C++学习七 C++实现add(1)(2)(3)
一、代码实现:
class Yoba { public: Yoba(int n) : _n(n) {} Yoba operator() (int n) { return Yoba(_n + n); } bool operator== (int n) { return _n == n; } int operator+ (int n) { return _n + n; } int operator- (int n) { return _n - n; } friend bool operator== (int n, const Yoba & y) { return n == y._n; } private: int _n; }; auto add(int n) { return Yoba(n); }
这里对于对于功能实现add(1)(2)(3), 这里用到了()符号的重载。
二、这里对于类的实现做一些讲解:
这里有一个例子:
class CountPeople { public: //构造函数 CountPeople() :number(0), _size(0), T(0) { cout << "number of the C is " << number << endl; } //析构函数 ~CountPeople() {} //初始化参数列表的结构 CountPeople(int n) :number(n) { cout << "number is "<<number<<endl; } //方法接口,operator 重载操作符() CountPeople operator() (int n) { return CountPeople(number + n); } int operator+ (int n) { return number + n; } friend bool operator== (const CountPeople& y,int n ) { return n == y.number; } // bool operator== (int n) { return n == number; } int GetNumber(); int GetSize(); private: int _size; int number; int T; };
上面是一个类的结构。
对于一些方法,可以在类的外部实现。
int CountPeople::GetNumber() { return number; } int CountPeople::GetSize() { return _size; }
一个类的结构:
构造函数
析构函数
私有变量
方法。
三、如果需要将类不放在main里面,那么在cpp里面的分布为:
| cpp | main.cpp | usage.cpp | usage.hpp |
| 内容 |
#include "usage.hpp" int main(void) { return 0; } |
类的方法具体内容 | 类的定义 |
具体分布如下:
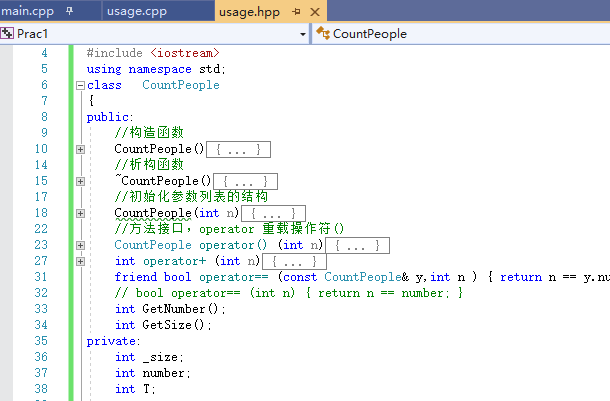
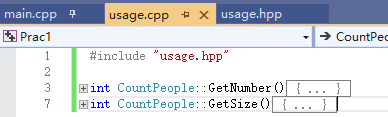

四、CountPeople(1)(3)的调用过程
先是调用CountPeople(1)
然后调用()重载函数
再调用CountPeople(3)
纵一苇之所如,临万顷之茫然。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号