表和表的关系 单表查询 多表查询 055
一 . 表和表的关系 ---外键的变种
一对多 或者 多对一 多对多 一对一
找出两张表之间的关系
分析步骤 :
# 1 先站在左表的角度去找
是否左表的多条记录可以对应右表的一条记录 , 如果是 则证明左表的一个字段
foreign key 右表的一个字段
# 2 再站在右表的角度去找
是否右表的多条记录可以对应左表的一条记录 , 如果是 则证明右表的一个字段
foreign key 坐标的一个字段
# 3 总结 :
# 多对一
如果只有步骤1 成立 则是左表多对一右表
如果只有步骤2 成立 则是右表多对一左表
# 多对多
步骤1和 2 同时成立 证明这两张表是一个双向的多对一 即多对多, 需要
定义一个这两张表的关系表来专门存放两者之间的关系
# 一对一
1 2 都不成立 而是左表的一条记录唯一对应右表的一条记录 , 反之亦然
这种情况很简单 , 就是在左表foreign key 右表的基础上 , 将左表的外键
字段设置成unique即可
多对一的关系 : 例如 一个出版社可以出版多本书
关联方式: foreign key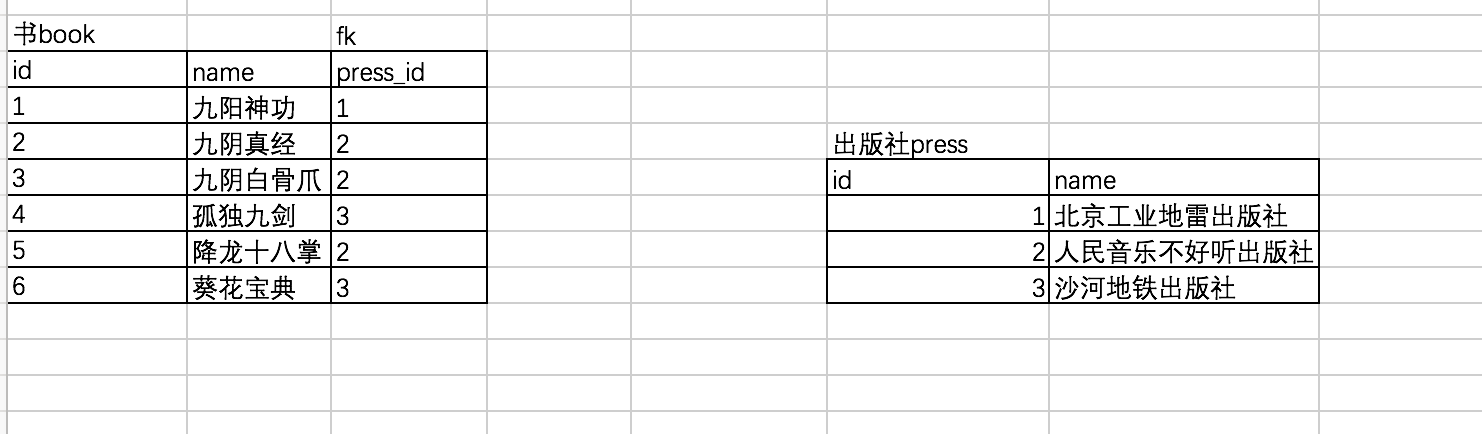
# 创建主表 create table press( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20) ); # 创建从表 create table book( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), press_id int not null, constraint fk_book_press foreign key(press_id) references press(id) on delete cascade on update cascade, ); # 先往被关联表中插入记录 insert into press(name) values ('北京工业地雷出版社'), ('人民音乐不好听出版社'), ('知识产权没有用出版社'); # 再往关联表中插入记录 insert into book(name,press_id) values ('九阳神功',1), ('九阴真经',2), ('九阴白骨爪',2), ('独孤九剑',3), ('降龙十巴掌',2), ('葵花宝典',3)
查询结果: mysql> select * from book; +----+-----------------+----------+ | id | name | press_id | +----+-----------------+----------+ | 1 | 九阳神功 | 1 | | 2 | 九阴真经 | 2 | | 3 | 九阴白骨爪 | 2 | | 4 | 独孤九剑 | 3 | | 5 | 降龙十巴掌 | 2 | | 6 | 葵花宝典 | 3 | +----+-----------------+----------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from press; +----+--------------------------------+ | id | name | +----+--------------------------------+ | 1 | 北京工业地雷出版社 | | 2 | 人民音乐不好听出版社 | | 3 | 知识产权没有用出版社 | +----+--------------------------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
多对多的 关系(作者与书籍的关系)
多对多 : 一个作者可以写多本书 一本书也可以有多个作者,双向的一对多,
即多对多 关联方式 : foreign key + 一张新的表
用户和博客 一对一关系 一个用户只能注册一个博客
关联方式 : foreign key + unique
# 例如 一个用户只能注册一个博客 # 两张表 : 用户表(user) 和 博客表(blog) # 创建用户表 create table user( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20) ); # 创建博客表 create table blog( id int primary key auto_increment, url varchar(100), user_id int unique, constraint fk_user foreign key(user_id) references user(id) on delete cascade on update cascade ); # 插入用户表中的记录 insert into user(name) values ('alex'), ('wusir'), ('egon'), ('xiaoma'); # 插入博客表的记录 insert into blog(url,user_id) values ('http://www.cnblog/alex',1), ('http://www.cnblog/wusir',1), ('http://www.cnblog/egon',1), ('http://www.cnblog/xiaoma',1),
单表查询 :
一 . 单表查询的语法 select 字段1,字段2,...from 表名 where 条件 group by field having 筛选条件 order by field limit 限制条数 二 . 关键字的执行优先级(重点) 关键字的执行优先级 from where group by having select distinct order by limit 1 . 找到表 : from 2 . 拿着where指定的约束条件 ,去文件/表中取出一条条记录 3 . 将取出的一条条记录进行分组 group by 如果没有 group by ,则整体作为一组 4 . 将分组的结果进行having过滤 5 . 执行select 6 . 去重 7 . 将结果按条件排序 : order by 8 . 限制结果的显示条数 例如 只看第一名
group by 是发生在where之后的,where条件是可选的
针对于相同字段进行归类
select * from employee group by post;
注意 : 分组之后 只能获取分组的字段,如果想获取组内的信息要通过聚合函数进行计算
聚合函数
max()最大值 min()最小值 sum()求和 count()求总个数 avg()求平均值 limit0,5第一个参数表示查询的起始位置 第二个参数表示参数的获取个数 0,5表示取前五名 2,5表示取3-7名 group-concat(name) 将选中的条件中的名称全部显示出来
虚拟表
# 起别名 select A.a from (select post,count(1) as a from employee group by post) as A 将第一次筛选出来的表作为主表进行第二次筛选

having
mysql5.7整体作为一组 可以执行sql
select * from employee having salary>1000000;
不加group 默认将整个表单分为一组
mysql 5.6 5.5
mysql> select * from employee having salary>1000000; ERROR 1463 (42000): Non-grouping field 'salary' is used in HAVING clause # 必须分组之后才能使用having
多表查询
语法:
select 字段列表 from 表1 inner |left |right |join 表2 on 表1.字段 = 表2.字段
多表连接查询
# 符合条件查询 select * from employee,department where employee.dep_id = department.id;
内连接
只获取匹配的数据
select * from employee inner join department on employee.dep_id = department.id;
左连接或者右连接
只显示左表或右表所有记录
select * from employee left join department on employee.dep_id = department.id;
全外连接
select * from employee left join department on employee.dep_id = department.id union select * from employee right join department on employee.dep_id = department.id;
子查询
#1:子查询是将一个查询语句嵌套在另一个查询语句中。 #2:内层查询语句的查询结果,可以为外层查询语句提供查询条件。 #3:子查询中可以包含:IN、NOT IN、ANY、ALL、EXISTS 和 NOT EXISTS等关键字 #4:还可以包含比较运算符:= 、 !=、> 、<等
#小练习
#查询平均年龄在25岁以上的部门名
select * from department where id in (select dep_id from employee group by dep_id having avg(age) > 25);


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号