基于C#的内网穿透学习笔记(附源码)
如何让两台处在不同内网的主机直接互连?你需要内网穿透!
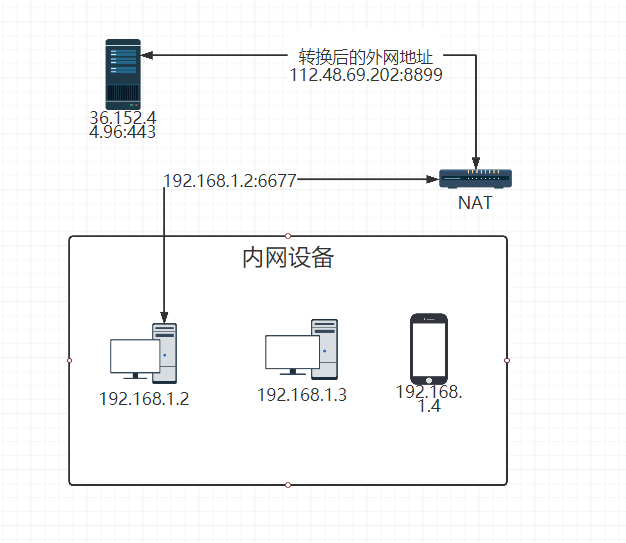
上图是一个非完整版内外网通讯图由内网端先发起,内网设备192.168.1.2:6677发送数据到外网时候必须经过nat会转换成对应的外网ip+端口,然后在发送给外网设备,外网设备回复数据也是发给你的外网ip+端口。这只是单向的内去外,那反过来,如果外网的设备需要主动访问我局域网里的某一个设备是无法访问的,因为这个时候还没做nat转换所以外网不知道你内网设备的应用具体对应的是哪个端口,这个时候我们就需要内网穿透了,内网穿透也叫NAT穿透;
(2)Address-Restricted cone NAT :限制地址,即只接收曾经发送到对端的IP地址来的数据包。
一旦一个内部地址(iAddr:port1)映射到外部地址(eAddr:port2),所有发自iAddr:port1的包都经由eAddr:port2向外发送。任意外部主机(hostAddr:any)都能通过给eAddr:port2发包到达iAddr:port1的前提是:iAddr:port1之前发送过包到hostAddr:any. "any"也就是说端口不受限制(只需知道某个转换后的外网ip+端口即可。)
(3)Port-Restricted cone NAT:类似受限制锥形NAT(Restricted cone NAT),但是还有端口限制。
(4)Symmetric NAT(对称NAT)
/// <summary> /// 打洞服务端,非常的简单,接收两个连接并且转发给对方; /// </summary> public class ServerListener : IServerListener { IPEndPoint EndPoint { get; set; } //消息委托 public delegate void EventMsg(object sender, string e); public static object obj = new object(); //通知消息 public event EventMsg NoticeMsg; //接收事件 public event EventMsg ReceivedMsg; /// <summary> /// 上次链接的 /// </summary> private Socket Previous; public ServerListener(IPEndPoint endpoint) { this.EndPoint = endpoint; } private Socket listener; public void Start() { this.listener = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); var connectArgs = new SocketAsyncEventArgs(); listener.Bind(EndPoint); listener.Listen(2); EndPoint = (IPEndPoint)listener.LocalEndPoint; connectArgs.Completed += OnAccept; //是否同步就完成了,同步完成需要自己触发 if (!listener.AcceptAsync(connectArgs)) OnAccept(listener, connectArgs); } byte[] bytes = new byte[400]; private void OnAccept(object sender, SocketAsyncEventArgs e) { Socket socket = null; try { var remoteEndPoint1 = e.AcceptSocket.RemoteEndPoint.ToString(); NoticeMsg?.Invoke(sender, $"客户端:{remoteEndPoint1}连接上我了!\r\n"); SocketAsyncEventArgs readEventArgs = new SocketAsyncEventArgs(); readEventArgs.Completed += OnSocketReceived; readEventArgs.UserToken = e.AcceptSocket; readEventArgs.SetBuffer(bytes, 0, 400); if (!e.AcceptSocket.ReceiveAsync(readEventArgs)) OnSocketReceived(e.AcceptSocket, readEventArgs); lock (obj) { socket = e.AcceptSocket; //上次有链接并且链接还”健在“ if (Previous == null||! Previous.Connected) { Previous = e.AcceptSocket; } else { //Previous.SendAsync()..? Previous.Send(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(remoteEndPoint1 + "_1")); socket.Send(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(Previous.RemoteEndPoint.ToString() + "_2")); NoticeMsg?.Invoke(sender, $"已经通知双方!\r\n"); Previous = null; } } e.AcceptSocket = null; if (e.SocketError != SocketError.Success) throw new SocketException((int)e.SocketError); if(!listener.AcceptAsync(e)) OnAccept(listener, e); } catch { socket?.Close(); } } public void Close() { using (listener) { // listener.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both); listener.Close(); } //throw new NotImplementedException(); } /// <summary> /// 此处留有一个小BUG,接收的字符串大于400的时候会有问题;可以参考客户端修改 /// </summary> public void OnSocketReceived(object sender, SocketAsyncEventArgs e) { Socket socket = e.UserToken as Socket; var remoteEndPoint = socket.RemoteEndPoint.ToString(); try { if (e.BytesTransferred > 0 && e.SocketError == SocketError.Success) { ReceivedMsg?.Invoke(sender, $"收到:{remoteEndPoint}发来信息:{Encoding.UTF8.GetString(e.Buffer, 0, e.BytesTransferred)}\r\n"); } else { socket?.Close(); NoticeMsg?.Invoke(sender, $"链接:{remoteEndPoint}释放啦!\r\n"); return; } if (!socket.ReceiveAsync(e)) OnSocketReceived(socket, e); } catch { socket?.Close(); } //{ // if (!((Socket)sender).AcceptAsync(e)) // OnSocketReceived(sender, e); //} //catch //{ // return; //} } }
2.客户端类 PeerClient用BeginReceive和EndReceive实现异步;
public class StateObject { public Socket workSocket = null; public const int BufferSize = 100; public byte[] buffer = new byte[BufferSize]; public List<byte> buffers = new List<byte>(); //是不是和服务器的链接 public bool IsServerCon = false; } /// <summary> /// 打洞节点客户端 实现的功能: /// 连接服务器获取对方节点ip /// 请求对方ip(打洞) /// 根据条件判断是监听连接还是监听等待连接 /// </summary> public class PeerClient : IPeerClient { //ManualResetEvent xxxxDone = new ManualResetEvent(false); //Semaphore /// <summary> /// 当前链接 /// </summary> public Socket Client { get;private set; } #region 服务端 public string ServerHostName { get;private set; } public int ServerPort { get; private set; } #endregion #region 接收和通知事件 public delegate void EventMsg(object sender, string e); //接收事件 public event EventMsg ReceivedMsg; //通知消息 public event EventMsg NoticeMsg; #endregion //本地绑定的节点 private IPEndPoint LocalEP; public PeerClient(string hostname, int port) { Client = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); this.ServerHostName = hostname; this.ServerPort = port; } /// <summary> /// 初始化客户端(包括启动) /// </summary> public void Init() { try { Client.Connect(ServerHostName, ServerPort); } catch (SocketException ex) { NoticeMsg?.Invoke(Client, $"连接服务器失败!{ex}!\r\n"); throw; } catch (Exception ex) { NoticeMsg?.Invoke(Client, $"连接服务器失败!{ex}!\r\n"); throw; } NoticeMsg?.Invoke(Client, $"连接上服务器了!\r\n"); var _localEndPoint = Client.LocalEndPoint.ToString(); LocalEP = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse(_localEndPoint.Split(':')[0]) , int.Parse(_localEndPoint.Split(':')[1])); Receive(Client); } private void Receive(Socket client) { try { StateObject state = new StateObject(); state.workSocket = client; state.IsServerCon = true; client.BeginReceive(state.buffer, 0, StateObject.BufferSize, 0, new AsyncCallback(ReceiveCallback), state); } catch (Exception e) { NoticeMsg?.Invoke(Client, $"接收消息出错了{e}!\r\n"); } } private void ReceiveCallback(IAsyncResult ar) { try { var state = (StateObject)ar.AsyncState; Socket _client = state.workSocket; //因为到这边的经常Connected 还是true //if (!_client.Connected) //{ // _client.Close(); // return; //} SocketError error = SocketError.Success; int bytesRead = _client.EndReceive(ar,out error); if (error == SocketError.ConnectionReset) { NoticeMsg?.Invoke(Client, $"链接已经释放!\r\n"); _client.Close(); _client.Dispose(); return; } if (SocketError.Success!= error) { throw new SocketException((int)error); } var arr = state.buffer.AsQueryable().Take(bytesRead).ToArray(); state.buffers.AddRange(arr); if (bytesRead >= state.buffer.Length) { _client.BeginReceive(state.buffer, 0, StateObject.BufferSize, 0, new AsyncCallback(ReceiveCallback), state); ////state.buffers.CopyTo(state.buffers.Count, state.buffer, 0, bytesRead); //_client.BeginReceive(state.buffer, 0, StateObject.BufferSize, 0, // new AsyncCallback(ReceiveCallback), state); } else { var _msg = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(state.buffers.ToArray()); ReceivedMsg?.Invoke(_client, _msg); if (state.IsServerCon) { _client.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both); _client.Close(); int retryCon = _msg.Contains("_1") ? 1 : 100; _msg = _msg.Replace("_1", "").Replace("_2", ""); TryConnection(_msg.Split(':')[0], int.Parse(_msg.Split(':')[1]), retryCon); return; } state = new StateObject(); state.IsServerCon = false; state.workSocket = _client; _client.BeginReceive(state.buffer, 0, StateObject.BufferSize, 0, new AsyncCallback(ReceiveCallback), state); } } catch (SocketException ex) { //10054 NoticeMsg?.Invoke(Client, $"链接已经释放!{ex}!\r\n"); } catch (Exception e) { NoticeMsg?.Invoke(Client, $"接收消息出错了2{e}!\r\n"); } } /// <summary> /// 打洞或者尝试链接 /// </summary> private void TryConnection(string remoteHostname, int remotePort,int retryCon) { Client = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); Client.SetSocketOption(SocketOptionLevel.Socket, SocketOptionName.ReuseAddress, true); var _iPRemotePoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse(remoteHostname), remotePort); Client.Bind(LocalEP); System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(retryCon==1?1:3*1000); for (int i = 0; i < retryCon; i++) { try { Client.Connect(_iPRemotePoint); NoticeMsg?.Invoke(Client, $"已经连接上:{remoteHostname}:{remotePort}!\r\n"); StateObject state = new StateObject(); state.workSocket = Client; state.IsServerCon = false; Client.BeginReceive(state.buffer, 0, StateObject.BufferSize, 0, new AsyncCallback(ReceiveCallback), state); return; } catch { NoticeMsg?.Invoke(Client, $"尝试第{i+1}次链接:{remoteHostname}:{remotePort}!\r\n"); } } if (retryCon==1) { Listening(LocalEP.Port); return; } NoticeMsg?.Invoke(Client, $"尝试了{retryCon}次都没有办法连接到:{remoteHostname}:{remotePort},凉了!\r\n"); } /// <summary> /// 如果连接不成功,因为事先有打洞过了,根据条件监听 等待对方连接来 /// </summary> private void Listening(int Port) { try { Client = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); Client.SetSocketOption(SocketOptionLevel.Socket, SocketOptionName.ReuseAddress, true); Client.Bind(new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Any, Port)); Client.Listen((int)SocketOptionName.MaxConnections); NoticeMsg?.Invoke(Client, $"开始侦听断开等待链接过来!\r\n"); StateObject state = new StateObject(); state.IsServerCon = false; var _socket = Client.Accept();//只有一个链接 不用BeginAccept Client.Close();//关系现有侦听 Client = _socket; state.workSocket = Client; NoticeMsg?.Invoke(Client, $"接收到来自{Client.RemoteEndPoint}的连接!\r\n"); Client.BeginReceive(state.buffer, 0, StateObject.BufferSize, 0, new AsyncCallback(ReceiveCallback), state); } catch (Exception ex) { NoticeMsg?.Invoke(Client, $"监听出错了{ex}凉了!\r\n"); } //scoket.send } /// <summary> /// 本例子只存在一个成功的链接,对成功的连接发送消息! /// </summary> /// <param name="strMsg"></param> public void Send(string strMsg) { byte[] bytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(strMsg); Client.BeginSend(bytes, 0, bytes.Length, 0, new AsyncCallback(SendCallback), Client); } private void SendCallback(IAsyncResult ar) { try { Socket _socket = (Socket)ar.AsyncState; //if(ar.IsCompleted) _socket.EndSend(ar); } catch (Exception e) { NoticeMsg?.Invoke(Client, $"发送消息出错了{e}!\r\n"); } } }
完整代码:
https://gitee.com/qqljcn/zsg_-peer-to-peer
Task+(TcpClient+TcpListener )|(UdpClient)实现 tcp|udp的打洞!这个就不贴代码了直接放码云连接
https://gitee.com/qqljcn/zsg_-peer-to-peer_-lite
1.本人是个老菜鸟代码仅供参考,都是挺久以前写的也没有经过严格的测试仅能演示这个例子,有不成熟的地方,烦请各位大神海涵指教;
2.不要都用本机试这个例子,本机不走nat
3.然后udp因为是无连接的所以打孔成功后不要等太久再发消息,nat缓存一过就失效了!
4.确定自己不是对称型nat的话,如果打洞不成功,那就多试几次!
5 .我这个例子代码名字叫 PeerToPeer 但不是真的p2p, 微软提供了p2p的实现 在using System.Net.PeerToPeer命名空间下。
以上是通过nat的方式,另外还有一种方式是,通过一个有外网ip的第三方服务器转发像 花生壳、nat123这类软件,也有做个小程序,并且自己在用以后演示;






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号