Day2 -2 变量
变量
构成
1. 变量名
必须是合法的标识符,即: A-Z,a-z, $, -
2.变量类型
八个基本类型:type, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean
引用类型:String 这种
3.作用域
类变量: static 变量,第一个{}的变量
eg:
public class helloWorld{
static double salary = 2500;
public static void main(String[], argus){
System.out.println(salary)
}
}
局部变量
在两个{}之间,即在main方法里面:必须声明和初始化值
点击查看代码
public class helloWorld{
public static void main(String[], argus){
int i;
System.out.println(i); // 无法输出,需要给i赋值
int j = 10; //赋值
System.out.println(j); //正常输出
}
}
实例变量
从属于对象。 例如HelloWorld 这个类.; 如果不自行初始化, 会输出这个类型的默认值,即: 0 or 0.0
boolean: 默认是false
除了基本类型其他默认是null
点击查看代码
public class helloWorld{
String name;
int age;
public static void main(String[], argus){
// 变量类型 变量名 值
HelloWorld hello = new HelloWorld(); - 待学习
System.out.println(hello.age); //输出 0
System.out.println(hello.name); // 输出 null
}
}
变量的命名规则
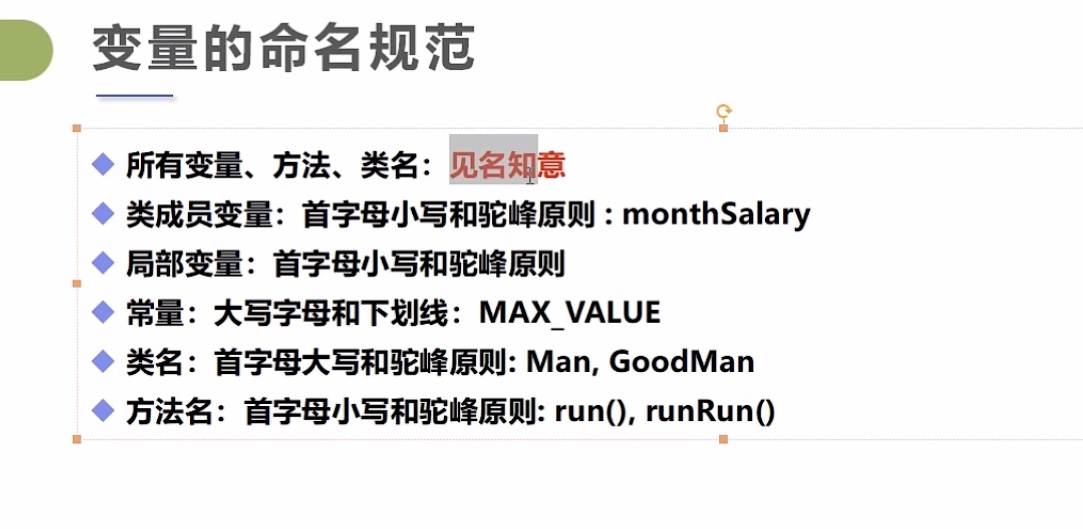
常量
- 特殊的变量,初始化后不可变。
- final 常量名(一般使用大写字母) = 值
public class HelloWorld {
static final double PI = 3.14; // final static 也一样行 : 变量类型前面属于修饰符,不存在先后顺序
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(PI);
}
}
作用域
作用域 (Scope) 指的是一个变量(或者方法、class)在代码中的可见性和生命周期,也就是在哪些位置你可以访问它、它能存在多久.
花括号 {} 确实会产生新的作用域。在这个范围里定义的变量、方法等,只能在这个范围里使用。如果超出范围,就会报错“找不到符号”。
posted on 2025-09-07 23:54 escapedlili 阅读(27) 评论(0) 收藏 举报



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号