Mybatis 的插件原理以及如何自定义插件
Mybatis 的插件原理以及如何自定义插件
1、简介
Mybatis的分页插件相信大家都使用过,那么可知道其中的实现原理?分页插件就是利用的Mybatis中的插件机制实现的,在Executor 的query 执行前后进行分页处理。此篇文章就来介绍以下Mybatis的插件机制以及在底层是如何实现的。本篇文章讲的一切内容都是基于Mybatis3.5 和SpringBoot-2.3.3.RELEASE 。
2、什么是插件?
插件是Mybatis中的最重要的功能之一,能够对特定组件的特定方法进行增强。MyBatis 允许你在映射语句执行过程中的某一点进行拦截调用。
默认情况下,MyBatis 允许使用插件来拦截的方法调用,包括:
- Executor: update , query , flushStatements , commit , rollback , getTransaction , close , isClosed
- ParameterHandler: getParameterObject , setParameters
- ResultSetHandler: handleResultSets , handleOutputParameters
- StatementHandler: prepare , parameterize , batch , update , query
3、如何自定义插件?
插件的实现其实很简单,只需要实现Mybatis提供的 Interceptor 这个接口即可, 源码如下:
public interface Interceptor {
// 拦截的方法
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
// 返回拦截器的代理对象
Object plugin(Object target);
// 设置一些属性
void setProperties(Properties properties);
}
4、举个栗子
有这样一个需求:需要在Mybatis执行的时候篡改selectByUserId 的参数值。
分析:修改SQL的入参,应该在哪个组件的哪个方法上拦截篡改呢?研究过源码的 估计都很清楚的知道, ParameterHandler 中的setParameters() 方法就是对参数进行处理的。因此肯定是拦截这个方法是最合适。
自定义的插件如下:
/**
* @Intercepts 注解标记这是一个拦截器, 其中可以指定多个@Signature
* @Signature 指定该拦截器拦截的是四大对象中的哪个方法
* type:拦截器的四大对象的类型
* method:拦截器的方法,方法名
* args:入参的类型,可以是多个,根据方法的参数指定,以此来区分方法的重载
*/
@Intercepts(
{@Signature(type = ParameterHandler.class, method = "setParameters", args = {PreparedStatement.class})})
public class ParameterInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("拦截器执行:" + invocation.getTarget());
// 目标对象
Object target = invocation.getTarget();
// 获取目标对象中所有属性的值,因为ParameterHandler使用的是DefaultParameterHandler,因此里面的所有的属性都封装在其中
MetaObject metaObject = SystemMetaObject.forObject(target);
// 使用xxx.xxx.xx的方式可以层层获取属性值,这里获取的是mappedStatement中的id值
String value = (String) metaObject.getValue("mappedStatement.id");
// 如果是指定的查询方法
if ("cn.cb.demo.dao.UserMapper.selectByUserId".equals(value)) {
// 设置参数的值是admin_1,即是设置id=admin_1,因为这里只有一个参数,可以这么设置,如果有多个需要需要循环
metaObject.setValue("parameterObject", "admin_1");
}
// 执行目标方法
return invocation.proceed();
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
// 如果没有特殊定制,直接使用Plugin这个工具类返回一个代理对象即可
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
}
}
- intercept 方法: 最终会拦截的方法,最重要的一个方法。
- plugin 方法: 返回一个代理对象,如果没有特殊要求,直接使用Mybatis的工具类Plugin 返回即可。
- setProperties : 设置一些属性,不重要。
用到哪些注解?
自定义插件需要用到两个注解,分别是: @Intercepts 和 @Signature 。
- @Intercepts :标注在实现类上,表示这个类是一个插件的实现类。
- @Signature :作为@Intercepts 的属性,表示需要增强Mybatis的某些组件中的某些方法(可以指定多个)。常用的属性如下:
Class<?> type() :指定哪个组件( Executor 、ParameterHandler 、ResultSetHandler 、 StatementHandler );
String method() :指定增强组件中的哪个方法,直接写方法名称。
Class<?>[] args() :方法中的参数,必须一一对应,可以写多个;这个属性非常重用,区分重载方法。
5、如何注入Mybatis?
上面已经将插件定义好了,那么如何注入到Mybatis中使其生效呢? 前提:由于本篇文章的环境是SpringBoot+Mybatis ,因此讲一讲如何在SpringBoot中将插件注入到Mybatis中。在Mybatis的自动配置类MybatisAutoConfiguration 中,注入SqlSessionFactory 的时候,有如下一段代码:
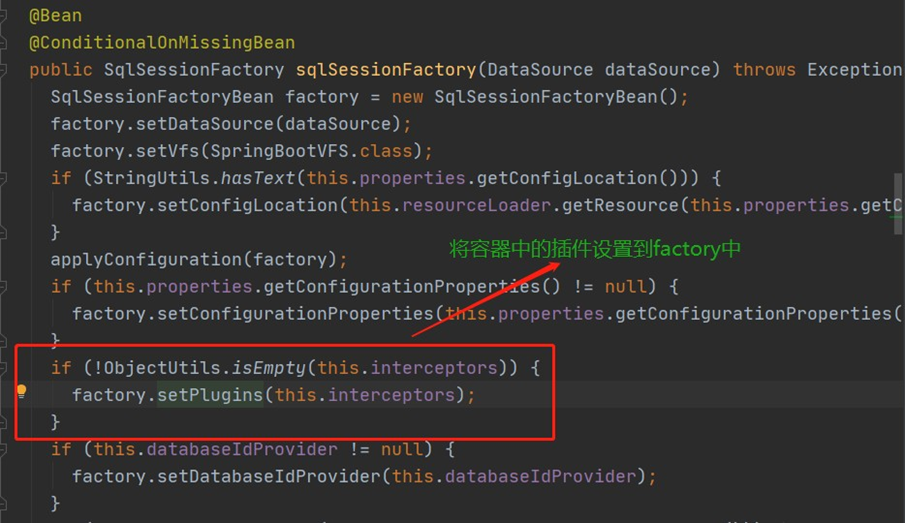
上图中的this.interceptors 是什么,从何而来,其实就是从容器中的获取的 ,如下一段代码:
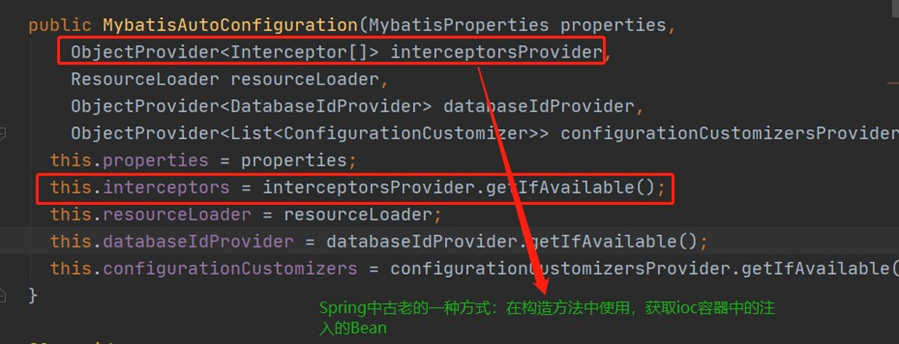
从上图我们知道,这插件最终还是从IOC容器中获取的Interceptor[] 这个Bean ,因此我们只需要在配置类中注入这个Bean 即可,如下代码:
/**
* @Configuration:这个注解标注该类是一个配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class MybatisConfig{
/**
* @Bean : 该注解用于向容器中注入一个Bean
* 注入Interceptor[]这个Bean
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Interceptor[] interceptors(){
// 创建ParameterInterceptor这个插件
ParameterInterceptor parameterInterceptor = new ParameterInterceptor();
// 放入数组返回
return new Interceptor[]{parameterInterceptor};
}
}
6、测试
此时自定义的插件已经注入了Mybatis中了,现在测试看看能不能成功执行呢?测试代码如下:
@Test
void contextLoads() {
//传入的是1222
UserInfo userInfo = userMapper.selectByUserId("1222");
System.out.println(userInfo);
}
测试代码传入的是1222 ,由于插件改变了入参,因此查询出来的应该是admin_1 这个人。
7、插件原理分析
插件的原理其实很简单,就是在创建组件的时候生成代理对象( Plugin ),执行组件方法的时候拦截即可。下面就来详细介绍一下插件在Mybatis底层是如何工作的 ? Mybatis的四大组件都是在Mybatis的配置类Configuration 中创建的,具体的方法如下:
1、 创建Executor
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
// 调用pluginAll方法,生成代理对象
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
2、创建ParameterHandler
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
// 调用pluginAll方法,生成代理对象
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
3、创建ResultSetHandler
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds,
ParameterHandler parameterHandler, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterHandler, resultHandler,
boundSql, rowBounds);
// 调用pluginAll方法,生成代理对象
resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}
4、创建StatementHandler
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject,
RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds,
resultHandler, boundSql);
// 调用pluginAll方法,生成代理对象
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
从上面的源码可以知道,创建四大组件的方法中都会执行pluginAll() 这个方法来生成一个代理对象。具体如何生成的,下面详解。
7.2、如何生成代理对象?
创建四大组件过程中都执行了pluginAll() 这个方法,此方法源码如下:
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
//循环遍历插件
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
// 调用插件的plugin()方法
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
// 返回
return target;
}
pluginAll() 方法很简单,直接循环调用插件的plugin() 方法,但是我们调用的是Plugin.wrap(target, this) 这行代码,因此要看一下wrap() 这个方法的源码,如下:
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
// 获取注解的@signature的定义
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
// 目标类
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
// 获取需要拦截的接口
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
// 生成代理对象
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
return target;
}
Plugin.wrap() 这个方法的逻辑很简单,判断这个插件是否是拦截对应的组件, 如果拦截了,生成代理对象( Plugin )返回,没有拦截直接返回,上面例子中生成的代理对象如下图:
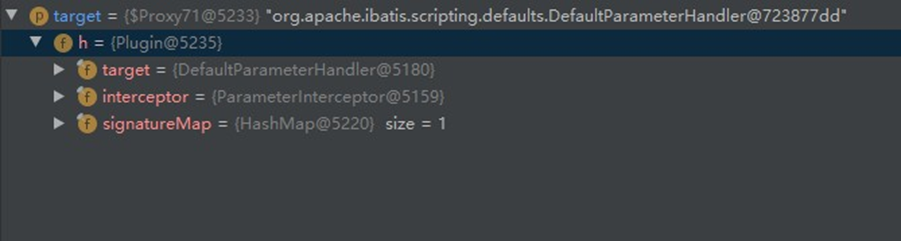
7.3、如何执行?
上面讲了Mybatis启动的时候如何根据插件生成代理对象的( Plugin )。现在就来看看这个代理对象是如何执行的?
既然是动态代理,肯定会执行的invoke() 这个方法, Plugin 类中的invoke() 源码如下:
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 获取@signature标注的方法
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
// 如果这个方法被拦截了
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
// 直接执行插件的intercept()这个方法
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
// 没有被拦截,执行原方法
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
逻辑很简单,这个方法被拦截了就执行插件的intercept() 方法,没有被拦截, 则执行原方法。
还是以上面自定义的插件来看看执行的流程:setParameters() 这个方法在PreparedStatementHandler 中被调用, 如下图:
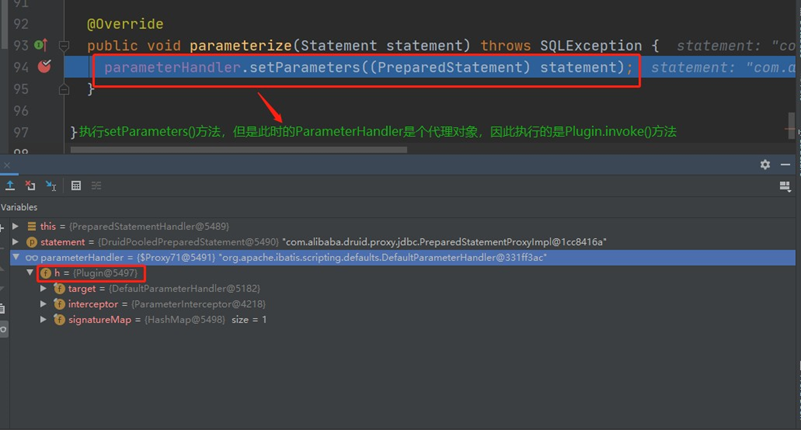
执行invoke() 方法,发现setParameters() 这个方法被拦截了,因此直接执行的是intercept() 方法。
8、总结
Mybatis中插件的原理其实很简单,分为以下几步:
- 在项目启动的时候判断组件是否有被拦截,如果没有直接返回原对象。
- 如果有被拦截,返回动态代理的对象( Plugin )。
- 执行到的组件的中的方法时,如果不是代理对象,直接执行原方法
- 如果是代理对象,执行Plugin 的invoke() 方法。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号