【图解设计模式系列】The Bridge Pattern: 桥接模式
桥接模式是用于把抽象化与实现化解耦,使得二者可以独立变化。这种模式涉及一个接口,作为一个桥梁,使得具体类的功能独立于接口实现类。两种类型的类可以在结构上改变而不彼此影响。
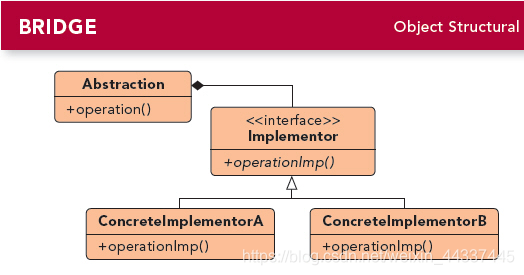
桥接模式包含如下几个角色:
Abstraction:抽象类角色。定义抽象类的接口并维护指向Implementor类的对象指针。
RefinedAbstraction:扩充抽象类。扩充Abstraction定义的接口。
Implementor:定义实现类的接口,该接口不一定要与Abstraction的接口完全一致。事实上这两个接口可以完全不同。一般而言,Implementor接口仅提供基本操作,而Abstraction则定义基于这些基本操作的较高层次的操作。
ConcreteImplementor:具体实现化角色的实现类。实现Implementor接口并定义它的具体实现。
实例
手机抽象类
abstract class Phone {
private String system;
private Software software;
public abstract void openSoftware();
public String getSystem() {
return system;
}
public void setSystem(String system) {
this.system = system;
}
public Software getSoftware() {
return software;
}
public void setSoftware(Software software) {
this.software = software;
}
}
安卓
class AndroidPhone extends Phone {
public AndroidPhone(Software software){
this.setSystem("Android");
this.setSoftware(software);
}
@Override
public void openSoftware() {
this.getSoftware().open(this);
}
}
IOS
class IOSPhone extends Phone {
public IOSPhone(Software software) {
this.setSystem("IOS");
this.setSoftware(software);
}
@Override
public void openSoftware() {
this.getSoftware().open(this);
}
}
软件接口
interface Software {
void open(Phone phone);
}
Chrome
class Chrome implements Software {
@Override
public void open(Phone phone) {
System.out.println("打开 " + phone.getSystem() + " 手机的 Chrome 浏览器");
}
}
Firefox
class FireFox implements Software {
@Override
public void open(Phone phone) {
System.out.println("打开 " + phone.getSystem() + " 手机的浏览器");
}
}
客户端
public class BridgeClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Software chrome = new Chrome();
Software firefox = new FireFox();
Phone androidPhone = new AndroidPhone(chrome);
androidPhone.openSoftware();
androidPhone.setSoftware(firefox);
androidPhone.openSoftware();
Phone iosPhone = new IOSPhone(chrome);
iosPhone.openSoftware();
iosPhone.setSoftware(firefox);
iosPhone.openSoftware();
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号