFen2 {
public static int huafen(int n,int m){
if (n==1 || m==1)
return 1;
else if (n<m)
return huafen(n,n);
else if (n==m)
return 1+huafen(n,m-1);
else
return huafen(n-m,m)+huafen(n,m-1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result=huafen(6,6);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
3 汉诺塔问题
问题
- 设a,b,c是3个塔座
- 开始时,在塔座a上有一叠共n个圆盘,这些圆盘自下而上,由大到小地叠在一起。各圆盘从小到大编号为1,2,…,n
- 要求将塔座a上的圆盘移到塔座b上,并仍按同样顺序叠置。在移动圆盘时应遵守以下移动规则:
- 每次只能移动1个圆盘
- 任何时刻都不允许将较大的圆盘压在较小的圆盘之上
- 在满足移动规则1和2的前提下,可将圆盘移至a,b,c中任一塔座上
public class Hanoi3 {
public static void move(String start,String end){
System.out.println(start+"--->"+end);
}
public static void hanoi(int n,String a,String b,String c){
if (n>0){
hanoi(n-1,a,c,b);
move(a,b);
hanoi(n-1,c,b,a);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a="a";
String b="b";
String c="c";
hanoi(3,a,b,c);
}
}
4递归式的解法
4.1代换法
- 先猜测解的形式,再数学归纳法证明
- 只适用于解的形式很容易猜的情形
- 如何猜测则需要经验
- 例:T(n)=2T(n/2)+n; T(n)=O(nlgn)
- T(n)=T(n/2)+1; T(n)=O(lgn)
4.2递归树方法
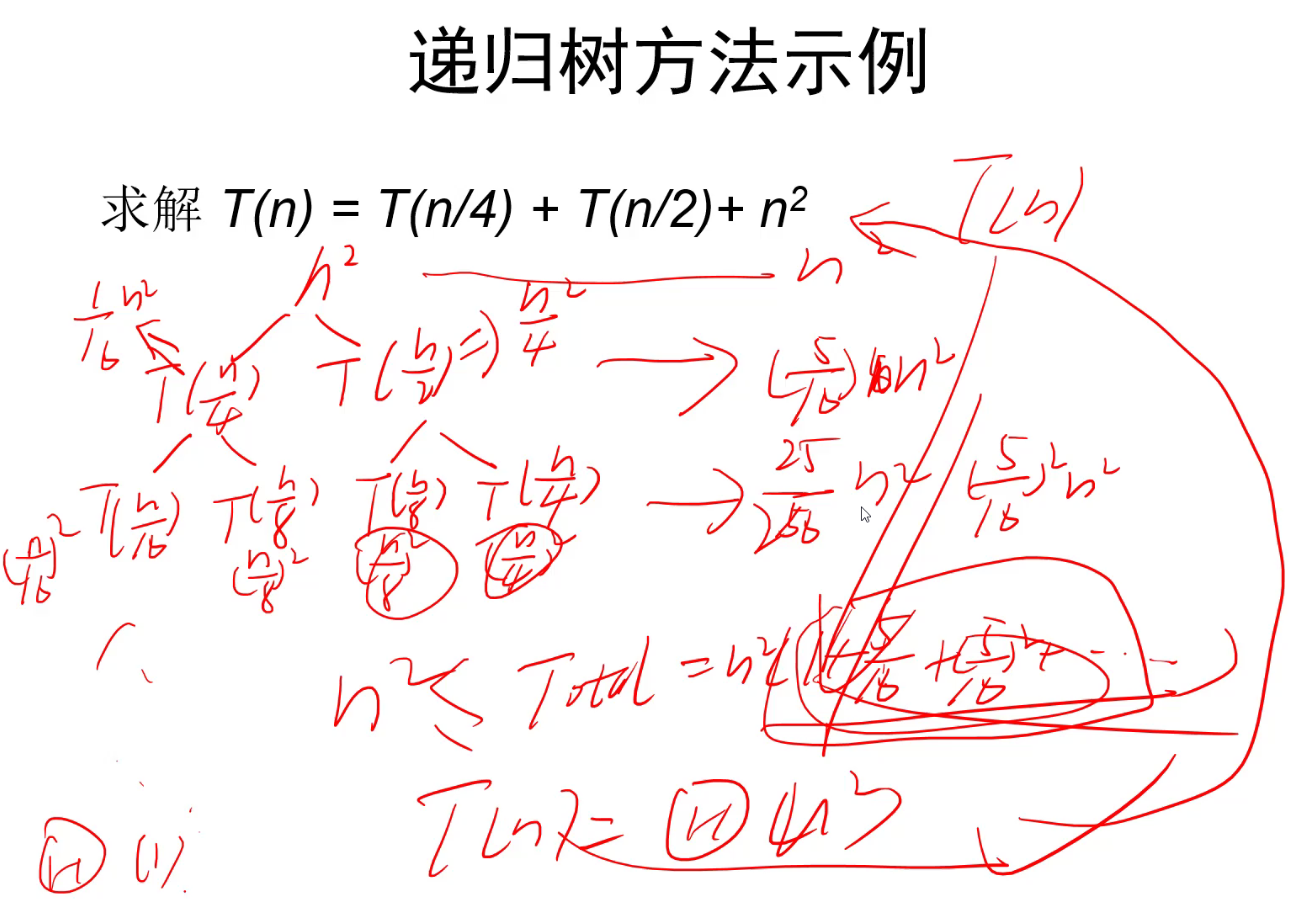
4.3主方法


后面两个不适用
5分治法
基本策略
- 分解(Divide):将原问题分解为子问题
- 解决(Conquer):求解子问题
- 合并(Combine):组合子问题的解得到原问题的解
适用条件
- 问题的规模缩小到一定程度就可以容易地解决
- 问题可以分解为若干个规模较小的相同问题,即该问题具有最优子结构性质
- 基于子问题的解可以合并为原问题的解
- 问题所分解出的各个子问题是相互独立的,即子问题之间不包含公共的子问题
平衡
- 使子问题规模尽量接近的做法,就是平衡
- 在使用分治法和递归时,要尽量把问题分成规模相等,或至少是规模相近的子问题以提高算法的效率
6二分搜索
public class ErFenChaZhao6 {
public static int binarySearch(int[] a,int r){
int start=0;
int end=a.length-1;
int mid=(end-start)/2;
int result=-1;
while (start<end){
if (r>a[mid])
start=mid+1;
else if (r<a[mid])
end=mid-1;
else{
result=mid;
return result;
}
mid=(end-start)/2;
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a=new int[]{1,3,5,7,9,11,222};
int r=3;
System.out.println(binarySearch(a,r));
}
}
7 求a ^ n
public class ancifang7 {
public static int an(int a,int n){
if (n==1)
return a;
if (n%2==0)
return an(a,n/2)*an(a,n/2);
if (n%2!=0)
return an(a,(n-1)/2)*an(a,(n-1)/2)*a;
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result=an(2,3);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
8 快速排序
概述
- 快速排序也属于交换排序
- 思想:在每一轮挑选一个基准元素,并让其他比它的元素移动到数列一边,比它小的元素移动到数列的另一边,从而把数列拆解成两个部分
- 总体时间复杂度是O(nlogn),空间复杂度是O(logn),是不稳定的
基准元素的选择
- 基准元素pivot,在分治过程中,以基准元素为中心,把其他元素移动到它的左右两边
- 最简单的方式就是选择数列的第一个元素
- 这样如果数列本身逆序就会形成极端情况,时间复杂读就变成O(n^2)
- 更好的是我们随机选择一个元素作为基准元素,并且让基准元素和数列首元素交换位置
public static void quickSort(int[] arr,int startIndex,int endIndex){
//递归结束条件:startIndex大于或等于endIndex
if (startIndex>=endIndex){
return;
}
//得到基准元素位置
int pivotIndex=partition(arr,startIndex,endIndex);
quickSort(arr,startIndex,pivotIndex-1);
quickSort(arr,pivotIndex+1,endIndex);
}
//分治,双边循环法
private static int partition(int[] arr,int startIndex,int endIndex){
//取第一个位置,(也可以选择随机位置)的元素作为基准元素
int pivot=arr[startIndex];
int left=startIndex;
int right=endIndex;
while (left!=right){
//控制right指针比较并左移
while (left<right && arr[right]>pivot){
right--;
}
//控制left指针比较并右移
while (left<right && arr[left]<=pivot){
left++;
}
//交换left和right指针所指向的元素
if (left<right){
int temp=arr[left];
arr[left]=arr[right];
arr[right]=temp;
}
}
//pivot和指针重合点交换
arr[startIndex]=arr[left];
arr[left]=pivot;
return left;
}
9 矩阵乘法
- 直接解法时间复杂度为Θ(n3),直接分治的时间复杂度也是Θ(n3)并不比直接计算好
- Strassen矩阵乘法分析时间复杂度也是Θ(n^2.81)


10 最大元,最小元
- 给定n个数据元素,找出其中的最大元和最小元
- 直接解法:逐个找,用n-1次比较来找出最大元,再用n-2次比较来找出最小元,比较次数(基本运算)为2n-3次
- 使用分治法
public class ZuiDaYuan10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] Max = new int[2];//由于Java 值传递 的原因,改为数组
int[] Min = new int[2];
int a[] = { 0, 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 2, 4, 19, 45, 23 };// 不用0位置
findMaMi(a, Max, Min, 1, 11);
System.out.println("Max=" + Max[1] + " Min=" + Min[1]);
}
public static void findMaMi(int[] a, int[] Max, int[] Min, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) {// 只有一个元素,大小值一样
Max[1] = Min[1] = a[r];
} else {
if (l == r - 1) { // 只有两个元素
if (a[l] > a[r]) {
Max[1] = a[l];
Min[1] = a[r];
} else {
Max[1] = a[r];
Min[1] = a[l];
}
} else {// 有多个元素
int hMax[] = { 0, 0 };
int hMin[] = { 0, 0 };
int m = (r + l) / 2;
findMaMi(a, hMax, hMin, l, m);
findMaMi(a, Max, Min, m + 1, r);
if (hMax[1] >= Max[1]) {
Max[1] = hMax[1];
}
if (Min[1] >= hMin[1]) {
Min[1] = hMin[1];
}
}
}
}
}
11 一维的最近点对问题
思路
- n个点退化为n个实数,最近点对即为这n个实数中相差最小的两个实数
- 分解:用各点坐标的中位数m作为分割点,分成两个点集
- 求解:在两个点集上分别找出其最接近点对{p1,p2}和
- 合并:整个点集的最近点对或者是{p1,p2},或者是{q1,q2},或者是某个{p3,q3},其中p3和q3分属两个点集;如果最近点对是{p3,q3},即|p3-q3|<d,则p3和q3两者与m的距离不超过d,即p3∈(m-d,m],q3∈(m,m+d]
//一维最近点对问题
public class ZuiJinDianDui12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入一共有多少个点:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
double[] arrays = new double[n];
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
System.out.println("请输入第"+(i+1)+"个点的坐标");
double x = scanner.nextDouble();
arrays[i]=x;
}
// 按照坐标升序排序
Arrays.sort(arrays);
double minDis = minDistance(arrays, 0, n - 1);
System.out.println("最短距离为:"+minDis);
}
//点对之间的最小距离
public static double minDistance(double[] arrays,int l,int r){
//同一个点,不存在点对,距离不能取0,返回最大值
if (l == r) {
return Double.MAX_VALUE;
}
//两个点
if (l + 1 == r) {
return arrays[r]-arrays[l];
}
//分治法
int center = l + (r - l) / 2;
double dis1 = minDistance(arrays, l, center);
double dis2 = minDistance(arrays, center + 1, r);
double minDis = Math.min(dis1, dis2);
ArrayList<Double> nearPoints = new ArrayList<>();
// 选出距离中间线小于minDis的点
for (Double p : arrays) {
if (Math.abs(arrays[center] - p) <= minDis) {
nearPoints.add(p);
}
}
for (int i=0;i<nearPoints.size();i++){
for (int j=i+1;j<nearPoints.size();j++){
double d=Math.abs(nearPoints.get(j)-nearPoints.get(i));
if (d<minDis){
minDis=d;
}
}
}
return minDis;
}
}
//二维最近点对问题
public class ZuiJinDianDui11 {
// 坐标点
static class Point {
public Point() {
}
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
double x;
double y;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入一共有多少个点:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
Point[] ps = new Point[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.println("请输入第"+(i+1)+"个点的x坐标");
double x = scanner.nextDouble();
System.out.println("请输入第"+(i+1)+"个点的y坐标");
double y = scanner.nextDouble();
ps[i] = new Point(x, y);
}
// 按照X轴坐标升序排序
Arrays.sort(ps, new Comparator<Point>() {
@Override
public int compare(Point o1, Point o2) {
if (o1.x < o2.x)
return -1;
if (o1.x > o2.x)
return 1;
if (o1.y < o2.y)
return -1;
if (o1.y > o2.y)
return 1;
return 0;
}
});
double minDis = minDistance(ps, 0, n - 1);
System.out.println("最短距离为:"+String.format("%.3f", minDis));//保留小数点后3位返回
}
//点对之间的最小距离
public static double minDistance(Point[] ps, int l, int r) {
//同一个点,不存在点对,距离不能取0,返回最大值
if (l == r) {
return Double.MAX_VALUE;
}
//两个点
if (l + 1 == r) {
return distance(ps[l], ps[r]);
}
//分治法
int center = l + (r - l) / 2;
double dis1 = minDistance(ps, l, center);
double dis2 = minDistance(ps, center + 1, r);
double minDis = Math.min(dis1, dis2);
ArrayList<Point> nearPoints = new ArrayList<>();
// 选出距离中间线小于minDis的点
for (Point p : ps) {
if (Math.abs(ps[center].x - p.x) <= minDis) {
nearPoints.add(p);
}
}
// 按照Y轴升序排序
Collections.sort(nearPoints, new Comparator<Point>() {
@Override
public int compare(Point o1, Point o2) {
if (o1.y < o2.y)
return -1;
if (o1.y > o2.y)
return 1;
if (o1.x < o2.x)
return -1;
if (o1.x > o2.x)
return 1;
return 0;
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < nearPoints.size(); i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < nearPoints.size(); j++) {
if (nearPoints.get(j).y - nearPoints.get(i).y > minDis) {
break;// 元素i+1离元素i更远,没必要继续比较
}
double d = distance(nearPoints.get(j), nearPoints.get(i));
if (d < minDis) {
minDis = d;
}
}
}
return minDis;
}
public static double distance(Point p1, Point p2) {
if (p1 == p2)
return 0;
return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(p1.x - p2.x, 2) + Math.pow(p1.y - p2.y, 2));
}
}
12 寻找顺序统计量问题
顺序统计量是什么
- 求第i小元素问题、选择问题:设集合S中共有n个数据元素,要在S中找出第i小元素
- 最小元:第1个顺序统计量
- 最大元:第n个顺序统计量
问题
- 如下假设:集合由n个数值不同的元素组成;在此假设下的结论可以推广到有重复数值的情形
- 输入:一个包含n个不同数的集合A和一个数i
- 输出:元素x,x为集合中第i小元素
求解方法
- 排序
- 期望线性时间
- 最坏情况线性时间
12.1期望线性时间
- 思路和快速一样,一趟排序后确定一个元素,该元素大于其左边所有元素,小于其右边所有元素
public class QiWangXianXingShiJian12 {
public static int select(int[] array, int sta, int end,int index){// index 要查找第index小的值
if(sta == end)
return array[sta];
int q = partition(array,sta,end) ;
int k = q - sta + 1;
if(k == index)
return array[q];
else if(index < k)
return select(array, sta, q-1, index);
else
return select(array, q+1, end, index - k);
}
public static int partition(int[] list ,int sta, int end){
int key = list[end];
int i,j;
i= sta -1; //注意初始值
for(j=sta;j < end ; j++){
if(list[j] <= key){
i++;
swap(list,i,j); // 先+1,后换
}
}
swap(list,i+1,end); // 注意i+1
return i+1;
}
public static void swap(int[] list, int i,int j){
int key = list[i];
list[i] = list[j];
list[j] = key;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array=new int[]{5,7,11,2,3,1,9};
int result = select(array, 0, array.length-1, 3);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
13 课后习题1
- 分别针对随机生成的若干组整数序列(比如规模为1000个数,10000个数,100000个数)进行排序,排序算法使用四种方法,至少包括以下三种经典方法:插入排序算法、合并排序算法和快速排序算法
- 在用不同的排序算法对多组整数进行排序时,统计各种情况下排序所耗费的时间,并对结果进行分析
- 思考:当要求为降序时,如何修改?并尝试实现
- 思考:如果随机生成了10个数,在使用快速排序进行排序时,尝试给出数组的演化情况
- 思考:排序算法的稳定性,时间性能,空间性能
public class PaiXu13 {
//1插入排序算法
public static void insertSort(int[] array){
for (int i=1;i<array.length;i++){
int insertValue=array[i];
int j=i-1;
//从右向左比较元素的同时,进行元素复制
for (;(j>=0)&&(insertValue<array[j]);j--){
array[j+1]=array[j];
}
//insertValue的值插入适当位置
array[j+1]=insertValue;
}
}
//2合并排序算法
public static void mergeSort(int[] array, int start, int end){
if(start<end){
//折半拆成两个小集合,分别进行扫描
int mid=(start+end)/2;
mergeSort(array,start,mid);
mergeSort(array,mid+1,end);
//把两个有序小集合,归并成一个大集合
merge(array,start,mid,end);
}
}
private static void merge(int[] array,int start,int mid,int end){
//开辟额外大集合,设置指针
int[] tempArray=new int[end-start+1];
int p1=start;
int p2=mid+1;
int p=0;
//比较两个小集合的元素,依次放入大集合
while ((p1<=mid) && (p2<=end)){
if (array[p1]<=array[p2]){
tempArray[p++]=array[p1++];
}
else {
tempArray[p++]=array[p2++];
}
}
//左侧小集合还有剩余,依次放入大集合尾部
while (p1<=mid){
tempArray[p++]=array[p1++];
}
//右侧小集合还有剩余,依次放入大集合尾部
while (p2<=end){
tempArray[p++]=array[p2++];
}
}
//3快速排序算法
public static void quickSort(int[] arr,int startIndex,int endIndex){
//递归结束条件:startIndex大于或等于endIndex
if (startIndex>=endIndex){
return;
}
//得到基准元素位置
int pivotIndex=partition(arr,startIndex,endIndex);
quickSort(arr,startIndex,pivotIndex-1);
quickSort(arr,pivotIndex+1,endIndex);
}
//分治,双边循环法
private static int partition(int[] arr,int startIndex,int endIndex){
//取第一个位置,(也可以选择随机位置)的元素作为基准元素
int pivot=arr[startIndex];
int left=startIndex;
int right=endIndex;
while (left!=right){
//控制right指针比较并左移
while (left<right && arr[right]>pivot){
right--;
}
//控制left指针比较并右移
while (left<right && arr[left]<=pivot){
left++;
}
//交换left和right指针所指向的元素
if (left<right){
int temp=arr[left];
arr[left]=arr[right];
arr[right]=temp;
}
}
//pivot和指针重合点交换
arr[startIndex]=arr[left];
arr[left]=pivot;
return left;
}
//选择排序
@Test
public void testInsertSort(){
int[] ints = new int[10000];
for (int i=0;i<10000;i++){
//随机生成[1,1000000]的数
ints[i]=(int)((Math.random()*1000000)+1);
}
long startTimeOfInsertSort = System.currentTimeMillis();
insertSort(ints);
long endTimeInsertSort = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("选择排序消耗时间为:"+(endTimeInsertSort-startTimeOfInsertSort)+"ms");//31ms
}
//合并排序
@Test
public void testMergeSort(){
int[] ints = new int[10000];
for (int i=0;i<10000;i++){
//随机生成[1,1000000]的数
ints[i]=(int)((Math.random()*1000000)+1);
}
long startTimeOfMergeSort = System.currentTimeMillis();
mergeSort(ints,0,ints.length-1);
long endTimeOfMergeSort = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("合并排序消耗时间为:"+(endTimeOfMergeSort-startTimeOfMergeSort)+"ms");//2ms
}
//快速排序
@Test
public void testQuickSort(){
int[] ints = new int[10000];
for (int i=0;i<10000;i++){
//随机生成[1,1000000]的数
ints[i]=(int)((Math.random()*1000000)+1);
}
long startTimeOfQuickSort = System.currentTimeMillis();
quickSort(ints,0,ints.length-1);
long endTimeOfQuickSort = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("快速排序消耗时间为:"+(endTimeOfQuickSort-startTimeOfQuickSort)+"ms");//2ms
}
}
14 课后习题2
- 在一个包含n个元素的多重集合S中,每个元素在S中出现的次数称为该元素的重数,多重集合S中重数最大的元素称为众数
- 举例来说,多重集合S={1,2,3,3,3,3,4,4,5},则多重集合S的众数是3,元素3的重数为4
- 现要求对随机生成的由n个自然数组成的多重集合S,编程计算S的众数及其重数
思路
- 我们先求出中位数的重数,再求出中位数第一次出现的位置(中位数可能有多个),如果发现这个位置左边的数的个数小于这个重数那么我们就不用再往左边寻找了,因为左边已经没有比这个中位数的重数更大的数了,右边同理
public class ZongShu14 {
public static int n=0;//存储众数
public static int s=0;//存储众数的重数
//统计中位数的重数
public static int count(int ints[],int start, int end){
int midNumber=ints[(start+end)/2];
int counts=0;
for (int i=0;i<ints.length;i++){
if (ints[i]==midNumber)
counts++;
}
return counts;
}
//统计中位数第一次出现的位置
public static int startIndex(int ints[],int start,int end){
int mid=(start+end)/2;
for (int i=start;i<end;i++){
if (ints[i]==ints[mid])
return i;
}
return 0;
}
public static void find(int ints[],int start,int end){
int mid=(start+end)/2;
int mids=count(ints,start,end);
int left=startIndex(ints,start,end);
if (mids>s){
s=mids;
n=ints[mid];
}
if (end+1-(left+mids)>s){
find(ints,left+mids,end);
}
if (left>s){
find(ints,start,left);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入共有多少个众数");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int number = scanner.nextInt();
int[] ints = new int[number];
for (int i=0;i<number;i++){
//随机生成0-99的自然数
ints[i]=(int)(Math.random()*100);
}
find(ints,0,number-1);
System.out.println("众数:"+n+" 重数:"+s);
}
}
15 课后习题3
- 最近点对问题描述:对平面上给定的N个点,给出所有点对的最短距离,即,输入是平面上的N个点,输出是N点中具有最短距离的两点
- 要求随机生成N个点的平面坐标,应用穷举法编程计算出所有点对的最短距离
- 要求随机生成N个点的平面坐标,应用分治法编程计算出所有点对的最短距离
public class ZuiJinDianDui15 {
// 坐标点
public static class Point {
public Point() {
}
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
double x;
double y;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入一共有多少个点:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
Point[] ps = new Point[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.println("请输入第"+(i+1)+"个点的x坐标");
double x = scanner.nextDouble();
System.out.println("请输入第"+(i+1)+"个点的y坐标");
double y = scanner.nextDouble();
ps[i] = new Point(x, y);
}
// 按照X轴坐标升序排序
Arrays.sort(ps, new Comparator<Point>() {
@Override
public int compare(Point o1, Point o2) {
if (o1.x < o2.x)
return -1;
if (o1.x > o2.x)
return 1;
if (o1.y < o2.y)
return -1;
if (o1.y > o2.y)
return 1;
return 0;
}
});
double minDisBF=minDistanceBF(ps);
System.out.println("使用暴力法最短距离为:"+String.format("%.3f", minDisBF));//保留小数点后3位返回
double minDis = minDistance(ps, 0, n - 1);
System.out.println("使用分治法最短距离为:"+String.format("%.3f", minDis));//保留小数点后3位返回
}
//点对之间的最小距离--穷举法
public static double minDistanceBF(Point[] ps){
double minDis=Double.MAX_VALUE;//初始化最短距离为最大值
for (int i=0;i<ps.length;i++){
for (int j=i+1;j<ps.length;j++){
double distance = distance(ps[i], ps[j]);
if (distance<minDis){
minDis=distance;
}
}
}
return minDis;
}
//点对之间的最小距离--分治法
public static double minDistance(Point[] ps, int l, int r) {
//同一个点,不存在点对,距离不能取0,返回最大值
if (l == r) {
return Double.MAX_VALUE;
}
//两个点
if (l + 1 == r) {
return distance(ps[l], ps[r]);
}
//分治法
int center = l + (r - l) / 2;
double dis1 = minDistance(ps, l, center);
double dis2 = minDistance(ps, center + 1, r);
double minDis = Math.min(dis1, dis2);
ArrayList<Point> nearPoints = new ArrayList<>();
// 选出距离中间线小于minDis的点
for (Point p : ps) {
if (Math.abs(ps[center].x - p.x) <= minDis) {
nearPoints.add(p);
}
}
// 按照Y轴升序排序
Collections.sort(nearPoints, new Comparator<Point>() {
@Override
public int compare(Point o1,Point o2) {
if (o1.y < o2.y)
return -1;
if (o1.y > o2.y)
return 1;
if (o1.x < o2.x)
return -1;
if (o1.x > o2.x)
return 1;
return 0;
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < nearPoints.size(); i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < nearPoints.size(); j++) {
if (nearPoints.get(j).y - nearPoints.get(i).y > minDis) {
break;// 元素i+1离元素i更远,没必要继续比较
}
double d = distance(nearPoints.get(j), nearPoints.get(i));
if (d < minDis) {
minDis = d;
}
}
}
return minDis;
}
public static double distance(Point p1, Point p2) {
if (p1 == p2)
return 0;
return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(p1.x - p2.x, 2) + Math.pow(p1.y - p2.y, 2));
}
}
16 课后习题4
- 随机给出一个整数序列,选出其中连续且非空的一段使得这段和最大
- 要求:使用分治法解决
思路
- 划分问题:把序列分成元素个数尽量相等的两半
- 递归求解:求出分别位于左半和右半的最佳序列
- 合并子问题:求出起点位于左半,终点位于右半的最佳序列,并与已得最佳序列进行比较
public class ZuiDaLianXuZiDuanHe16 {
public static int maxsum(int[]a,int l,int r){
if(l==r){
return a[l];
}
int mid = (l+r)/2;
int lsum = maxsum(a,l,mid);//左区间
int rsum = maxsum(a,mid+1,r);//右区间
int sum1=0,sum2=0;
int lefts=0,rights=0;
for(int i=l;i<=mid;i++){
lefts+=a[i];
if(lefts>sum1){
sum1=lefts;
}
}
for(int i=mid+1;i<r;i++){
rights+=a[i];
if(rights>sum2){
sum2=rights;
}
}
int msum=sum1+sum2;
return Math.max(Math.max(lsum,rsum),msum);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("输入整数序列个数");
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=in.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
//随机生成-100-99
a[i]=(int) (Math.random()*200-100);
}
int ans = maxsum(a,0,n-1);
if(ans<0){
ans=0;
}
System.out.println("数组为:"+ Arrays.toString(a));
System.out.println("最大连续子段和为:"+ans);
}
}
17 课后习题5
- 判断一棵树是否为二叉搜索树
思路
- 1可以中序遍历,如果所有元素递增有序则是二叉搜索树
- 2可以递归遍历左右子树,定义一个前置指针,若前置指针所指的值大于当前指针所指的值,则肯定不是二叉搜索树
public class ErChaSouSuoShu17 {
//树节点定义
public static class TreeNode{
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x){
val=x;
}
}
static TreeNode pre=null;//执行当前节点的前指针
static boolean flag=true;
public static boolean isBST(TreeNode root){
if (root==null)
return true;
inorder(root);
return flag;
}
public static void inorder(TreeNode root){
if (root!=null){
//递归遍历左指针
inorder(root.left);
//若前指针所指的值小于当前值,则肯定不是二叉搜索树
if (pre != null && pre.val>=root.val)
flag=false;
pre=root;
//递归遍历右指针
inorder(root.right);
}
}
}
19 课后习题8
题目
- 漂亮数组:给定一个长度为N的数组arr,该数组由1到N的整数来组成,且满足arr[k]*2不等于arr[i]+arr[j] (i<k<j)
- 例如:长度为4的数组:{2,1,4,3} ,长度为8的数组:[1,5,3,7,2,6,4,8]
public class PiaoLiangShuZu19 {
Map<Integer, int[]> memo;
public int[] beautifulArray(int N) {
memo = new HashMap();
return f(N);
}
public int[] f(int N) {
if (memo.containsKey(N))
return memo.get(N);
int[] ans = new int[N];
if (N == 1) {
ans[0] = 1;
} else {
int t = 0;
for (int x: f((N+1)/2)) // odds
ans[t++] = 2*x - 1;
for (int x: f(N/2)) // evens
ans[t++] = 2*x;
}
memo.put(N, ans);
return ans;
}
}
20 课后习题9
题目
- 重建二叉树:输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历结果,请构建二叉树并返回其根节点。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字
思路
- 先找出根节点,然后利用递归方法构造二叉树
public class ChongJianErChaShu20 {
//树节点定义
public static class TreeNode{
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x){
val=x;
}
}
//递归(传入数组的拷贝)
public static TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int[] pre,int[] in){
if (pre==null ||in==null ||pre.length==0||in.length==0){
return null;
}
if (pre.length!=in.length){
return null;
}
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(pre[0]);
for(int i=0;i<pre.length;i++){
if (pre[0]==in[i]){
root.left=reConstructBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre,1,i+1),Arrays.copyOfRange(in,0,i));
root.right=reConstructBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre,i+1,in.length),Arrays.copyOfRange(in,i+1,in.length));
}
}
return root;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] pre = {1, 2, 4, 7, 3, 5, 6, 8};
int[] in=new int[]{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6};
TreeNode treeNode = reConstructBinaryTree(pre, in);
System.out.println(treeNode);
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号