RandomAccess 接口的作用
RandomAccess 接口的作用
1、简介
RandomAccess 接口是一个空接口,只是一个标记接口,用以标记实现的List集合具备快速随机访问的能力。那么什么是随机访问的能力呢?其实很简单,随机访问就是随机的访问List中的任何一个元素。所有的List实现都支持随机访问的,只是基于基本结构的不同,实现的速度不同罢了,这里的快速随机访问,那么就不是所有List集合都支持了。
- ArrayList:基于数组实现,天然带下标,可以实现常量级的随机访问,复杂度为O(1)。
- LinkedList:基于链表实现,随机访问需要依靠遍历实现,复杂度为O(n)。
public interface RandomAccess { }
二者的差距显而易见,所以ArrayList具备快速随机访问功能,而LinkedList没有。我们也能看到:
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{}
2、测试
2.1、实现了 RandomAccess 的 ArrayList
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 500000; i++) {
arrayList.add(i);
}
long s = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {
Integer integer = arrayList.get(i);
}
long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
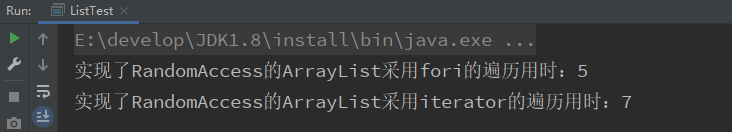
System.out.println("实现了RandomAccess的ArrayList采用fori的遍历用时:" + (e - s));
long s2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
Iterator<Integer> iterator = arrayList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer next = iterator.next();
}
long e2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("实现了RandomAccess的ArrayList采用iterator的遍历用时:" + (e2 - s2));
}
测试结果:
2.2、没有实现 RandomAccess的 LinkedList
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
linkedList.add(i);
}
long s = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.size(); i++) {
Integer integer = linkedList.get(i);
}
long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
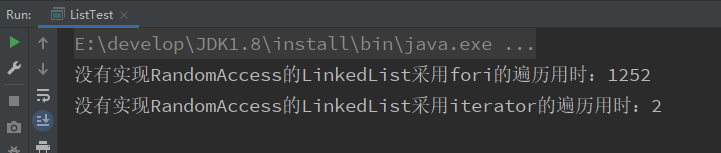
System.out.println("没有实现RandomAccess的LinkedList采用fori的遍历用时:" + (e - s));
long s2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
Iterator<Integer> iterator = linkedList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer next = iterator.next();
}
long e2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("没有实现RandomAccess的LinkedList采用iterator的遍历用时:" + (e2 - s2));
}
测试结果:
3、总结
ArrayList用for循环遍历比iterator迭代器遍历快,LinkedList用iterator迭代器遍历比for循环遍历快,所以说,当我们在做项目时,应该考虑到List集合的不同子类采用不同的遍历方式,能够提高性能!那怎么判断出接收的List子类是ArrayList还是LinkedList呢? 这时就需要用 instanceof 来判断List集合子类是否实现RandomAccess接口!
public void loop(List list) {
if (list instanceof RandomAccess) {
// for循环
System.out.println("采用for循环遍历");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
} else {
// 迭代器
System.out.println("采用迭代器遍历");
Iterator it = list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号