(九) SpringMVC JSON 数据转换
(九) SpringMVC JSON 数据转换
1、简介:
我们知道,Http请求和响应报文本质上都是一串字符串,当请求报文来到java世界,它会被封装成为一个ServletInputStream的输入流,供我们读取报文。响应报文则是通过一个ServletOutputStream的输出流,来输出响应报文。我们从流中,只能读取到原始的字符串报文,同样,我们往输出流中,也只能写原始的字符。而在java世界中,处理业务逻辑,都是以一个个有业务意义的对象为处理维度的,那么在报文到达SpringMVC和从SpringMVC出去,都存在一个字符串到java对象的阻抗问题。这一过程,不可能由开发者手工转换。
在SpringMVC中,它是 HttpMessageConverter 机制。我们先来看看这个接口。
2、HttpMessageConverter 接口
package org.springframework.http.converter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.http.HttpInputMessage;
import org.springframework.http.HttpOutputMessage;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
public interface HttpMessageConverter<T> {
boolean canRead(Class<?> clazz, MediaType mediaType);
boolean canWrite(Class<?> clazz, MediaType mediaType);
List<MediaType> getSupportedMediaTypes();
T read(Class<? extends T> clazz, HttpInputMessage inputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException;
void write(T t, MediaType contentType, HttpOutputMessage outputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException;
}
HttpMessageConverter 接口的定义出现了成对的canRead(),read()和canWrite(),write()方法,MediaType是对请求的Media Type属性的封装。
举个例子,当我们声明了下面这个处理方法:
@RequestMapping(value="/string", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public @ResponseBody String readString(@RequestBody String string) {
return "Read string '" + string + "'";
}
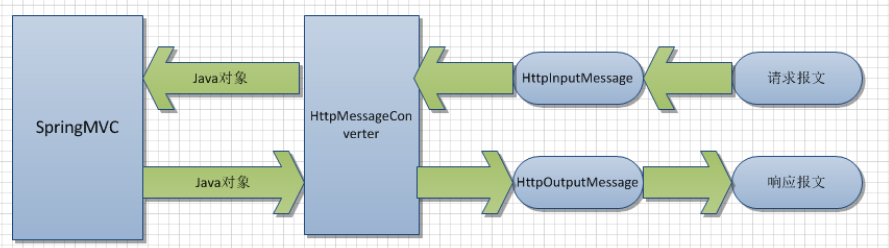
在SpringMVC进入readString方法前,会根据@RequestBody注解选择适当的HttpMessageConverter实现类来将请求参数解析到string变量中,具体来说是使用了StringHttpMessageConverter类,它的canRead()方法返回true,然后它的read()方法会从请求中读出请求参数,绑定到readString()方法的string变量中。
当SpringMVC执行readString方法后,由于返回值标识了@ResponseBody,SpringMVC将使用StringHttpMessageConverter的write()方法,将结果作为String值写入响应报文,当然,此时canWrite()方法返回true。
我们可以用下面的图,简单描述一下这个过程:
3、 RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor
将上述过程集中描述的一个类是 org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor,这个类同时实现了 HandlerMethodArgumentResolver和 HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler 两个接口。前者是将请求报文绑定到处理方法形参的策略接口,后者则是对处理方法返回值进行处理的策略接口。两个接口的源码如下:
3.1、HandlerMethodArgumentResolver
package org.springframework.web.method.support;
import org.springframework.core.MethodParameter;
import org.springframework.web.bind.WebDataBinder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.support.WebDataBinderFactory;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.NativeWebRequest;
public interface HandlerMethodArgumentResolver {
boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter);
Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest,
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception;
}
3.2、 HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler
package org.springframework.web.method.support;
import org.springframework.core.MethodParameter;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.NativeWebRequest;
public interface HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler {
boolean supportsReturnType(MethodParameter returnType);
void handleReturnValue(Object returnValue,
MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception;
}
RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor 这个类,同时充当了方法参数解析和返回值处理两种角色。我们从它的源码中,可以找到上面两个接口的方法实现。
3.3、对HandlerMethodArgumentResolver 接口的实现:
public boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter) {
return parameter.hasParameterAnnotation(RequestBody.class);
}
public Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest, WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception {
Object argument = readWithMessageConverters(webRequest, parameter, parameter.getGenericParameterType());
String name = Conventions.getVariableNameForParameter(parameter);
WebDataBinder binder = binderFactory.createBinder(webRequest, argument, name);
if (argument != null) {
validate(binder, parameter);
}
mavContainer.addAttribute(BindingResult.MODEL_KEY_PREFIX + name, binder.getBindingResult());
return argument;
}
3.4、对HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler接口的实现
public boolean supportsReturnType(MethodParameter returnType) {
return returnType.getMethodAnnotation(ResponseBody.class) != null;
}
public void handleReturnValue(Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest)
throws IOException, HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
if (returnValue != null) {
writeWithMessageConverters(returnValue, returnType, webRequest);
}
}
看完上面的代码,整个HttpMessageConverter消息转换的脉络已经非常清晰。因为两个接口的实现,分别是以是否有@RequestBody和@ResponseBody为条件,然后分别调用HttpMessageConverter来进行消息的读写。
4、SpringMVC 与 JSON 类库整合介绍
上面我们了解了原理下面介绍与一些成熟JSON类库的整合就容易了
在 SpringMVC 中,对 jackson 和 gson 都提供了相应的支持,就是如果使用这两个作为 JSON 转换器,只需要添加对应的依赖就可以了,返回的对象和返回的集合、Map 等都会自动转为 JSON,但是,如果使用 fastjson,除了添加相应的依赖之外,还需要自己手动配置HttpMessageConverter 转换器。其实前两个也是使用 HttpMessageConverter 转换器,但是是 SpringMVC 自动提供的,SpringMVC 没有给 fastjson 提供相应的转换器。
4.1、jackson
jackson 是一个使用比较多,时间也比较长的 JSON 处理工具,在SpringBoot中默认使用它。在 SpringMVC中使用 jackson ,只需要添加 jackson 的依赖即可:
<!-- jackson支持包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId>
<version>2.9.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId>
<version>2.9.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.5</version>
</dependency>
依赖添加成功后,凡是在接口中直接返回的对象,集合等等,都会自动转为JSON。在 jackson 中,实现 HttpMessageConverter 的名字叫做 MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter,而这个东西的初始化,则由SpringMVC 来完成。除非自己有一些自定义配置的需求,否则一般来说不需要自己提供 MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter。
4.1.1、Jackson自定义序列化与反序列化
@Configuration
public class JacksonConfig {
@Bean
public Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilderCustomizer customizer() {
return b ->
b.simpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
// long类型转string, 前端处理Long类型,数值过大会丢失精度
.serializerByType(Long.class, ToStringSerializer.instance)
.serializerByType(Long.TYPE, ToStringSerializer.instance)
.serializationInclusion(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL)
//指定反序列化类型,也可以使用@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd")替代。主要是mvc接收日期时使用
.deserializerByType(LocalDate.class, new LocalDateDeserializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd")))
.deserializerByType(LocalDateTime.class, new LocalDateTimeDeserializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")))
// 日期序列化,主要返回数据时使用
.serializerByType(LocalDate.class, new LocalDateSerializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd")))
.serializerByType(LocalDateTime.class, new LocalDateTimeSerializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")));
}
}
4.2、gson
gson 是 Google 推出的一个 JSON 解析器,主要在 Android 开发中使用较多,不过,Web 开发中也是支持这个的,而且 SpringMVC 还针对 Gson 提供了相关的自动化配置,以致我们在项目中只要添加 gson 依赖,就可以直接使用 gson 来做 JSON 解析了。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.code.gson</groupId>
<artifactId>gson</artifactId>
<version>2.8.6</version>
</dependency>
如果项目中,同时存在 jackson 和 gson 的话,那么默认使用的是 jackson,为社么呢?在 org.springframework.http.converter.support.AllEncompassingFormHttpMessageConverter 类的构造方法中,加载顺序就是先加载 jackson 的HttpMessageConverter,后加载 gson 的 HttpMessageConverter。加完依赖之后,就可以直接返回 JSON 字符串了。使用 Gson 时,如果想做自定义配置,则需要自定义 HttpMessageConverter。
4.3、fastjson
fastjson 号称最快的 JSON 解析器,但是也是这三个中 BUG 最多的一个。在 SpringMVC 并没针对 fastjson 提供相应的 HttpMessageConverter,所以,fastjson 在使用时,一定要自己手动配置 HttpMessageConverter(前面两个如果没有特殊需要,直接添加依赖就可以了)
使用 fastjson,我们首先添加 fastjson 依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.60</version>
</dependency>
首先新建一配置类来添加配置 FastJsonHttpMessageConverter,Spring4.x开始推荐使用Java配置加注解的方式,也就是无xml文件,SpringBoot就更是了。
@Configuration
public class HttpMessageConverterConfig {
/**
* 引入Fastjson解析json,不使用默认的jackson
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public HttpMessageConverters fastJsonHttpMessageConverters() {
FastJsonHttpMessageConverter fastConverter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter();
//2、添加fastjson的配置信息
FastJsonConfig fastJsonConfig = new FastJsonConfig();
SerializerFeature[] serializerFeatures = new SerializerFeature[]{
// 是否输出为null的字段,若为null 则显示该字段
// SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue,
// 数值字段如果为null,则输出为0
// SerializerFeature.WriteNullNumberAsZero,
// List字段如果为null,输出为[],而非null
// SerializerFeature.WriteNullListAsEmpty,
// 字符类型字段如果为null,输出为"",而非null
// SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty,
// Boolean字段如果为null,输出为false,而非null
// SerializerFeature.WriteNullBooleanAsFalse,
// Json 格式化
SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat,
// Date的日期转换器
SerializerFeature.WriteDateUseDateFormat,
// 循环引用
SerializerFeature.DisableCircularReferenceDetect,
};
fastJsonConfig.setDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
fastJsonConfig.setSerializerFeatures(serializerFeatures);
fastJsonConfig.setCharset(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
fastConverter.setFastJsonConfig(fastJsonConfig);
fastConverter.setSupportedMediaTypes(Lists.newArrayList(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON));
//4、将convert添加到converters中
HttpMessageConverter<?> converter = fastConverter;
return new HttpMessageConverters(converter);
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号