Java数据结构——栈
栈的特点:
先进后出,就像现实生活中叠盘子和取盘子一样。
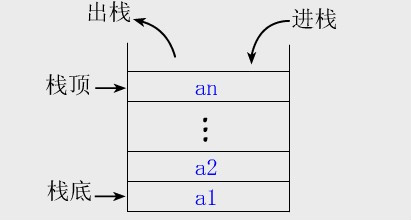
三种实现方式:
- 顺序存储实现方式(静态栈)
- 链式存储实现方式(动态栈)
- 基于LinkedList实现的栈结构
顺序存储实现方式:
public class MyStack {
private Object[] data = null;
private int top = -1;
private int maxSize = 10;
// 无参构造
public MyStack() {
super();
}
// 自定义栈的大小
public MyStack(int maxSize) {
super();
if (maxSize > 0) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
data = new Object[maxSize];
top = -1;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("初始化容量不能为0!");
}
}
// 判空
public boolean empty() {
if (top == -1) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
// 进栈
public boolean push(Object obj) {
if (top == maxSize - 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈已满,不能执行进栈操作!");
} else {
data[++top] = obj;
return true;
}
}
// 出栈
public Object pop() {
if (top == -1) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈为空,不能执行出栈操作!");
} else {
return data[top--];
}
}
// 查看栈顶元素
public Object peek() {
if (top == -1) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈为空,不能查看栈顶元素!");
} else {
return data[top];
}
}
// 返回元素的位置
public int search(Object obj) {
int i = top;
int result = 0;
while (top != -1) {
if (peek() == obj) {
result = top + 1;
break;
} else {
top--;
}
}
top = i;
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyStack stack = new MyStack(4);
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
System.out.println(stack.peek());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.peek());
System.out.println(stack.search(1));
}
}
链式存储实现方式:
public class MyLinkedStack {
// 节点
private class Node {
Object data;
Node next;
public Node() {
}
public Node(Object data, Node next) {
super();
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
Node top; // 栈顶节点
int maxSize = 5;// 栈的容量限制
int size = 0; // 记录某个时刻栈的大小
public MyLinkedStack() {
top = null;
}
// 返回栈的大小
public int length() {
return size;
}
// 判空
public boolean empty() {
return size == 0;
}
// 进栈
public boolean push(Object obj) {
if (size > maxSize) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈满");
} else {
top = new Node(obj, top);
size++;
return true;
}
}
// 查看栈顶元素
public Object peek() {
if (empty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈空");
} else {
return top.data;
}
}
// 出栈
public Object pop() {
if (empty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈空");
} else {
Node node = top;
top = top.next;
node.next = null;
size--;
return node.data;
}
}
// 返回元素位置
public int search(Object obj) {
Node node = top;
int count = 0;
while (top != null) {
if (peek() == obj) {
break;
} else {
count++;
top = top.next;
}
}
top = node;
return size-count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedStack stack = new MyLinkedStack();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
System.out.println(stack.peek());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.peek());
System.out.println(stack.search(1));
}
}
基于LinkedList实现的栈结构:
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class MyListStack {
private LinkedList<Object> list = new LinkedList<Object>(); // 链式集合
// 判空
public boolean empty() {
return list.isEmpty();
}
// 进栈
public void push(Object obj) {
list.addFirst(obj);
}
// 取得栈顶元素
public Object peek() {
return list.getFirst();
}
// 出栈
public Object pop() {
return list.removeFirst();
}
// 打印栈
public String printStack() {
return list.toString();
}
// 查找某个位置上的元素
public Object search(int index) {
return list.get(index);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyListStack stack = new MyListStack();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
System.out.println(stack.printStack());
System.out.println(stack.peek());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.peek());
System.out.println(stack.search(0));
System.out.println(stack.printStack());
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号