算法日志8:百特热达斯特
前言
本文为回溯法刷题记录
如何理解回溯法
回溯法解决的问题都可以抽象为树形结构,是的,我指的是所有回溯法的问题都可以抽象为树形结构!
因为回溯法解决的都是在集合中递归查找子集,集合的大小就构成了树的宽度,递归的深度就构成了树的深度。
递归就要有终止条件,所以必然是一棵高度有限的树(N叉树)。
回溯三部曲
- 函数入参和出参
回溯算法中函数返回值一般为void。 - 递归终止条件
- 单层递归的逻辑
组合
class Solution {
public:
//函数和返回值参数
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
void getres(int n, int k, int l){
//终止条件
if(path.size() == k){
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
//单层逻辑
for(int i = l; i <= n;i++){
path.push_back(i);
getres(n, k, i+1);
path.pop_back();
}
}
vector<vector<int>> combine(int n, int k) {
getres(n,k,1);
return res;
}
};
组合(剪枝)
class Solution {
public:
//函数和返回值参数
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
void getres(int n, int k, int l){
//终止条件
if(path.size() == k){
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
/*
接下来看一下优化过程如下:
已经选择的元素个数:path.size();
所需需要的元素个数为: k - path.size();
列表中剩余元素(n-i) >= 所需需要的元素个数(k - path.size())
在集合n中至多要从该起始位置 : i <= n - (k - path.size()) + 1,开始遍历
为什么有个+1呢,因为包括起始位置,我们要是一个左闭的集合。
举个例子,n = 4,k = 3, 目前已经选取的元素为0(path.size为0),n - (k - 0) + 1 即 4 - ( 3 - 0) + 1 = 2。
*/
//单层逻辑
for(int i = l; i <= n-k+path.size()+1;i++){
path.push_back(i);
getres(n, k, i+1);
path.pop_back();
}
}
vector<vector<int>> combine(int n, int k) {
getres(n,k,1);
return res;
}
};
组合综合III
普通
class Solution {
public:
//入参出参
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
int sum = 0;
void bfs(int len, int tar, int l){
//终止条件
if(path.size() == len){
if(sum == tar) res.push_back(path);
return;
}
//单层逻辑
for(int i = l; i <= 9;i++){
path.push_back(i);
sum+=i;
bfs(len, tar, i+1);
path.pop_back();
sum-=i;
}
}
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
bfs(k,n,1);
return res;
}
};
剪枝
class Solution {
public:
//入参出参
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
int sum = 0;
void bfs(int len, int tar, int l){
//终止条件
if(path.size() == len){
if(sum == tar) res.push_back(path);
return;
}
// 9 - i传入下一层大小
// len - path.size()剩余层数
// 9-i>=len- path.size() ==> i<=9-len+path.size()
// 然后再加i <= 9-len+path.size()+1
//单层逻辑
for(int i = l; i <= 9-len+path.size()+1;i++){
path.push_back(i);
sum+=i;
bfs(len, tar, i+1);
path.pop_back();
sum-=i;
}
}
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
bfs(k,n,1);
return res;
}
};
电话号码的字母组合
将字符转为字符串
下面的代码:
vector<string> arr;
arr.push_back(""+'a');
表达式 "" + 'a' 的含义:
"" 是一个空的字符串字面量(类型为 const char[1]).
'a' 是一个字符(类型为 char).
在 C++ 中,"" + 'a' 实际上是将 'a' 的 ASCII 值(97)作为偏移量加到 "" 的地址上。这会导致生成一个指向无效内存的指针,行为未定义。
如果想要将'a'转为字符串类型, 要写string("") + 'a',
to_string('a')也是不行的!,to_string只能用于数字,如果使用to_string('a') 会得到'a'的ASCII 值构成的字符串,即得到"97"
所以,在c++中,如果想把字符型数据转为字符串,有如下方法
使用 std::string(1, c) 构造字符串。
使用字符串拼接(std::string("") + c)。
使用 std::stringstream
将整型、浮点型数据转换为字符串
使用 std::to_string
C++11 引入了 std::to_string 函数,可以直接将数值类型(如 int、float、double 等)转换为字符串。
int i = 123;
float f = 45.67f;
double d = 89.123456;
std::string str_i = std::to_string(i); // 整型转字符串
std::string str_f = std::to_string(f); // 浮点型转字符串
std::string str_d = std::to_string(d); // 双精度浮点型转字符串
将字符串转换为整型、浮点型数据
使用 std::stoi、std::stof、std::stod
C++11 提供了标准库函数,用于将字符串转换为数值类型:
std::stoi:字符串转整型。
std::stof:字符串转单精度浮点型。
std::stod:字符串转双精度浮点型。
std::string str_i = "123";
std::string str_f = "45.67";
std::string str_d = "89.123456";
int i = std::stoi(str_i); // 字符串转整型
float f = std::stof(str_f); // 字符串转浮点型
double d = std::stod(str_d); // 字符串转双精度浮点型
题解
class Solution {
public:
//入参出参
vector<string> map = {"","","abc","def","ghi","jkl","mno","pqrs","tuv","wxyz"};
string path;
vector<string> res;
void bfs(string digits, int cur, int len){
//终止条件
if(cur == len){
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
//单层逻辑
string s = map[(int)(digits[cur]-'0')];
for(int i = 0 ; i< s.size();i++){
path+=s[i];
bfs(digits, cur+1, len);
path.pop_back();
}
}
vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {
if(digits == "") return res;
bfs(digits,0, digits.size());
return res;
}
};
题解2:
class Solution {
public:
//入参出参
vector<string> map = {"","","abc","def","ghi","jkl","mno","pqrs","tuv","wxyz"};
vector<string> path;
vector<string> res;
void bfs(string &digits, int cur, int len){
//终止条件
if(cur == len){
string tmp ="";
for(auto i:path){
tmp+=i;
}
res.push_back(tmp);
return;
}
//单层逻辑
string s = map[(int)(digits[cur]-'0')];
for(int i = 0 ; i< s.size();i++){
path.push_back(string("")+s[i]);
bfs(digits, cur+1, len);
path.pop_back();
}
}
vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {
if(digits == "") return res;
bfs(digits,0, digits.size());
return res;
}
};
组合总和
错误代码
class Solution {
public:
//出参入参
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
int sum = 0;
void bfs(vector<int>& arr, int tar){
//终止条件
if(sum > tar) return;
if(sum == tar){
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
//单层逻辑
for(auto elem:arr){
path.push_back(elem);
sum+=elem;
bfs(arr, tar);
sum-=elem;
path.pop_back();
}
}
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {
bfs(candidates,target);
return res;
}
};
错误原因分析
例如
candidates = [2,3,6,7]
target = 7
如果使用上面的代码,最后的结果是
[[2,2,3],[2,3,2],[3,2,2],[7]]
发现有重复的,[2,3,2] 和 [3,2,2]都和[2,2,3]重复了,
所以我们这样取数就可以
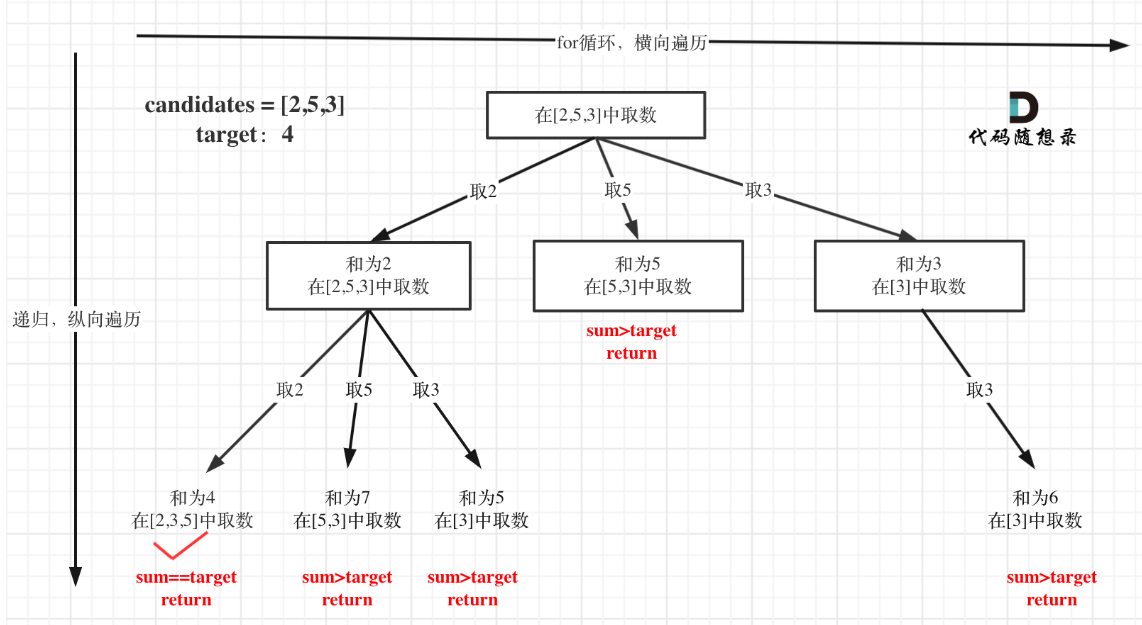
情况A: 第一次取2,下一次可以取[2,3,6,7]
情况B: 第一次取3,下一次就取[3,6,7]
情况B中,下一次取数就不需要再取2了,因为假设第一次取3,下一次取2,这种情况其实在情况A的遍历过程中已经出现了,只不过情况B此种情况下是[3,2,...], 而情况A是[2,3,...], 明显出现了重复
所以正确的代码如下
class Solution {
public:
//出参入参
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
int sum = 0;
void bfs(vector<int>& arr, int tar, int l){
//终止条件
if(sum > tar) return;
if(sum == tar){
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
//单层逻辑
for(int i =l ;i < arr.size();i++){
path.push_back(arr[i]);
sum+=arr[i];
bfs(arr, tar,i);
sum-=arr[i];
path.pop_back();
}
}
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {
bfs(candidates,target,0);
return res;
}
};
组合总和 II
class Solution {
public:
//出入参
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
int sum = 0;
void bfs(vector<int> & arr, int tar, int cur){
//终止条件
if(sum > tar){
return;
}
if(sum == tar){
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
//单层逻辑
//同树层去重,同树枝不去重
unordered_map<int, int> map;
for(int i = cur; i<arr.size();i++){
map[arr[i]]++;
if(map[arr[i]] >= 2){
//cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
continue;
}
// cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
path.push_back(arr[i]);
sum+=arr[i];
bfs(arr, tar, i+1);
path.pop_back();
sum-=arr[i];
}
}
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum2(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {
sort(candidates.begin(), candidates.end());
bfs(candidates,target,0);
return res;
}
};
分割回文串
class Solution {
public:
bool isreverse(string &tar){
int l = 0;
int r = tar.size()-1;
while(r>=l){
if(tar[l] != tar[r]) return false;
r--;
l++;
}
return true;
}
vector<vector<string>> res;
vector<string> path;
void bfs(string tar, int l, int r){
//终止条件
if(l > r) {
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
//单层逻辑
for(int i = l; i<= r;i++){
string tmp = tar.substr(l, i-l+1);
if(isreverse(tmp)){
path.push_back(tmp);
bfs(tar, i+1, r);
path.pop_back();
}
else continue;
}
}
vector<vector<string>> partition(string s) {
bfs(s, 0, s.size()-1);
return res;
}
};
复原ip 地址
class Solution {
public:
bool ipcheck(string tar){
if(tar.size()<=0 || tar.size() > 3) return false;
if(tar[0] == '0' && tar.size()>1) return false;
int num = stoi(tar);
if(num>255 || num < 0) return false;
return true;
}
vector<string>res;
string path;
int count = 0;
void bfs(string tar, int l, int r){
if(count == 3){
string tmp = tar.substr(l, r-l+1);
if(ipcheck(tmp)){
path+=tmp;
res.push_back(path);
}
return;
}
if(l>r) return;
for(int i = l; i<=r;i++){
string tmp = tar.substr(l, i-l+1);
if(ipcheck(tmp)){
count++;
string tmp_path = path;
path+=tmp;
path+=".";
bfs(tar,i+1,r);
count--;
path = tmp_path;
}
}
}
vector<string> restoreIpAddresses(string s) {
bfs(s,0,s.size()-1);
return res;
}
};
子集
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
void bfs(vector<int> & nums, int l, int r){
//终止条件
if(l>r) return;
//单层逻辑
for(int i = l; i<=r; i++){
path.push_back(nums[i]);
res.push_back(path);
bfs(nums,i+1,r);
path.pop_back();
}
}
vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums) {
res.push_back(vector<int>(0));
bfs(nums, 0, nums.size()-1);
return res;
}
};
子集II
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
void bfs(vector<int>& nums, int l, int r){
if(l>r) return;
for(int i = l; i<=r;i++){
if(i>l && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) continue;
path.push_back(nums[i]);
res.push_back(path);
bfs(nums, i+1, r);
path.pop_back();
}
}
vector<vector<int>> subsetsWithDup(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
res.push_back(vector<int>(0));
bfs(nums, 0, nums.size()-1);
return res;
}
};
递增子序列
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
void bfs(vector<int> & nums, int l, int r){
//终止条件
if(path.size() >=2) {
res.push_back(path);
}
if(l>r) return;
//单层循环
unordered_map<int, int> map;
for(int i = l; i<= r; i++){
map[nums[i]]++;
if((path.size() == 0 || path[path.size()-1] <= nums[i]) && map[nums[i]] == 1){
path.push_back(nums[i]);
bfs(nums,i+1, r);
path.pop_back();
}
}
}
vector<vector<int>> findSubsequences(vector<int>& nums) {
bfs(nums, 0 , nums.size()-1);
return res;
}
};
全排列
class Solution {
public:
//出入参
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
int cnt = 0;
void bfs(vector<int> & nums, vector<bool> &used){
//终止条件
if(cnt == nums.size()) {
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
//单层逻辑
for(int i =0; i< nums.size(); i++){
if(!used[i]){
used[i] = 1;
cnt++;
path.push_back(nums[i]);
bfs(nums, used);
used[i] = 0;
cnt--;
path.pop_back();
}
}
}
vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<bool> used(nums.size(), 0);
bfs(nums, used);
return res;
}
};
全排列II
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
void bfs(vector<int> &nums, vector<bool> & used){
if(path.size() == nums.size()){
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i<nums.size();i++){
if(i>0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1] && used[i-1] == false) continue;
if(!used[i]){
used[i] = 1;
path.push_back(nums[i]);
bfs(nums, used);
used[i] = 0;
path.pop_back();
}
}
}
vector<vector<int>> permuteUnique(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<bool> used(nums.size(), 0);
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
bfs(nums, used);
return res;
}
};
重新安排行程
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<string, map<string, int>> targets;
vector<string> path;
int len;
bool dfs(string key){
if(path.size() == len){
return true;
}
for(auto &cur:targets[key]){
if(cur.second){
cur.second--;
path.push_back(cur.first);
if(dfs(cur.first)) return true;
cur.second++;
path.pop_back();
}
}
return false;
}
vector<string> findItinerary(vector<vector<string>>& tickets) {
len = tickets.size()+1;
for(auto &tic: tickets){
targets[tic[0]][tic[1]]++;
}
path.push_back("JFK");
dfs("JFK");
return path;
}
};
n皇后
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string>> res;
vector<string> path;
bool check(int row, int col, int n){
//检查列重复
for(int i = 0; i <n ;i++){
if(path[i][col] == 'Q') return 0;
}
//检查对角线
int i = row-1,j = col-1;
while(i>=0 && j>=0){
if(path[i][j] == 'Q') return 0;
i--;
j--;
}
i = row-1, j = col+1;
while(j<n && i>=0){
if(path[i][j] == 'Q') return 0;
i--;
j++;
}
return 1;
}
void dfs(int n, int row){
if(row == n){
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
for(int col = 0; col<n; col++){
if(check(row, col, n)){
path[row][col] = 'Q';
dfs(n, row+1);
path[row][col] = '.';
}
}
}
vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) {
path = vector<string>(n, string(n,'.'));
dfs(n, 0);
return res;
}
};



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号