Springboot Endpoint之二:Endpoint源码剖析
spring boot 中有关endpoint的实现,细心的朋友可以发现,在org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint.mvc 包下也有一系列的xxxEndpoint,这又是为什么呢?
原因是: 我们很多情况下,都是访问接口的方式获取应用的监控,之前的分析是其实现的底层,要想实现通过接口访问,还需要对其进行包装一番,org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint.mvc 包下的实现就是干的这种事,下面,先看下springboot的actuator包的mvc下定义的类:
整体实现思路是将端点(Endpoint)适配委托给MVC层策略端点(MvcEndpoint),再通过端点MVC适配器(EndpointMvcAdapter)将端点暴露为HTTP请求方式的MVC端点,最后分别使用端点自动配置(EndpointAutoConfiguration)和MVC方式暴露端点的配置(EndpointWebMvcManagementContextConfiguration)来注入端点组件和端点处理程序映射组件、MVC端点注册表组件、MVC端点组件。
其中,端点处理程序映射(EndpointHandlerMapping)通过Spring MVC方式来暴露MVC端点。最后,本文以“shutdown端点示例”收尾。
现在就按照整体实现思路来剖析HTTP端点的实现原理。
一、类图
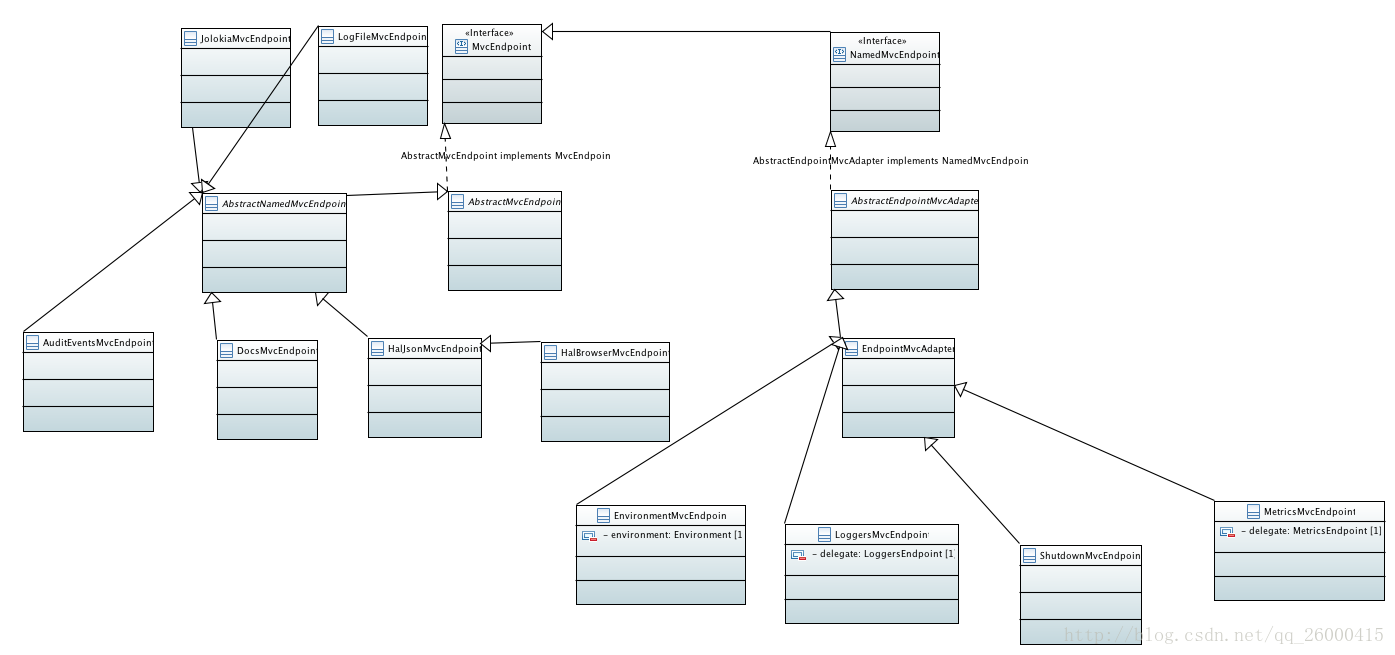
首先找到AbstractEndpoint,
1、端点接口(Endpoint<T>)
/** * An endpoint that can be used to expose useful information to operations. Usually * exposed via Spring MVC but could also be exposed using some other technique. Consider * extending {@link AbstractEndpoint} if you are developing your own endpoint. * <p>一个端点可以用于暴露操作的实用信息。 * * @param <T> the endpoint data type (端点数据类型) * @see AbstractEndpoint */ // 核心接口 端点接口 public interface Endpoint<T> { /** * 端点的逻辑标识(字母、数字和下划线('_')) */ String getId(); /** * 端点是否启用 */ boolean isEnabled(); /** * 端点是否输出敏感数据(安全提示) */ boolean isSensitive(); // 核心接口 调用端点,并返回调用结果 T invoke(); }
其抽象实现基类 AbstractEndpoint<T>
/** * Abstract base for {@link Endpoint} implementations. * * @param <T> the endpoint data type (端点数据类型) */ // 核心类 端点实现的抽象基类 public abstract class AbstractEndpoint<T> implements Endpoint<T>, EnvironmentAware { private Environment environment; /** * Endpoint identifier. With HTTP monitoring the identifier of the endpoint is mapped * to a URL (e.g. 'foo' is mapped to '/foo'). * 端点标识符 */ private String id; /** * Mark if the endpoint exposes sensitive information. */ private Boolean sensitive; /** * 是否启动端点 */ private Boolean enabled; public AbstractEndpoint(String id, boolean sensitive, boolean enabled) { setId(id); this.sensitiveDefault = sensitive; this.enabled = enabled; } @Override public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) { this.environment = environment; } public void setId(String id) { Assert.notNull(id, "Id must not be null"); Assert.isTrue(ID_PATTERN.matcher(id).matches(), "Id must only contains letters, numbers and '_'"); this.id = id; } @Override public boolean isEnabled() { return EndpointProperties.isEnabled(this.environment, this.enabled); } }
2、MVC层策略端点(MvcEndpoint)
/** * 实现类允许使用@RequestMapping和完整的Spring MVC机制, * 但不能在类型级别使用@Controller或@RequestMapping,因为这将导致路径的双重映射, * 一次通过常规MVC处理程序映射,一次通过{@link EndpointHandlerMapping}。 * * @author Dave Syer * @see NamedMvcEndpoint */ // 核心接口 在端点之上的MVC层策略 public interface MvcEndpoint { /** * 禁用端点的响应实体 */ ResponseEntity<Map<String, String>> DISABLED_RESPONSE = new ResponseEntity<>( Collections.singletonMap("message", "This endpoint is disabled"), HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND); // 核心方法 返回端点的MVC路径 String getPath(); /** * 返回端点是否暴露敏感信息。 */ boolean isSensitive(); // 核心方法 返回端点暴露的类型/null @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") Class<? extends Endpoint> getEndpointType(); }
2.1、包括逻辑名称的MVC端点(NamedMvcEndpoint)
/** * 名称提供了引用端点的一致方式。 * * @author Madhura Bhave * @since 1.5.0 */ // 包括逻辑名称的MVC端点 public interface NamedMvcEndpoint extends MvcEndpoint { /** * 返回端点的逻辑名称。 */ String getName(); }
3、端点MVC适配器(EndpointMvcAdapter)
/** * 暴露端点({@link Endpoint})为MVC端点({@link MvcEndpoint})的适配器。 */ // 端点MVC适配器 public class EndpointMvcAdapter extends AbstractEndpointMvcAdapter<Endpoint<?>> { /** * Create a new {@link EndpointMvcAdapter}. * @param delegate the underlying {@link Endpoint} to adapt. (用于适配的底层端点) */ public EndpointMvcAdapter(Endpoint<?> delegate) { super(delegate); // 委托代理 } // 核心实现 以HTTP GET方式调用 @Override @ActuatorGetMapping @ResponseBody public Object invoke() { return super.invoke(); // 向上调用,链式模式 } }
其抽象实现基类 AbstractEndpointMvcAdapter<E extends Endpoint<?>>
/** * MVC端点({@link MvcEndpoint})实现的抽象基类。 * * @param <E> The delegate endpoint (代理的端点) * @author Dave Syer * @since 1.3.0 */ public abstract class AbstractEndpointMvcAdapter<E extends Endpoint<?>> implements NamedMvcEndpoint { /** * 被代理的底层端点(端点子类) */ private final E delegate; /** * 端点URL路径 */ private String path; public AbstractEndpointMvcAdapter(E delegate) { Assert.notNull(delegate, "Delegate must not be null"); this.delegate = delegate; } // 核心实现 调用底层端点,并返回调用结果 protected Object invoke() { if (!this.delegate.isEnabled()) { // 端点被禁用 // Shouldn't happen - shouldn't be registered when delegate's disabled return getDisabledResponse(); } return this.delegate.invoke(); // 调用端点 } public E getDelegate() { return this.delegate; } @Override public String getName() { return this.delegate.getId(); // name = id } @Override public String getPath() { return (this.path != null ? this.path : "/" + this.delegate.getId()); // "/id" } public void setPath(String path) { while (path.endsWith("/")) { path = path.substring(0, path.length() - 1); } if (!path.startsWith("/")) { path = "/" + path; } this.path = path; } @Override @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") public Class<? extends Endpoint> getEndpointType() { return this.delegate.getClass(); } }
4、端点组件自动配置
基于Spring Boot的自动配置机制(Auto-configuration),其自动配置文件位于spring-boot-actuator资源目录下的META-INF/spring.factories文件:
# 启用自动配置 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ ... org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.EndpointAutoConfiguration,\ ... # 管理上下文配置 org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.ManagementContextConfiguration=\ org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.EndpointWebMvcManagementContextConfiguration,\ ...
4.1、公共管理的端点自动配置(EndpointAutoConfiguration)
/** * {@link EnableAutoConfiguration Auto-configuration} for common management * {@link Endpoint}s. */ // 核心类 公共管理的端点自动配置 @Configuration // 组件配置 @AutoConfigureAfter({ FlywayAutoConfiguration.class, LiquibaseAutoConfiguration.class }) @EnableConfigurationProperties(EndpointProperties.class) // 启用配置属性(端点属性) public class EndpointAutoConfiguration { @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public EnvironmentEndpoint environmentEndpoint() { return new EnvironmentEndpoint(); } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public HealthEndpoint healthEndpoint() { return new HealthEndpoint( this.healthAggregator == null ? new OrderedHealthAggregator() : this.healthAggregator, this.healthIndicators == null ? Collections.<String, HealthIndicator>emptyMap() : this.healthIndicators); } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public TraceEndpoint traceEndpoint() { return new TraceEndpoint(this.traceRepository == null ? new InMemoryTraceRepository() : this.traceRepository); } @Bean @ConditionalOnBean(ConditionEvaluationReport.class) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) public AutoConfigurationReportEndpoint autoConfigurationReportEndpoint() { return new AutoConfigurationReportEndpoint(); } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public ShutdownEndpoint shutdownEndpoint() { return new ShutdownEndpoint(); } }
4.2、全局的端点属性(EndpointProperties)
/** * Global endpoint properties. * <p>全局的端点属性。 * * @since 1.3.0 */ @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "endpoints") // 端点属性配置前缀 public class EndpointProperties { private static final String ENDPOINTS_ENABLED_PROPERTY = "endpoints.enabled"; private static final String ENDPOINTS_SENSITIVE_PROPERTY = "endpoints.sensitive"; /** * Enable endpoints. * 启用端点 */ private Boolean enabled = true; /** * Default endpoint sensitive setting. */ private Boolean sensitive; public static boolean isEnabled(Environment environment, Boolean enabled) { if (enabled != null) { return enabled; } if (environment != null && environment.containsProperty(ENDPOINTS_ENABLED_PROPERTY)) { return environment.getProperty(ENDPOINTS_ENABLED_PROPERTY, Boolean.class); } return true; } }
4.3、外部化配置的注解(ConfigurationProperties)
/** * 如果要绑定和验证一些外部属性(例如来自.properties文件),请将其添加到@Configuration类中的类定义或@Bean方法。 * <p> * Note that contrary to {@code @Value}, SpEL expressions are not evaluated since property * values are externalized. * * @author Dave Syer * @see ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor * @see EnableConfigurationProperties */ // 外部化配置的注解 @Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface ConfigurationProperties { // 属性的名称前缀 @AliasFor("value") String prefix() default ""; }
5、MVC方式暴露端点的配置(EndpointWebMvcManagementContextConfiguration)
/** * Configuration to expose {@link Endpoint} instances over Spring MVC. * * @author Dave Syer * @since 1.3.0 */ // 核心类 通过MVC方式来暴露端点的配置 @ManagementContextConfiguration @EnableConfigurationProperties({ HealthMvcEndpointProperties.class, EndpointCorsProperties.class }) public class EndpointWebMvcManagementContextConfiguration { private final HealthMvcEndpointProperties healthMvcEndpointProperties; /** * 管理服务器的属性 */ private final ManagementServerProperties managementServerProperties; private final EndpointCorsProperties corsProperties; /** * 端点处理程序的映射定制程序 */ private final List<EndpointHandlerMappingCustomizer> mappingCustomizers; // 核心方法 注入端点处理程序映射组件 @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean // 组件未注入 public EndpointHandlerMapping endpointHandlerMapping() { // 注册的MVC端点集合 Set<MvcEndpoint> endpoints = mvcEndpoints().getEndpoints(); CorsConfiguration corsConfiguration = getCorsConfiguration(this.corsProperties); // 端点处理程序映射 EndpointHandlerMapping mapping = new EndpointHandlerMapping(endpoints, corsConfiguration); // 管理端点的上下文路径前缀 mapping.setPrefix(this.managementServerProperties.getContextPath()); // MVC端点安全处理程序拦截器 MvcEndpointSecurityInterceptor securityInterceptor = new MvcEndpointSecurityInterceptor( this.managementServerProperties.getSecurity().isEnabled(), this.managementServerProperties.getSecurity().getRoles()); mapping.setSecurityInterceptor(securityInterceptor); for (EndpointHandlerMappingCustomizer customizer : this.mappingCustomizers) { customizer.customize(mapping); } return mapping; } // 核心方法 注入MVC端点注册表组件 @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean // 组件未注入 public MvcEndpoints mvcEndpoints() { return new MvcEndpoints(); } @Bean @ConditionalOnBean(EnvironmentEndpoint.class) @ConditionalOnEnabledEndpoint("env") public EnvironmentMvcEndpoint environmentMvcEndpoint(EnvironmentEndpoint delegate) { return new EnvironmentMvcEndpoint(delegate); } @Bean @ConditionalOnBean(HealthEndpoint.class) @ConditionalOnEnabledEndpoint("health") public HealthMvcEndpoint healthMvcEndpoint(HealthEndpoint delegate) { HealthMvcEndpoint healthMvcEndpoint = new HealthMvcEndpoint(delegate, this.managementServerProperties.getSecurity().isEnabled()); if (this.healthMvcEndpointProperties.getMapping() != null) { healthMvcEndpoint .addStatusMapping(this.healthMvcEndpointProperties.getMapping()); } return healthMvcEndpoint; } // 注入关闭应用程序的MVC端点组件 @Bean @ConditionalOnBean(ShutdownEndpoint.class) // 组件已实例化 @ConditionalOnEnabledEndpoint(value = "shutdown", enabledByDefault = false) // 端点已启用 public ShutdownMvcEndpoint shutdownMvcEndpoint(ShutdownEndpoint delegate) { return new ShutdownMvcEndpoint(delegate); } }
5.1、MVC端点注册表(MvcEndpoints)
/** * 所有MVC端点组件的注册表,以及一组用于包装尚未公开的MVC端点的现有端点实例的通用工厂。 */ // 核心类 MVC端点注册表 public class MvcEndpoints implements ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean { /** * 应用上下文 */ private ApplicationContext applicationContext; /** * MVC端点集合 */ private final Set<MvcEndpoint> endpoints = new HashSet<>(); /** * MVC端点类型集合 */ private Set<Class<?>> customTypes; @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { this.applicationContext = applicationContext; } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { // 现有的MVC端点列表 Collection<MvcEndpoint> existing = BeanFactoryUtils .beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(this.applicationContext, MvcEndpoint.class) // MVC端点 .values(); this.endpoints.addAll(existing); this.customTypes = findEndpointClasses(existing); // 现有的代理端点列表 @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") Collection<Endpoint> delegates = BeanFactoryUtils .beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(this.applicationContext, Endpoint.class) // 端点 .values(); for (Endpoint<?> endpoint : delegates) { if (isGenericEndpoint(endpoint.getClass()) && endpoint.isEnabled()) { EndpointMvcAdapter adapter = new EndpointMvcAdapter(endpoint); // 端点MVC适配器 // 端点路径 String path = determinePath(endpoint, this.applicationContext.getEnvironment()); if (path != null) { adapter.setPath(path); } this.endpoints.add(adapter); } } } private Set<Class<?>> findEndpointClasses(Collection<MvcEndpoint> existing) { Set<Class<?>> types = new HashSet<>(); for (MvcEndpoint endpoint : existing) { Class<?> type = endpoint.getEndpointType(); // 端点类型 if (type != null) { types.add(type); } } return types; } // 核心方法 返回注册的MVC端点集合 public Set<MvcEndpoint> getEndpoints() { return this.endpoints; } /** * 返回指定类型的MVC端点集合。 */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public <E extends MvcEndpoint> Set<E> getEndpoints(Class<E> type) { Set<E> result = new HashSet<>(this.endpoints.size()); for (MvcEndpoint candidate : this.endpoints) { if (type.isInstance(candidate)) { result.add((E) candidate); } } return Collections.unmodifiableSet(result); // 不可修改的集合 } // 通用的端点 private boolean isGenericEndpoint(Class<?> type) { return !this.customTypes.contains(type) && !MvcEndpoint.class.isAssignableFrom(type); } private String determinePath(Endpoint<?> endpoint, Environment environment) { // 配置属性 ConfigurationProperties configurationProperties = AnnotationUtils .findAnnotation(endpoint.getClass(), ConfigurationProperties.class); if (configurationProperties != null) { return environment.getProperty(configurationProperties.prefix() + ".path"); } return null; } }
5.2、端点处理程序映射(EndpointHandlerMapping)
/** * @RequestMapping的语义应该与普通的@Controller相同, * 但是端点不应该被注释为@Controller,否则它们将被正常的MVC机制映射。 * <p> * <p>映射的目标之一是支持作为HTTP端点工作的端点, * 但是当没有HTTP服务器(类路径上没有Spring MVC)时,仍然可以提供有用的服务接口。 * 注意:具有方法签名的任何端点将在非Servlet环境下中断。 */ // 核心类 通过端点的逻辑标识将端点映射到URL的处理程序映射 public class EndpointHandlerMapping extends AbstractEndpointHandlerMapping<MvcEndpoint> { /** * Create a new {@link EndpointHandlerMapping} instance. All {@link Endpoint}s will be * detected from the {@link ApplicationContext}. The endpoints will accepts CORS * requests based on the given {@code corsConfiguration}. * @param endpoints the endpoints (MVC端点列表) * @param corsConfiguration the CORS configuration for the endpoints * @since 1.3.0 */ public EndpointHandlerMapping(Collection<? extends MvcEndpoint> endpoints, CorsConfiguration corsConfiguration) { super(endpoints, corsConfiguration); } }
其抽象实现基类 AbstractEndpointHandlerMapping<E extends MvcEndpoint>
/** * @RequestMapping的语义应该与普通的@Controller相同, * 但是端点不应该被注释为@Controller,否则它们将被正常的MVC机制映射。 * <p>映射的目标之一是支持作为HTTP端点工作的端点, * 但是当没有HTTP服务器(类路径上没有Spring MVC)时,仍然可以提供有用的服务接口。 * 注意:具有方法签名的任何端点将在非Servlet环境下中断。 * * @param <E> The endpoint type (端点类型) */ // 核心类 通过端点的逻辑标识将端点映射到URL的处理程序映射的抽象基类 public abstract class AbstractEndpointHandlerMapping<E extends MvcEndpoint> extends RequestMappingHandlerMapping { /** * MVC端点集合 */ private final Set<E> endpoints; /** * 安全处理程序拦截器 */ private HandlerInterceptor securityInterceptor; /** * CORS配置 */ private final CorsConfiguration corsConfiguration; /** * 端点的映射路径前缀 */ private String prefix = ""; private boolean disabled = false; /** * Create a new {@link AbstractEndpointHandlerMapping} instance. All {@link Endpoint}s * will be detected from the {@link ApplicationContext}. The endpoints will accepts * CORS requests based on the given {@code corsConfiguration}. * <p>将从应用上下文检测到所有端点。 * @param endpoints the endpoints * @param corsConfiguration the CORS configuration for the endpoints * @since 1.3.0 */ public AbstractEndpointHandlerMapping(Collection<? extends E> endpoints, CorsConfiguration corsConfiguration) { this.endpoints = new HashSet<>(endpoints); postProcessEndpoints(this.endpoints); this.corsConfiguration = corsConfiguration; // By default the static resource handler mapping is LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 1 // and the RequestMappingHandlerMapping is 0 (we ideally want to be before both) // 默认情况下,静态资源处理程序映射的顺序是 LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 1 setOrder(-100); setUseSuffixPatternMatch(false); } /** * Post process the endpoint setting before they are used. Subclasses can add or * modify the endpoints as necessary. * <p>在使用之前,后处理端点设置。 * @param endpoints the endpoints to post process */ protected void postProcessEndpoints(Set<E> endpoints) { } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { super.afterPropertiesSet(); if (!this.disabled) { // 端点处理程序被禁用 for (MvcEndpoint endpoint : this.endpoints) { detectHandlerMethods(endpoint); } } } // 核心实现 注册端点处理程序方法及其唯一映射 @Override @Deprecated protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, RequestMappingInfo mapping) { if (mapping == null) { return; } String[] patterns = getPatterns(handler, mapping); if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(patterns)) { super.registerHandlerMethod(handler, method, withNewPatterns(mapping, patterns)); } } private String[] getPatterns(Object handler, RequestMappingInfo mapping) { if (handler instanceof String) { // 组件名称 handler = getApplicationContext().getBean((String) handler); } Assert.state(handler instanceof MvcEndpoint, "Only MvcEndpoints are supported"); String path = getPath((MvcEndpoint) handler); // MVC端点路径 return (path == null ? null : getEndpointPatterns(path, mapping)); } protected String getPath(MvcEndpoint endpoint) { return endpoint.getPath(); } // 核心实现 返回端点的路径列表 private String[] getEndpointPatterns(String path, RequestMappingInfo mapping) { // 路径模式前缀 String patternPrefix = StringUtils.hasText(this.prefix) ? this.prefix + path : path; // 默认的路径集合 Set<String> defaultPatterns = mapping.getPatternsCondition().getPatterns(); if (defaultPatterns.isEmpty()) { // 端点路径 return new String[] { patternPrefix, patternPrefix + ".json" }; } List<String> patterns = new ArrayList<>(defaultPatterns); for (int i = 0; i < patterns.size(); i++) { patterns.set(i, patternPrefix + patterns.get(i)); // 端点请求路径 } return patterns.toArray(new String[patterns.size()]); } // 新的端点路径 private RequestMappingInfo withNewPatterns(RequestMappingInfo mapping, String[] patternStrings) { // 模式请求条件 PatternsRequestCondition patterns = new PatternsRequestCondition(patternStrings, null, null, useSuffixPatternMatch(), useTrailingSlashMatch(), null); return new RequestMappingInfo(patterns, mapping.getMethodsCondition(), mapping.getParamsCondition(), mapping.getHeadersCondition(), mapping.getConsumesCondition(), mapping.getProducesCondition(), mapping.getCustomCondition()); } // 核心实现 获取处理程序执行链 @Override protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) { HandlerExecutionChain chain = super.getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request); if (this.securityInterceptor == null || CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) { return chain; } return addSecurityInterceptor(chain); } private HandlerExecutionChain addSecurityInterceptor(HandlerExecutionChain chain) { // 处理程序拦截器 List<HandlerInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>(); if (chain.getInterceptors() != null) { interceptors.addAll(Arrays.asList(chain.getInterceptors())); } // 添加安全处理程序拦截器 interceptors.add(this.securityInterceptor); return new HandlerExecutionChain(chain.getHandler(), interceptors.toArray(new HandlerInterceptor[interceptors.size()])); } // 获取端点的路径 public String getPath(String endpoint) { return this.prefix + endpoint; } // 返回MVC端点集合 public Set<E> getEndpoints() { return Collections.unmodifiableSet(this.endpoints); // 不可修改的集合 } }
5.3、组件存在条件(OnBeanCondition)
5.3.1、未注入组件条件(ConditionalOnMissingBean)
/** * 仅当指定的组件类型或名称尚未包含在{@link BeanFactory}中时才匹配的条件。 */ @Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnBeanCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnMissingBean { /** * The class type of bean that should be checked. The condition matches when each * class specified is missing in the {@link ApplicationContext}. * @return the class types of beans to check */ // 组件的类型 Class<?>[] value() default {}; String[] type() default {}; /** * The class type of beans that should be ignored when identifying matching beans. * @return the class types of beans to ignore * @since 1.2.5 */ Class<?>[] ignored() default {}; String[] ignoredType() default {}; // 装饰组件的注解类型 Class<? extends Annotation>[] annotation() default {}; // 组件的名称列表 String[] name() default {}; // 应用上下文层次结构的搜索策略 SearchStrategy search() default SearchStrategy.ALL; }
5.3.2、组件条件(ConditionalOnBean)
/** * 仅当指定的组件类型或名称已经包含在{@link BeanFactory}中时才匹配的条件 */ @Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnBeanCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnBean { /** * The class type of bean that should be checked. The condition matches when all of * the classes specified are contained in the {@link ApplicationContext}. * @return the class types of beans to check */ // 组件的类型 Class<?>[] value() default {}; String[] type() default {}; // 装饰组件的注解类型 Class<? extends Annotation>[] annotation() default {}; // 组件的名称列表 String[] name() default {}; // 应用上下文层次结构的搜索策略 SearchStrategy search() default SearchStrategy.ALL; }
5.3.3、启用端点条件(ConditionalOnEnabledEndpoint)
/** * 检查端点是否启用的条件。 * 如果endpoints.<name>.enabled属性的值是true,则匹配。 * * @since 1.2.4 */ // 启用端点上的条件 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE }) @Documented @Conditional(OnEnabledEndpointCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnEnabledEndpoint { // 端点的名称 String value(); /** * Returns whether or not the endpoint is enabled by default. */ boolean enabledByDefault() default true; }
6、shutdown端点示例
6.1、关闭应用程序的端点(ShutdownEndpoint)
/** * {@link Endpoint} to shutdown the {@link ApplicationContext}. * <p>用于优雅地关闭应用上下文({@link ApplicationContext})的端点。 * 允许应用以优雅的方式关闭 * * @author Dave Syer * @author Christian Dupuis * @author Andy Wilkinson */ @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "endpoints.shutdown") // 属性前缀配置 public class ShutdownEndpoint extends AbstractEndpoint<Map<String, Object>> implements ApplicationContextAware { // 应用上下文感知 /** 无关闭上下文信息 */ private static final Map<String, Object> NO_CONTEXT_MESSAGE = Collections .unmodifiableMap(Collections.<String, Object>singletonMap("message", "No context to shutdown.")); /** 关闭信息 */ private static final Map<String, Object> SHUTDOWN_MESSAGE = Collections .unmodifiableMap(Collections.<String, Object>singletonMap("message", "Shutting down, bye...")); /** * 可配置的应用上下文 */ private ConfigurableApplicationContext context; /** * Create a new {@link ShutdownEndpoint} instance. */ public ShutdownEndpoint() { super("shutdown", true, false); } // 核心实现 新启线程来关闭应用上下文,并释放所有资源和锁 @Override public Map<String, Object> invoke() { if (this.context == null) { return NO_CONTEXT_MESSAGE; } try { return SHUTDOWN_MESSAGE; } finally { Thread thread = new Thread(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(500L); // 使当前正在执行的线程休眠(500ms) } catch (InterruptedException ex) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); // 如果出现中断异常,则中断当前线程 } ShutdownEndpoint.this.context.close(); // 关闭应用上下文,并释放所有资源和锁 }); thread.setContextClassLoader(getClass().getClassLoader()); // 本类的类加载器 thread.start(); } } // 核心实现 设置可配置的应用上下文 @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException { if (context instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) { this.context = (ConfigurableApplicationContext) context; } } }
6.2、关闭应用程序的MVC端点(ShutdownMvcEndpoint)
/** * 暴露关闭应用上下文端点({@link ShutdownEndpoint})为MVC端点({@link MvcEndpoint})的适配器。 */ // 关闭应用程序的MVC端点 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "endpoints.shutdown") // 属性前缀配置 public class ShutdownMvcEndpoint extends EndpointMvcAdapter { public ShutdownMvcEndpoint(ShutdownEndpoint delegate) { super(delegate); // 委托代理 } // 核心实现 以HTTP POST方式调用 @PostMapping(produces = { ActuatorMediaTypes.APPLICATION_ACTUATOR_V1_JSON_VALUE, MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE }) @ResponseBody @Override public Object invoke() { if (!getDelegate().isEnabled()) { // 端点被禁用 return getDisabledResponse(); } return super.invoke(); // 向上调用,链式模式 } }
至此,HTTP端点实现原理就全部分析完成。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号