tftp-hpa
git clone https://github.com/asciiprod/tftp-hpa.git Cloning into 'tftp-hpa'... remote: Enumerating objects: 98, done. remote: Total 98 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 98 Unpacking objects: 100% (98/98), done.
[root@centos7 tftp-hpa]# grep -i cross -rn * INSTALL:152: If you are _building_ compiler tools for cross-compiling, you should INSTALL:156: If you want to _use_ a cross compil
where SYSTEM can have one of these forms: OS KERNEL-OS See the file `config.sub' for the possible values of each field. If `config.sub' isn't included in this package, then this package doesn't need to know the host type. If you are _building_ compiler tools for cross-compiling, you should use the `--target=TYPE' option to select the type of system they will produce code for. If you want to _use_ a cross compiler, that generates code for a platform different from the build platform, you should specify the host platform (i.e., that on which the generated programs will eventually be run) with `--host=TYPE'. In this case, you should also specify the build platform with `--build=TYPE', because, in this case, it may not be possible to guess the build platform (it sometimes involves compiling and running simple test programs, and this can't be done if the compiler is a cross compiler). Sharing Defaults ================ If you want to set default values for `configure' scripts to share, you can create a site shell script called `config.site' that gives default values for variables like `CC', `cache_file', and `prefix'. `configure' looks for `PREFIX/share/config.site' if it exists, then `PREFIX/etc/config.site' if it exists. Or, you can set the `CONFIG_SITE' environment variable to the location of the site script. A warning: not all `configure' scripts look for a site script. Environment Variables ===================== Variables not defined in a site shell script can be set in the environment passed to configure. However, some packages may run configure again during the build, and the customized values of these variables may be lost. In order to avoid this problem, you should set them in the `configure' command line, using `VAR=value'. For example: ./configure CC=/usr/local2/bin/gcc will cause the specified gcc to be used as the C compiler (unless it is overridden in the site shell script).
./configure CC=riscv64-linux-gnu-gcc --host=aarch64-linux-gnu --build=riscv64-linux-gnu --prefix=/home/ubuntu/tftp-hpa/build checking for aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc... riscv64-linux-gnu-gcc checking whether the C compiler works... yes checking for C compiler default output file name... a.out checking for suffix of executables... checking whether we are cross compiling... yes checking for suffix of object files... o checking whether we are using the GNU C compiler... yes checking whether riscv64-linux-gnu-gcc accepts -g... yes checking for riscv64-linux-gnu-gcc option to accept ISO C89... none needed checking how to run the C preprocessor... riscv64-linux-gnu-gcc -E checking for grep that handles long lines and -e... /bin/grep checking for egrep... /bin/grep -E checking for ANSI C header files... yes checking for sys/types.h... yes checking for sys/stat.h... yes checking for stdlib.h... yes checking for string.h... yes checking for memory.h... yes checking for strings.h... yes checking for inttypes.h... yes checking for stdint.h... yes checking for unistd.h... yes checking minix/config.h usability... no checking minix/config.h presence... no checking for minix/config.h... no checking whether it is safe to define __EXTENSIONS__... yes checking for library containing strerror... none required checking for aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc... (cached) riscv64-linux-gnu-gcc checking whether we are using the GNU C compiler... (cached) yes checking whether riscv64-linux-gnu-gcc accepts -g... (cached) yes checking for riscv64-linux-gnu-gcc option to accept ISO C89... (cached) none needed checking for an ANSI C-conforming const... yes checking for inline... inline checking if riscv64-linux-gnu-gcc accepts -W... yes checking if riscv64-linux-gnu-gcc accepts -Wall... yes checking if riscv64-linux-gnu-gcc accepts -Wpointer-arith... yes checking if riscv64-linux-gnu-gcc accepts -Wbad-function-cast... yes checking if riscv64-linux-gnu-gcc accepts -Wcast-equal... no checking if riscv64-linux-gnu-gcc accepts -Wstrict-prototypes... yes
make
make install
其中tftp在__install/bin里面,in.tftpd在__install/sbin/里面
root@ubuntu:/home/ubuntu/tftp-hpa# ls build/ bin sbin share root@ubuntu:/home/ubuntu/tftp-hpa# ls build/bin/ tftp root@ubuntu:/home/ubuntu/tftp-hpa# ls build/bin/tftp build/bin/tftp root@ubuntu:/home/ubuntu/tftp-hpa# ls build/sbin/ in.tftpd root@ubuntu:/home/ubuntu/tftp-hpa#
2.使用 a.服务器in.tftpd ./in.tftpd -l -s /data b.客户端tftp ./tftp 192.168.1.1 put 1.txt
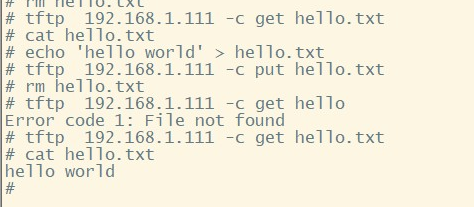
busybox tftp
tftp –g –l 目标文件名 –r 源文件名 服务器地址
如命令
tftp –g –l B.txt –r A.txt 192.168.1.2
的作用是从server中的tftp根目录下,下载文件A.txt到Client并更名为B.txt;若不更名,B.txt就改为A.txt.
-
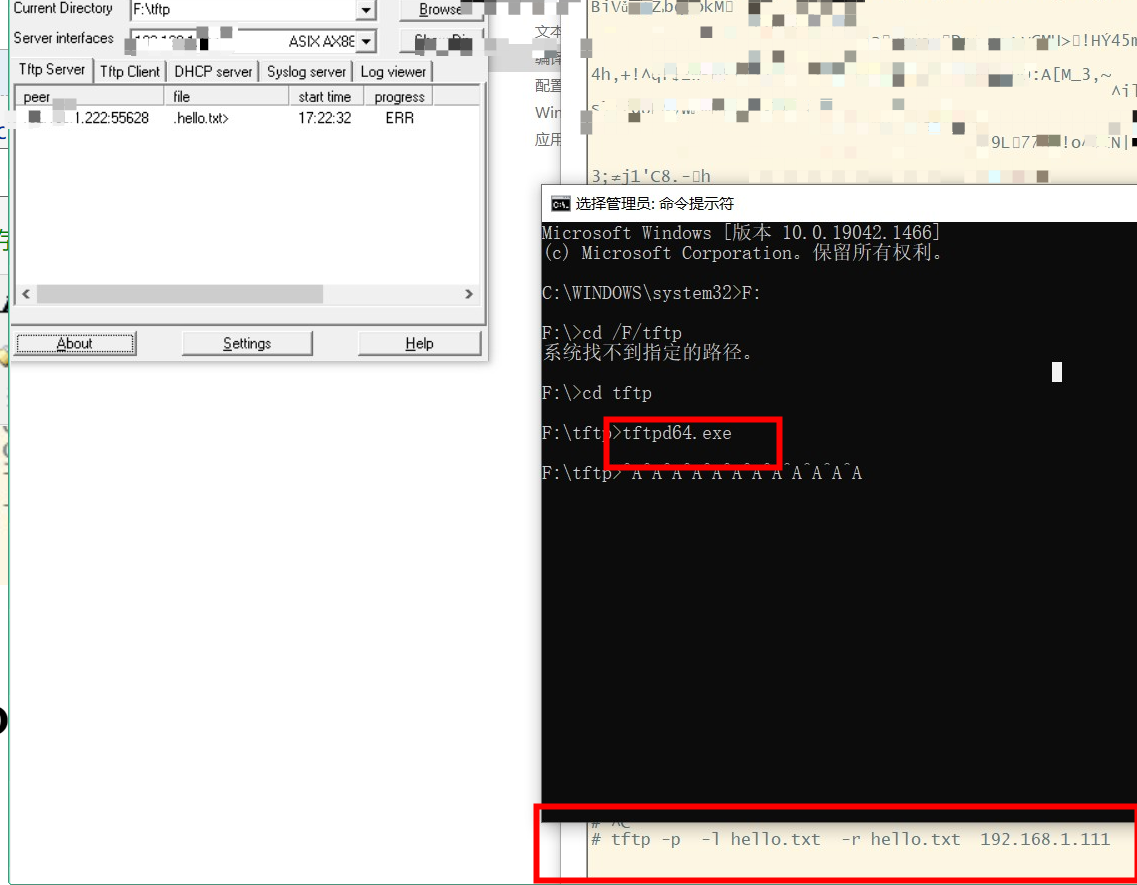
从Clinet上传文件到Server时,使用下面的命令
tftp –p –r 目标文件名 -l 源文件名 服务器地址如命令tftp –p –r D.txt –l C.txt 192.168.1.2的作用是从Client上传文件C.txt到Server的tftp根目标下,并更名为D.txt;若不更名,D.txt就改为C.txt.
这个命令一般是用于下载或上传后进行更改文件名,如若不更改文件名,可使用以下简单命令




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号