4、基础语法,条件判断,循环语句 5、绑定样式,触发操作
一、vue 常用的指令
v-if 指令 # 条件渲染
v-show # 条件渲染
v-else # 条件渲染
v-for # 循环遍历
v-bind # 绑定样式
v-on # 绑定动作
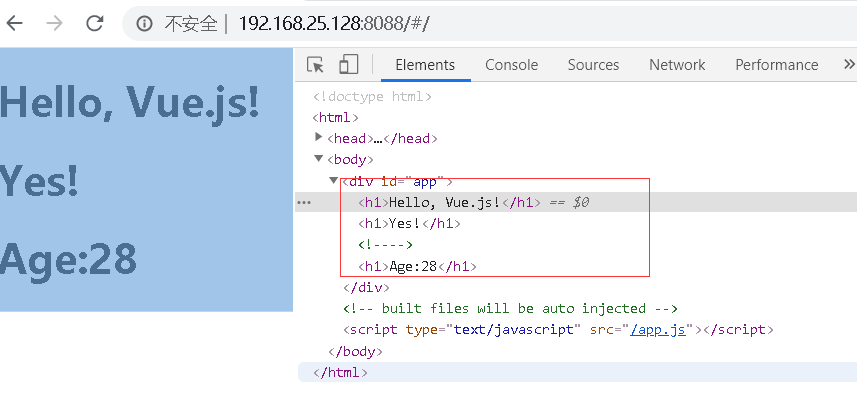
v-if 指令

<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>Hello, Vue.js!</h1>
<h1 v-if="yes">Yes!</h1> <!--// 拿到正确返回值则条件成功显示-->
<h1 v-if="no">No!</h1>
<h1 v-if="age >= 25">Age:{{ age }}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return {
yes: true,
no: false,
age: 28,
}
}
}
</script>
 、
、
可以是布尔运算和条件判断:当然也可以用v-show,但是v-show 和v-if 的区别是,v-if 不会把不满足的条件渲染到html
v-show 指令

<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>Hello, Vue.js!</h1>
<h1 v-show="yes">Yes!</h1> <!--// 拿到正确返回值则条件成功显示-->
<h1 v-show="no">No!</h1>
<h1 v-show="age >= 25">Age:{{ age }}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return {
yes: true,
no: false,
age: 28,
}
}
}
</script>
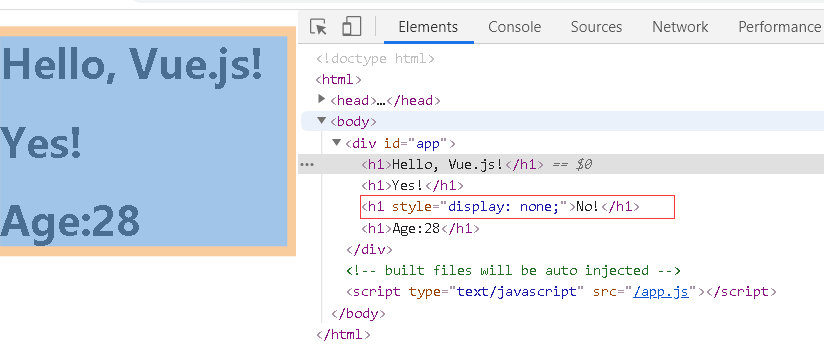
v-shou而是展示成display: none
v-else 指令 条件判断
举例 判断age 小于 25 时,返回 else 参数,了解原理,主要用于登录页面

<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>Hello, Vue.js!</h1>
<h1 v-if="yes">Yes!</h1> <!--// 拿到正确返回值则条件成功显示-->
<h1 v-if="no">No!</h1>
<h1 v-if="age >= 25">Age:{{ age }}</h1>
<h1 v-else="age">Age<=25</h1> <!--不满足v-if时,生效-->
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return {
yes: true,
no: false,
age: 18,
}
}
}
</script>
用户已经登录,显示注销,没有则登录,后面配合token判断这个值

<template>
<div id="app">
<button v-if="admin">注销</button>
<button v-else>登录</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return {
admin: false // 用户已经登录,显示注销,没有则登录,后面配合token判断这个值
}
},
}
</script>
v-for 遍历循环
v-for 遍历一个
元组或列表
循环的时候可以加 index位置,

<template>
<div id="app">
<li v-for="a in datalist">
{{a}}
</li>
<li v-for="(value,index) in datalist"> <!--打印所在的位置-->
{{value}}:{{index}}
</li>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return {
datalist:['张三','李四','王五']
}
},
}
</script>
字典循环

<template>
<div id="app">
<li v-for="(value,key,index) in datalist"> <!--字典循环key value与Python相反-->
{{key}}:{{value}}:{{index}} <!--值格式 a:张三:0 -->
</li>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return {
datalist: {'a':'张三','b':'李四','c':'wangwu'}
}
},
}
</script>
循环字典里数据到table表格,字典外面是 [] 列表形式

<template>
<div id="app">
<table border="1"> <!--table表格-->
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Name</th> <!--标题-->
<th>Age</th>
<th>Sex</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody> <!--body数据-->
<tr v-for="person in people">
<td>{{ person.name }}</td>
<td>{{ person.age }}</td>
<td>{{ person.sex }}</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return {
people: [{ // 循环 字典里数据到table表格,字典外面是 [] 列表形式
name: 'Jack',
age: 30,
sex: 'Male'
}, {
name: 'Bill',
age: 26,
sex: 'Male'
}, {
name: 'Tracy',
age: 22,
sex: 'Female'
}, {
name: 'Chris',
age: 36,
sex: 'Male'
}]
}
}
}
</script>
5、绑定样式与方法触发
v-bind # 绑定样式
动态地绑定一个或多个特性,或一个组件 prop 到表达式。
在绑定 class 或 style 特性时,支持其它类型的值,如数组或对象。可以通过下面的教程链接查看详情。
在绑定 prop 时,prop 必须在子组件中声明。可以用修饰符指定不同的绑定类型。
没有参数时,可以绑定到一个包含键值对的对象。注意此时 class 和 style 绑定不支持数组和对象。
<!-- 绑定一个属性 --> <img v-bind:src="imageSrc"> <!-- 缩写 --> <img :src="imageSrc"> <!-- with inline string concatenation --> <img :src="'/path/to/images/' + fileName"> <!-- class 绑定 --> <div :class="{ red: isRed }"></div> <div :class="[classA, classB]"></div> <div :class="[classA, { classB: isB, classC: isC }]"> <!-- style 绑定 --> <div :style="{ fontSize: size + 'px' }"></div> <div :style="[styleObjectA, styleObjectB]"></div> <!-- 绑定一个有属性的对象 --> <div v-bind="{ id: someProp, 'other-attr': otherProp }"></div> <!-- 通过 prop 修饰符绑定 DOM 属性 --> <div v-bind:text-content.prop="text"></div> <!-- prop 绑定. “prop” 必须在 my-component 中声明。 --> <my-component :prop="someThing"></my-component> <!-- XLink --> <svg><a :xlink:special="foo"></a></svg>
绑定跳转连接 v-bind 在a标签可以绑定 data定义的url变量

<<template> <div id="app"> <a v-bind:href="url">好123跳转连接</a> <!--v-bind可以绑定返回url值--> <br> <a href="http://www.baidu.com">百度跳转连接</a> <!--不加v-bind,只能直接写地址,填写变量url不生效--> <br> <a :href="url">好123</a> <!--简写 :href 加上冒号可以实现绑定变量--> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'App', data(){ return { url: "http://www.hao123.com" } } } </script> App.vue
绑定样式

<template> <div id="app"> <a :class="classstatus">连接</a> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'App', data(){ return { classstatus: "red" } } }

<template> <div id="app"> <a v-bind:style="[a,b]">连接</a> <br> <br> <a :style="[a,b]">连接2</a> <!--简写--> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'App', data(){ return { a:{'color':'red'}, b:{'backgroundColor':'blue'} } } } </script>
Element-UI https://element.eleme.cn/
绑定Element样式

<template> <div id="app"> <el-button v-bind:type="status">{{host_status}}</el-button> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'App', data(){ return { status:'danger', host_status:'主机异常' } } } </script>
v-on # 绑定动作
v-on 绑定触发操作,调用Elemet-ui 按钮样式。
理解:script中的参数: data存放数据地方 methods 触发操作动作地方

<template> <div id="app"> <el-button v-on:click="say">触发</el-button> <el-button type="primary" round>测试引入按钮样式主要按钮</el-button> <el-button v-bind:type="status" round>{{ message}}</el-button> <!--传值Element-ui的type样式,message 状态信息--> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'App', data(){ // 存放数据地方 return { status:'success', message: '主机正常' } }, methods: { // methods 触发操作动作地方 say(){ this.status='warning', this.message='主机异常' } } } </script> <!--v-on:clieck="say"--> <!--<el-button @click="say">say hi</el-button>--> <!--v-bind:type ==== :type-->
本文来自博客园,作者:王竹笙,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/edeny/p/12591676.html







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号