BLOG-1
前言: 总结三次题目集的知识点、题量、难度等情况
题目集一:
单步电梯调度问题
一.设计与分析:
源代码设计:
电梯类:
1 private int Max_Floor; // 最大楼层 2 private int Min_Floor; // 最小楼层 3 private static int Current_Floor = 0; // 当前楼层 4 private static String Direction = "UP"; // 运行方向(UP/DOWN) 5 private static String Status = "STOP"; // 运行状态(STOP/RUN) 6 private static Queue<String> InnerRequestQue = new LinkedList<>(); // 内部请求队列 7 private static Queue<String> OutRequestQue = new LinkedList<>(); // 外部请求队列 8 // 构造方法 9 public Elevator(int Max_Floor, int Min_Floor, Queue<String> InnerRequest, Queue<String> OutRequest) 10 11 // 获取内部请求的楼层和方向 12 public static int[] GetInFD() 13 14 // 获取外部请求的楼层和方向 15 public static int[] GetOutFD() 16 17 // 判断下一次要去的楼层和方向 18 public static int[] GetNextFD(int in_f_d[], int out_f_d[]) 19 20 // 运行电梯到目标楼层 21 public static void RunElevator(int[] next_f_d) 22 23 // 格式化输出电梯状态 24 public static void GetPrintf(int Current_Floor, String Direction, String Status) 25 26 // 运行整部电梯 27 public static void Opreation()
主类:
1 static Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); // 输入扫描器 2 static Queue<String> InnerRequestQue = new LinkedList<>(); // 内部请求队列 3 static Queue<String> OutRequestQue = new LinkedList<>(); // 外部请求队列 4 5 // 主方法 6 public static void main(String[] args) 7 8 // 循环读取请求 9 public static void GetRequestScanf()
源代码分析:
1.圈复杂度分析:
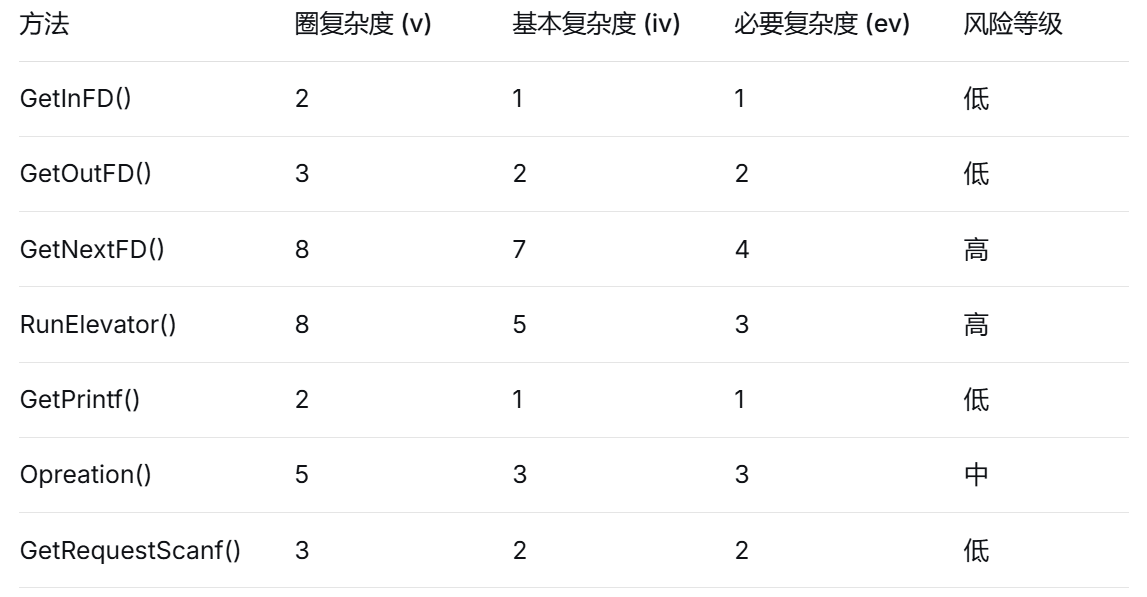
可以看到为改进的第一次电梯代码因为只设计了一个电梯类,一些方法的圈复杂度很高。
2.类图:
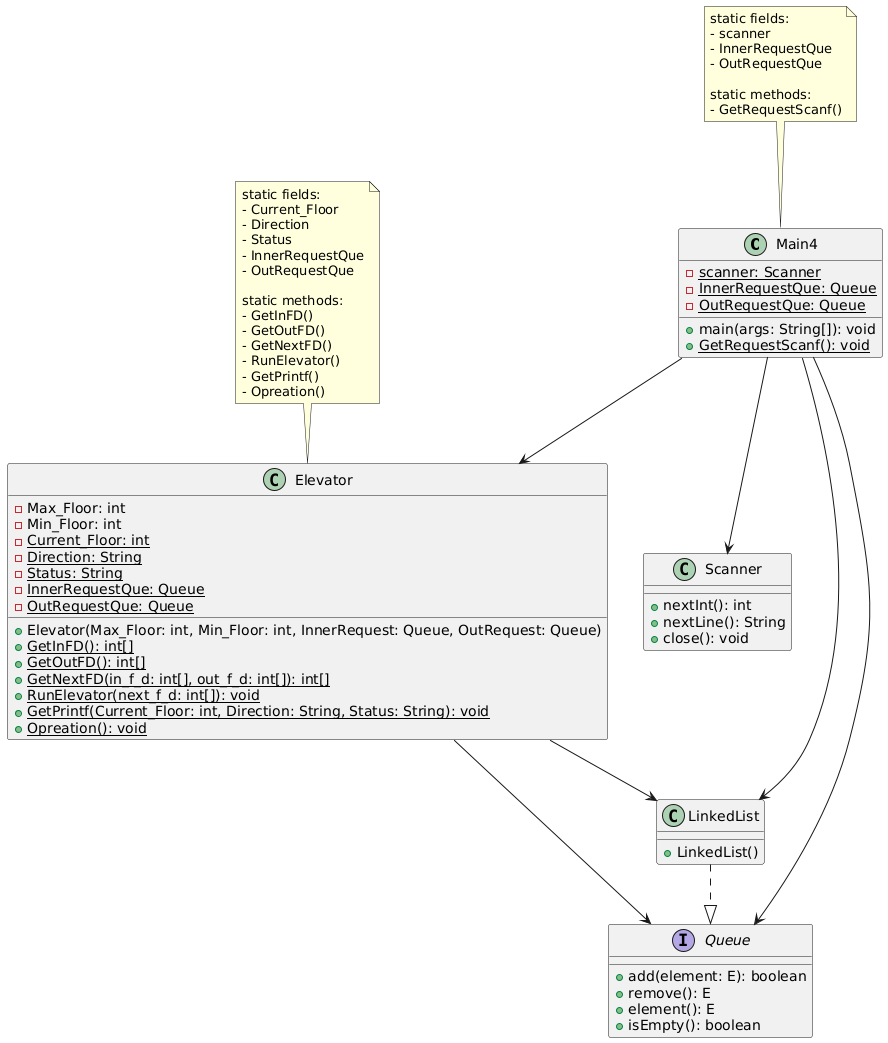
二.采坑心得:
本题目的重点在于如何设计正确的优先级,来选择出下一个要去的楼层。根据输入输出样例和题意很容易得出方向优先考虑,距离其次考虑的基本理念。但外部请求有一个乘客请求方向会让题目变得复杂。当请求方向与电梯前往目标运行方向不相同时需要特别考虑,这是我认为容易踩坑的地方,也是本题目的核心设计。
三.改进建议:
1.本次设计因为没有深入理解static变量,使用了太多static变量,实际应用中可能会出现很多问题,需要更改逻辑来消除静态变量。2.如“设计与分析”所示,本次设计圈复杂度过高,电梯类的设计也不符合单一功能原则,最需要改进的就是类设计的优化
题目集二:
单部电梯调度程序(类设计)
一.设计与分析:
源代码设计:
Direction枚举:
UP, DOWN, STOP
State枚举:
MOVING, STOPPED
电梯类:
1 private int currentFloor; // 当前楼层 2 private Direction direction; // 运行方向 3 private State state; // 运行状态 4 private int minFloor; // 最小楼层 5 private int maxFloor; // 最大楼层
// 构造方法
public Elevator(int minFloor, int maxFloor)
// Getter和Setter方法
public int getCurrentFloor()
public void setCurrentFloor(int currentFloor)
public Direction getDirection()
public void setDirection(Direction direction)
public State getState()
public void setState(State state)
public int getMinFloor()
public int getMaxFloor()
// 业务方法
public boolean isValidFloor(int floor) // 验证楼层是否有效
public void moveUp() // 向上移动一层
public void moveDown() // 向下移动一层
public void openDoor() // 开门操作
控制器类:
1 private Elevator elevator; // 电梯对象 2 private RequestQueue queue; // 请求队列 3 // 构造方法 4 public Controller() 5 public Controller(Elevator elevator, RequestQueue queue) 6 7 // Getter和Setter方法 8 public Elevator getElevator() 9 public void setElevator(Elevator elevator) 10 public RequestQueue getQueue() 11 public void setQueue(RequestQueue queue) 12 13 // 核心业务方法 14 public void processRequests() // 处理所有请求 15 private void handleExternalRequest() // 处理外部请求 16 private void handleInternalRequest() // 处理内部请求 17 private void removeRequests(int currentFloor) // 移除已处理的请求 18 19 // 辅助方法 20 private Direction internalRequestDirect() // 获取内部请求方向 21 private Direction externalRequestDirect() // 获取外部请求方向 22 private int externalRequestDistance() // 计算外部请求距离 23 private int internalRequestDistance() // 计算内部请求距离
请求队列类:
1 private LinkedList<Integer> internalRequests = new LinkedList<>(); // 内部请求队列 2 private LinkedList<ExternalRequest> externalRequests = new LinkedList<>(); // 外部请求队列 3 // 添加请求方法 4 public void addInternalRequest(int floor) // 添加内部请求 5 public void addExternalRequest(int floor, Direction direction) // 添加外部请求 6 7 // 查询方法 8 public boolean isEmpty() // 判断队列是否为空 9 public boolean hasInternalRequests() // 是否有内部请求 10 public boolean hasExternalRequests() // 是否有外部请求 11 12 // Getter方法 13 public LinkedList<Integer> getInternalRequests() // 获取内部请求队列 14 public LinkedList<ExternalRequest> getExternalRequests() // 获取外部请求队列
外部请求类
1 private int floor; // 请求楼层 2 private Direction direction; // 请求方向 3 // 构造方法 4 public ExternalRequest(int floor, Direction direction) 5 6 // Getter方法 7 public int getFloor() 8 public Direction getDirection()
圈复杂度分析:
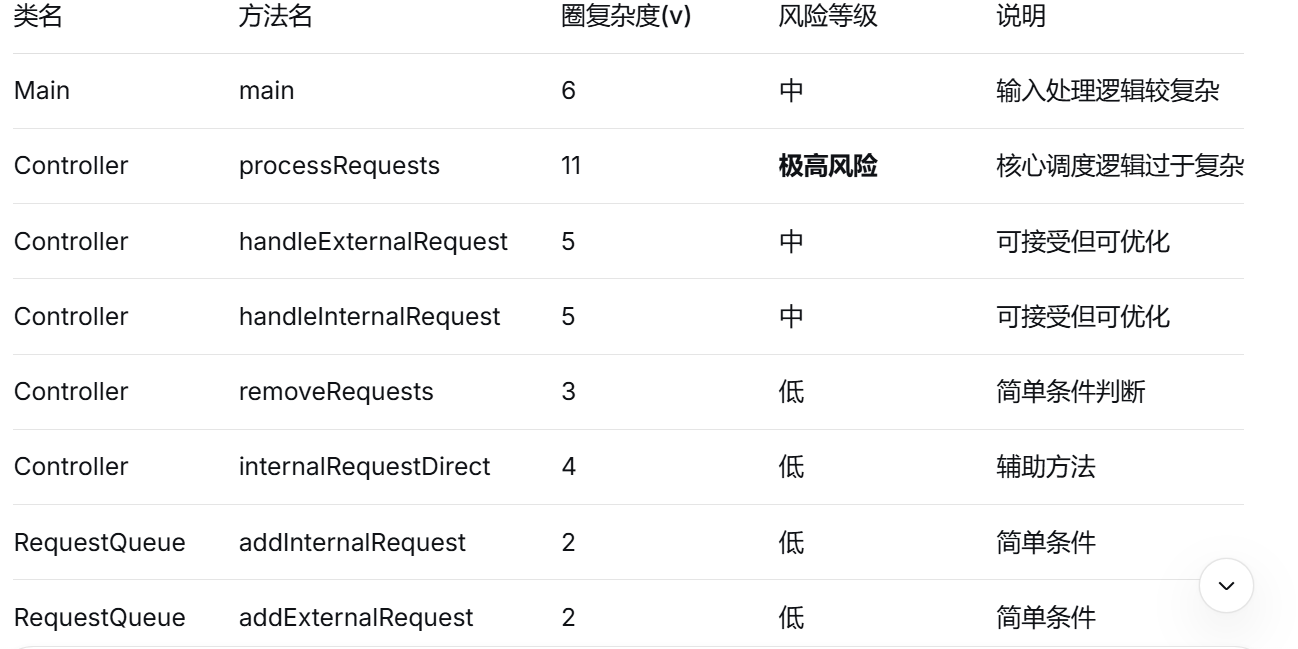
类图:
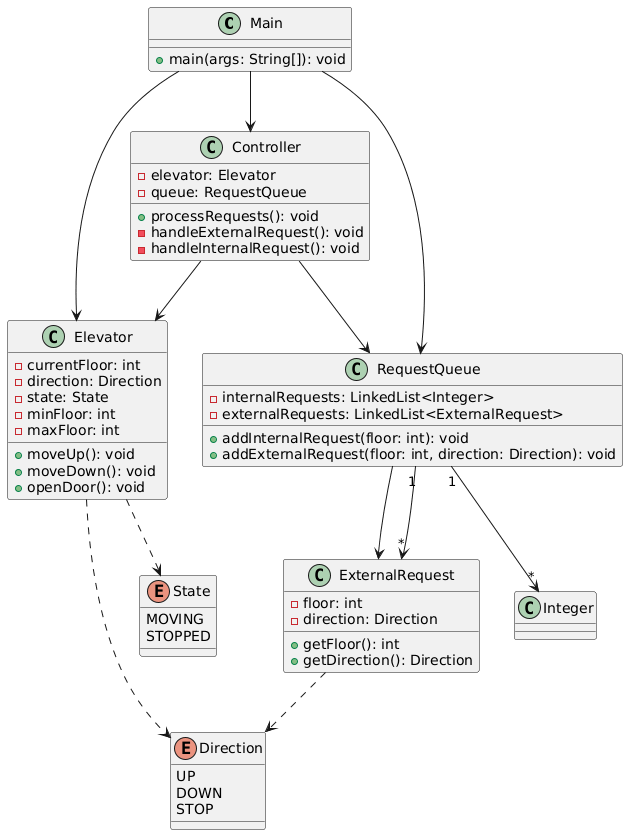
二.采坑心得:
本次题目其实将第一次题目拆分成了多个类,重难点和第一次作业一样,Controler类中处理请求方法圈复杂度太高的原因是虽然分成了多个类,但代码核心集中在了一个方法中,所以设计代码要尽量多分几个方法。
三.改进建议:
本次迭代要求忽略重复请求,我是在输入中处理的,使得主类中代码较为冗杂,建议单独列出一个方法将重复请求在队列中处理掉。
题目集三:
单部电梯调度程序(类设计-迭代)
一.设计与分析:
源代码设计:
Direction枚举:
UP, DOWN, IDLE
State枚举:
MOVING, STOPPED
乘客类:
1 private Integer sourceFloor = null; // 源楼层(外部请求) 2 private Integer destinationFloor = null; // 目标楼层 3 // 构造方法 4 public Passenger() // 无参构造 5 public Passenger(Integer sourceFloor, Integer destinationFloor) // 外部请求初始化 6 public Passenger(Integer destinationFloor) // 内部请求初始化 7 8 // Getter和Setter 9 public Integer getSourceFloor() 10 public void setSourceFloor(Integer sourceFloor) 11 public Integer getDestinationFloor() 12 public void setDestinationFloor(Integer destinationFloor) 13 14 // 业务方法 15 public Direction getDirection() // 获取外部请求目标方向
队列请求类:
private static RequestQueue instance; // 单例实例 private LinkedList<Passenger> internalRequests = new LinkedList<>(); // 内部请求队列 private LinkedList<Passenger> externalRequests = new LinkedList<>(); // 外部请求队列 // 构造方法 private RequestQueue() // 私有构造 // 单例方法 public static RequestQueue getQueueInstance() // 获取单例实例 // Getter和Setter public LinkedList<Passenger> getInternalRequests() public void setInternalRequests(LinkedList<Passenger> internalRequests) public LinkedList<Passenger> getExternalRequests() public void setExternalRequests(LinkedList<Passenger> externalRequests) // 业务方法 public void addInternalRequest(Passenger passenger) // 添加内部请求 public void addExternalRequest(Passenger passenger) // 添加外部请求
电梯类:
private static Elevator instance; // 单例实例 private int currentFloor; // 当前楼层 private Direction direction = Direction.UP; // 运行方向 private State state = State.STOPPED; // 运行状态 private int maxFloor; // 最大楼层 private int minFloor; // 最小楼层 // 构造方法 private Elevator(int minFloor, int maxFloor) // 私有构造 // 单例方法 public static Elevator getElevatorInstance(int minFloor, int maxFloor) // 获取单例实例 // Getter和Setter public int getCurrentFloor() public void setCurrentFloor(int currentFloor) public Direction getDirection() public void setDirection(Direction direction) public State getState() public void setState(State state) public int getMaxFloor() public int getMinFloor() // 业务方法 public boolean isValidFloor(int floor) // 验证楼层是否有效
控制类:
private Elevator elevator; // 电梯实例 private RequestQueue queue; // 请求队列实例 // 构造方法 public Controller(Elevator elevator, RequestQueue queue) // Getter和Setter public Elevator getElevator() public void setElevator(Elevator elevator) public RequestQueue getQueue() public void setQueue(RequestQueue queue) // 核心业务方法 public int getNextFloor() // 获取下一目标楼层 public Direction getDirection(int floor) // 获取前往某请求方向 public boolean shouldStop(int floor) // 检查当前楼层是否需要停留 public void removeRequestsAtCurrentFloor() // 移除当前楼层的请求 public void moveOneFloor() // 移动到下一层 public void moveToFloor(int targetFloor) // 运行到目标楼层 public void printFloorInfo(int currentFloor, Direction direction, boolean shouldStop) // 格式化输出 public void GO() // 运行电梯
主类:
static Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); // 输入扫描器 static int Max_Floor, Min_Floor; // 楼层范围 // 主方法 public static void main(String[] args) // 辅助方法 public static void readRequestScanf(RequestQueue queue) // 读取请求输入 public static boolean isValidScanf(int floor) // 验证输入楼层有效性
圈复杂度分析:
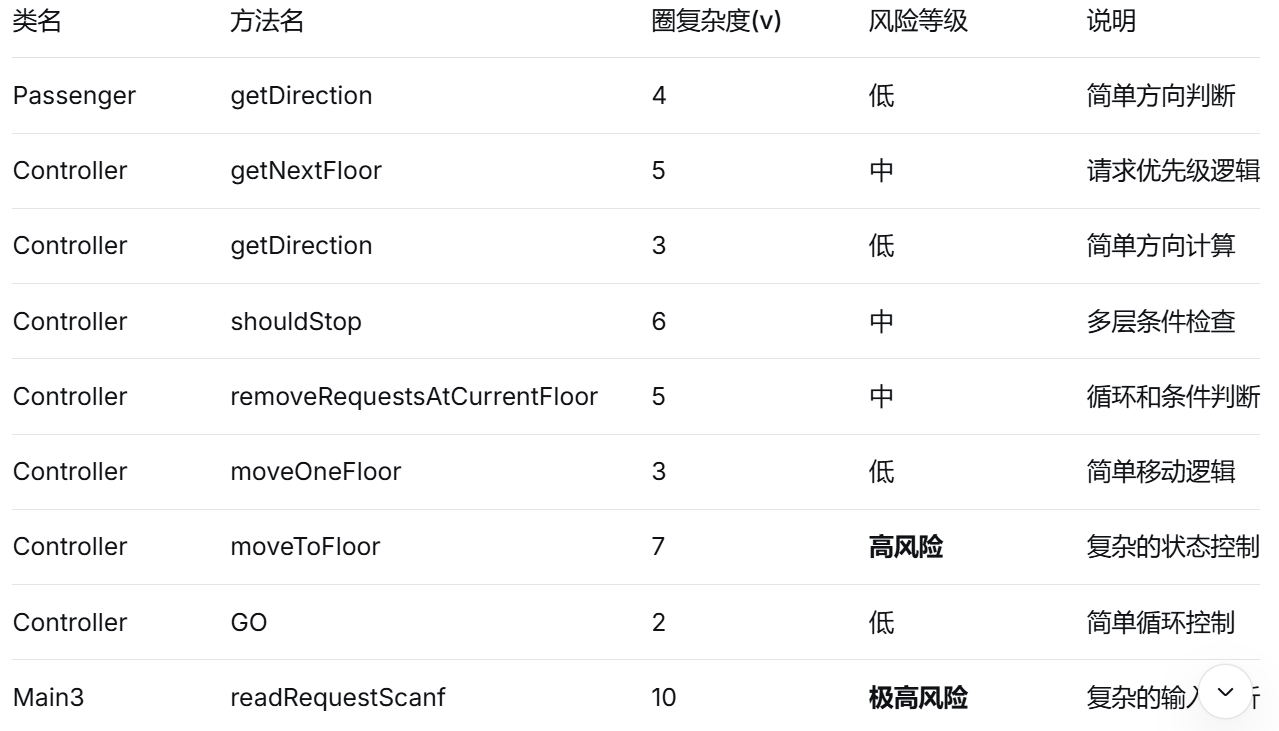
类图:
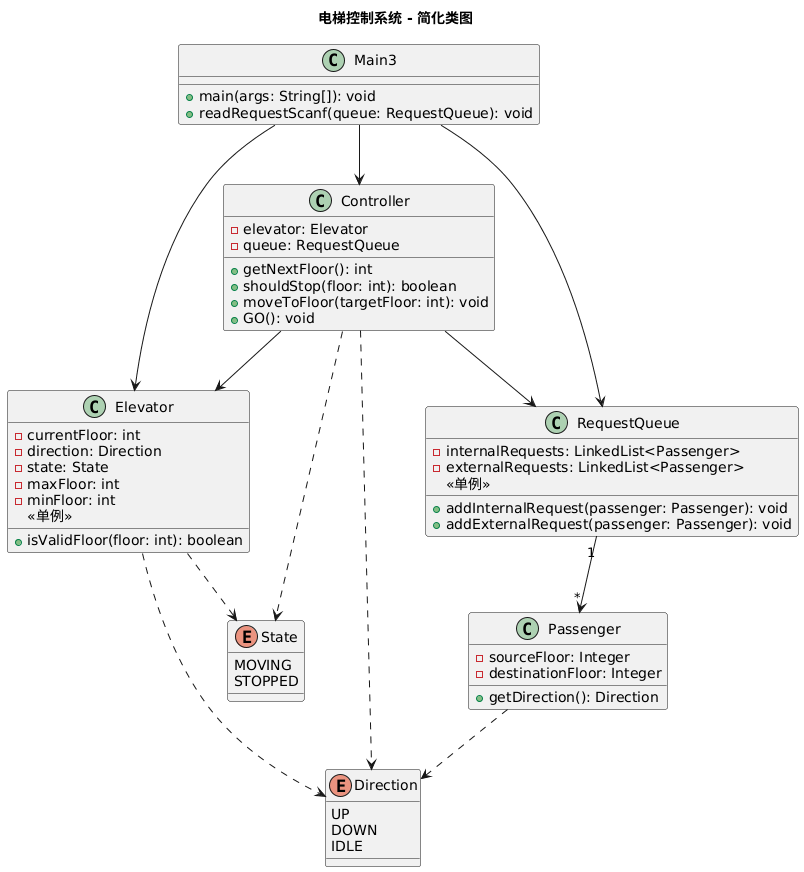
二.采坑心得:
本此迭代用passsenger类代替了两种队列,同时外部请求出现了请求源楼层和请求目标楼层,而我又在输入时处理重复请求就导致读取输入时圈复杂度过高。但核心代码的圈复杂度得到了优化。此外,pta中我有一个得分点一直是运行超时,推测是处理队列请求的逻辑以及出队的时机有问题,导致某个情况下代码陷入了死循环。
三.改进建议:
根据踩坑心得,建议单独写一个处理输入的方法把数据全部读取到队列后再处理;另外,建议出队的时机放到电梯运行过程中,而不是获取到下一目标楼层后直接出队。
总结:
第一次作业思维还停留在面向过程。代码的核心是一个庞大的控制流程,用大量的if-else和状态变量来描述电梯“下一步该怎么做”。这导致主运行方法异常庞大,圈复杂度极高。二、三次作业逐渐学会了面向对象的“职责分配”。我意识到,系统应该由多个各司其职的对象协作完成,另外,让我感悟更深的是,类功能的分配更大程度上是让代码封装性更好,可读性更高,而设计出好的方法才更能降低代码的圈复杂度。除了知识上的收获,我还意识到,自己动手做一个较为复杂的项目,能大大提高自己思考,创作,解决问题的能力。
意见:通过本次大作业,我觉得完成困难的原因是一些联系实际的的情况没有考虑到,建议可以用(注意)为同学们标注出一些特殊情况。另外,二三次作业都给出了类图,我觉得有些限制了我的思维,我的大部分代码都是完全按照给出的类图设计的,建议只给出基本要求,各个类的方法可以让同学自己先思考,后期再给出更好的类设计。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号