nginx Ingress openresty
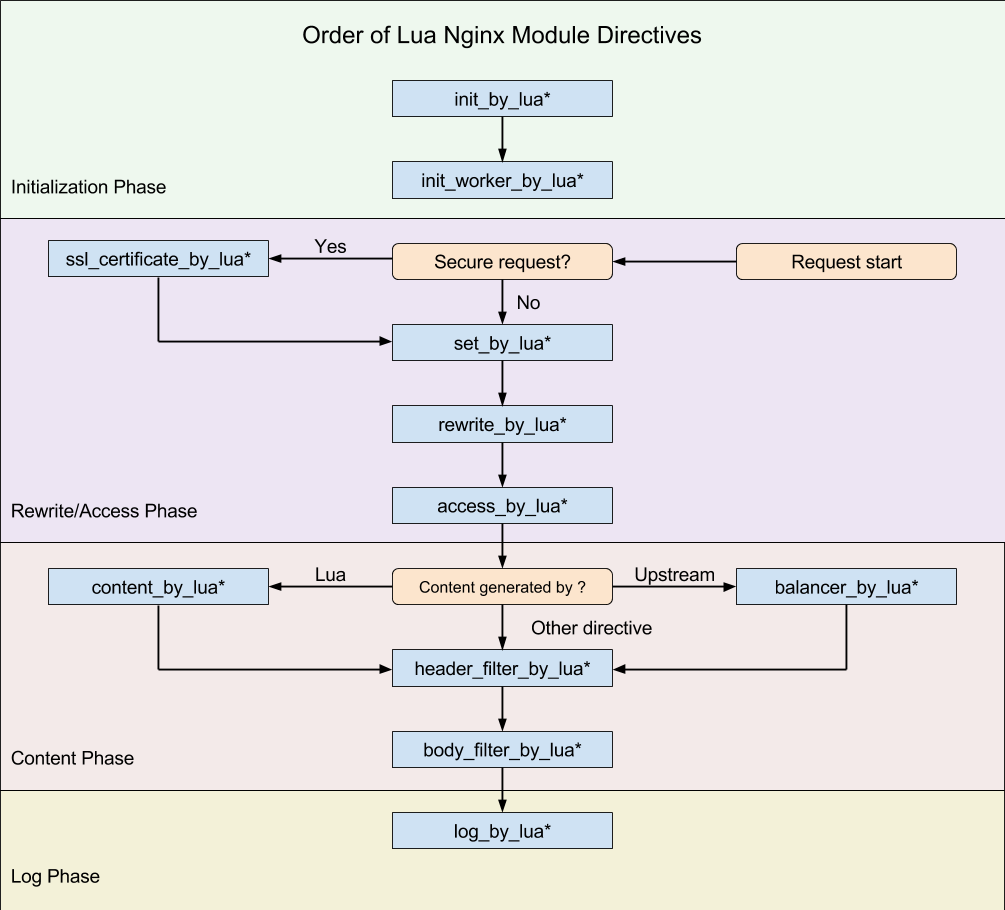
OpenResty 处理一个请求,它的处理流程请参考下图(从 Request start 开始):
我们在这里做个测试,示例代码如下:
[root@centos7 work]# cat conf/nginx.conf worker_processes 1; pid logs/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { server { listen 7777; server_name localhost; location /mixed { set_by_lua_block $res { ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "set_by_lua*") } rewrite_by_lua_block { ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "rewrite_by_lua*") } access_by_lua_block { ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "access_by_lua*") } content_by_lua_block { ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "content_by_lua*") } header_filter_by_lua_block { ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "header_filter_by_lua*") } body_filter_by_lua_block { ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "body_filter_by_lua*") } log_by_lua_block { ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "log_by_lua*") } } } }
curl -I http://127.0.0.1:7777/mixed
执行结果日志(截取了一下):
set_by_lua*
rewrite_by_lua*
access_by_lua*
content_by_lua*
header_filter_by_lua*
body_filter_by_lua*
log_by_lua*
![]()
这几个阶段的存在,应该是 OpenResty 不同于其他多数 Web 平台编程的最明显特征了。由于 Nginx 把一个请求分成了很多阶段,这样第三方模块就可以根据自己行为,挂载到不同阶段进行处理达到目的。OpenResty 也应用了同样的特性。所不同的是,OpenResty 挂载的是我们编写的 Lua 代码。
这样我们就可以根据我们的需要,在不同的阶段直接完成大部分典型处理了。
set_by_lua*: 流程分支处理判断变量初始化rewrite_by_lua*: 转发、重定向、缓存等功能(例如特定请求代理到外网)access_by_lua*: IP 准入、接口权限等情况集中处理(例如配合 iptable 完成简单防火墙)content_by_lua*: 内容生成header_filter_by_lua*: 响应头部过滤处理(例如添加头部信息)body_filter_by_lua*: 响应体过滤处理(例如完成应答内容统一成大写)log_by_lua*: 会话完成后本地异步完成日志记录(日志可以记录在本地,还可以同步到其他机器)
实际上我们只使用其中一个阶段 content_by_lua*,也可以完成所有的处理。但这样做,会让我们的代码比较臃肿,越到后期越发难以维护。把我们的逻辑放在不同阶段,分工明确,代码独立,后期发力可以有很多有意思的玩法。
举一个例子,如果在最开始的开发中,请求体和响应体都是通过 HTTP 明文传输,后面需要使用 aes 加密,利用不同的执行阶段,我们可以非常简单的实现:
# 明文协议版本
location /mixed {
content_by_lua_file ...; # 请求处理
}
# 加密协议版本
location /mixed {
access_by_lua_file ...; # 请求加密解码
content_by_lua_file ...; # 请求处理,不需要关心通信协议
body_filter_by_lua_file ...; # 应答加密编码
}
内容处理部分都是在 content_by_lua* 阶段完成,第一版本 API 接口开发都是基于明文。为了传输体积、安全等要求,我们设计了支持压缩、加密的密文协议(上下行),痛点就来了,我们要更改所有 API 的入口、出口么?
最后我们是在 access_by_lua* 完成密文协议解码,body_filter_by_lua* 完成应答加密编码。如此一来世界都宁静了,我们没有更改已实现功能的一行代码,只是利用 OpenResty 的阶段处理特性,非常优雅的解决了这个问题。
不同的阶段,有不同的处理行为,这是 OpenResty 的一大特色。学会它,适应它,会给你打开新的一扇门。这些东西不是 OpenResty 自身所创,而是 Nginx module 对外开放的处理阶段。理解了他,也能更好的理解 Nginx 的设计思维。
demo1
基于Nginx或是OpenResty的Ingress实现使用 了类似下方的多域名配置, 通过不同的server_name选择合适的后端服务.
[root@centos7 work]# cat conf/nginx.conf worker_processes 1; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { upstream backend_apache{ server 10.111.63.105:80; } upstream backend_nginx{ server 10.99.87.66:8097; } server { listen 7777; server_name apache.com; location / { proxy_pass http://backend_apache; } } server { listen 7777; server_name nginx.com; location / { proxy_pass http://backend_nginx; } } }
[root@centos7 work]# nginx -p `pwd`/ -c conf/nginx.conf [root@centos7 work]# curl -i "apache.com" http://localhost:7777 HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently Date: Fri, 06 Aug 2021 08:07:30 GMT Server: Apache X-Redirect-By: WordPress Location: http://www.apache.com/ Content-Length: 0 Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8 HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: openresty/1.19.3.2 Date: Fri, 06 Aug 2021 08:07:33 GMT Content-Type: text/html Content-Length: 45 Connection: keep-alive Last-Modified: Mon, 11 Jun 2007 18:53:14 GMT ETag: "2d-432a5e4a73a80" Accept-Ranges: bytes <html><body><h1>It works!</h1></body></html> [root@centos7 work]# curl -i "nginx.com" http://localhost:7777 HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently Server: nginx/1.19.10 Date: Fri, 06 Aug 2021 08:08:01 GMT Content-Type: text/html Content-Length: 170 Connection: keep-alive Keep-Alive: timeout=15 Location: https://www.nginx.com/ <html> <head><title>301 Moved Permanently</title></head> <body> <center><h1>301 Moved Permanently</h1></center> <hr><center>nginx/1.19.10</center> </body> </html> HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: openresty/1.19.3.2 Date: Fri, 06 Aug 2021 08:08:04 GMT Content-Type: text/html Content-Length: 45 Connection: keep-alive Last-Modified: Mon, 11 Jun 2007 18:53:14 GMT ETag: "2d-432a5e4a73a80" Accept-Ranges: bytes <html><body><h1>It works!</h1></body></html> [root@centos7 work]# curl -I -H "nginx.com" http://localhost:7777 HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: openresty/1.19.3.2 Date: Fri, 06 Aug 2021 08:09:57 GMT Content-Type: text/html Content-Length: 45 Connection: keep-alive Last-Modified: Mon, 11 Jun 2007 18:53:14 GMT ETag: "2d-432a5e4a73a80" Accept-Ranges: bytes [root@centos7 work]# curl -I -H "apache.com" http://localhost:7777 HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: openresty/1.19.3.2 Date: Fri, 06 Aug 2021 08:10:09 GMT Content-Type: text/html Content-Length: 45 Connection: keep-alive Last-Modified: Mon, 11 Jun 2007 18:53:14 GMT ETag: "2d-432a5e4a73a80" Accept-Ranges: bytes [root@centos7 work]#
demo2动态upstream
[root@centos7 work]# cat conf/nginx.conf worker_processes 1; pid logs/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { #include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; log_format main ' - [] "" ' ' "" ' '"" ""'; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65; lua_shared_dict upstreams 1m; # 声明一个ngx多进程全局共享内存区域,_G 作为基于shm的Lua字典的存储空间ngx.shared.<name> upstream apache_upstream { # 配置后端服务器组 server 10.244.243.197:80; server 10.244.129.184:80; } upstream nginx_upstream { # 配置后端服务器组 server 10.244.41.1:80; server 10.244.41.2:80; } server { listen 7777; server_name localhost; access_log logs/80.access.log main; error_log logs/80.error.log error; location = /_switch_upstream { content_by_lua_block{ local ups = ngx.req.get_uri_args()["upstream"] if ups == nil or ups == "" then ngx.say("upstream is nil 1") return nil end local host = ngx.var.http_host local upstreams = ngx.shared.upstreams local ups_src = upstreams:get(host) ngx.say("Current upstream is :",ups_src) ngx.log(ngx.WARN, host, " change upstream from ", ups_src, " to ", ups) local succ, err, forcible = upstreams:set(host, ups) ngx.say(host, " change upstream from ", ups_src, " to ", ups) } } location / { set_by_lua_block $my_upstream { local ups = ngx.shared.upstreams:get(ngx.var.http_host) if ups ~= nil then ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "get [", ups,"] from ngx.shared") return ups end return "apache_upstream" } #proxy_next_upstream off; #proxy_set_header X-Real-IP ; #proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For ; #proxy_set_header Host ; #proxy_http_version 1.1; #proxy_set_header Connection ""; proxy_pass http://$my_upstream ; } } }
[root@centos7 work]# curl -I -H "locahost" http://localhost:7777 HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: openresty/1.19.3.2 Date: Fri, 06 Aug 2021 08:50:05 GMT Content-Type: text/html Content-Length: 45 Connection: keep-alive Last-Modified: Mon, 11 Jun 2007 18:53:14 GMT ETag: "2d-432a5e4a73a80" Accept-Ranges: bytes [root@centos7 work]# curl http://localhost:7777 <html><body><h1>It works!</h1></body></html> [root@centos7 work]# curl http://localhost:7777/_switch_upstream?upstream=nginx_upstream Current upstream is :nil localhost:7777 change upstream from nil to nginx_upstream [root@centos7 work]# curl http://localhost:7777/_switch_upstream?upstream=nginx_upstream Current upstream is :nginx_upstream localhost:7777 change upstream from nginx_upstream to nginx_upstream [root@centos7 work]# curl http://localhost:7777/_switch_upstream?upstream=apache_upstream Current upstream is :nginx_upstream localhost:7777 change upstream from nginx_upstream to apache_upstream [root@centos7 work]# curl -I -H "locahost" http://localhost:7777/_switch_upstream?upstream=apache_upstream HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: openresty/1.19.3.2 Date: Fri, 06 Aug 2021 08:51:19 GMT Content-Type: application/octet-stream Connection: keep-alive [root@centos7 work]#
balancer_by_lua_block
[root@centos7 work]# kubectl exec -it ingress-nginx-controller-7478b9dbb5-6qk65 -n ingress-nginx -- cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf | grep balancer_by_lua -A 10 -B 5 # ### server 0.0.0.1; # placeholder balancer_by_lua_block { balancer.balance() } keepalive 320; keepalive_timeout 60s; keepalive_requests 10000; } -- error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log notice; upstream upstream_balancer { server 0.0.0.1:1234; # placeholder balancer_by_lua_block { tcp_udp_balancer.balance() } } server { listen 127.0.0.1:10247; access_log off; content_by_lua_block {
[root@centos7 work]# cat conf/nginx.conf worker_processes 1; daemon off; error_log /dev/stdout; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { upstream backend { server 0.0.0.1; # just an invalid address as a place holder balancer_by_lua_block { local balancer = require "ngx.balancer" -- well, usually we calculate the peer's host and port -- according to some balancing policies instead of using -- hard-coded values like below local host = "10.103.182.145" local port = 80 local ok, err = balancer.set_current_peer(host, port) if not ok then ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "failed to set the current peer: ", err) return ngx.exit(500) end } keepalive 10; # connection pool } server { # this is the real entry point listen 7777; location / { # make use of the upstream named "backend" defined above: #proxy_pass http://backend/fake; proxy_pass http://backend; proxy_set_header Connection ""; } } server { # this server is just for mocking up a backend peer here... listen 127.0.0.2:8080; location = /fake { echo "this is the fake backend peer..."; } } }
[root@centos7 work]# curl http://localhost:7777 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Welcome to nginx!</title> <style> body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto; font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1> <p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and working. Further configuration is required.</p> <p>For online documentation and support please refer to <a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/> Commercial support is available at <a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p> <p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p> </body> </html>
stream subsystem
worker_processes 1; daemon off; error_log /dev/stdout; events { worker_connections 1024; } stream { upstream backend { server 0.0.0.1:1234; # just an invalid address as a place holder balancer_by_lua_block { local balancer = require "ngx.balancer" -- well, usually we calculate the peer's host and port -- according to some balancing policies instead of using -- hard-coded values like below local host = "10.103.182.145" local port = 80 local ok, err = balancer.set_current_peer(host, port) if not ok then ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "failed to set the current peer: ", err) return ngx.exit(500) end } } server { # this is the real entry point listen 7777; proxy_pass backend; }
[root@centos7 work]# curl http://localhost:7777 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Welcome to nginx!</title> <style> body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto; font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1> <p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and working. Further configuration is required.</p> <p>For online documentation and support please refer to <a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/> Commercial support is available at <a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p> <p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p> </body> </html>
content_by_lua_block
# default server, used for NGINX healthcheck and access to nginx stats server { listen unix:/tmp/nginx-status-server.sock; set $proxy_upstream_name "internal"; keepalive_timeout 0; gzip off; access_log off; location /healthz { return 200; } location /is-dynamic-lb-initialized { content_by_lua_block { local configuration = require("configuration") local backend_data = configuration.get_backends_data() if not backend_data then ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR) return end ngx.say("OK") ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_OK) } } location /nginx_status { stub_status on; } location /configuration { # this should be equals to configuration_data dict client_max_body_size 10m; client_body_buffer_size 10m; proxy_buffering off; content_by_lua_block { configuration.call() } } location / { content_by_lua_block { ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_NOT_FOUND) } } }
与其他 location 配合
nginx 世界的 location 是异常强大的,毕竟 nginx 的主要应用场景是在负载均衡、API server,在不同 server、location 之间跳转更是家常便饭。利用不同 location 的功能组合,我们可以完成内部调用、流水线方式跳转、外部重定向等几大不同方式,下面将给大家介绍几个主要应用,就当抛砖引玉。
内部调用
例如对数据库、内部公共函数的统一接口,可以把它们放到统一的 location 中。通常情况下,为了保护这些内部接口,都会把这些接口设置为 internal 。这么做的最主要好处就是可以让这个内部接口相对独立,不受外界干扰。
worker_processes 1; daemon off; pid logs/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024; } http{ server { location = /sum { internal; content_by_lua_block { ngx.sleep(0.1) local args = ngx.req.get_uri_args() ngx.print(tonumber(args.a) + tonumber(args.b)) } } location = /subduction { internal; content_by_lua_block { ngx.sleep(0.1) local args = ngx.req.get_uri_args() ngx.print(tonumber(args.a) - tonumber(args.b)) } } location = /app/test_parallels { content_by_lua_block { local start_time = ngx.now() local res1, res2 = ngx.location.capture_multi( { {"/sum", {args={a=3, b=8}}}, {"/subduction", {args={a=3, b=8}}} }) ngx.say("status:", res1.status, " response:", res1.body) ngx.say("status:", res2.status, " response:", res2.body) ngx.say("time used:", ngx.now() - start_time) } } location = /app/test_queue { content_by_lua_block { local start_time = ngx.now() local res1 = ngx.location.capture_multi( { {"/sum", {args={a=3, b=8}}} }) local res2 = ngx.location.capture_multi( { {"/subduction", {args={a=3, b=8}}} }) ngx.say("status:", res1.status, " response:", res1.body) ngx.say("status:", res2.status, " response:", res2.body) ngx.say("time used:", ngx.now() - start_time) } } } }
[root@centos7 ~]# curl 127.0.0.1/app/test_parallels status:200 response:11 status:200 response:-5 time used:0.10099983215332 [root@centos7 ~]# curl 127.0.0.1/app/test_queue status:200 response:11 status:200 response:-5 time used:0.20099997520447 [root@centos7 ~]#
利用 ngx.location.capture_multi 函数,直接完成了两个子请求并行执行。当两个请求没有相互依赖,这种方法可以极大提高查询效率。两个无依赖请求,各自是 100ms,顺序执行需要 200ms,但通过并行执行可以在 100ms 完成两个请求。实际生产中查询时间可能没这么规整,但思想大同小异,这个特性是很有用的。
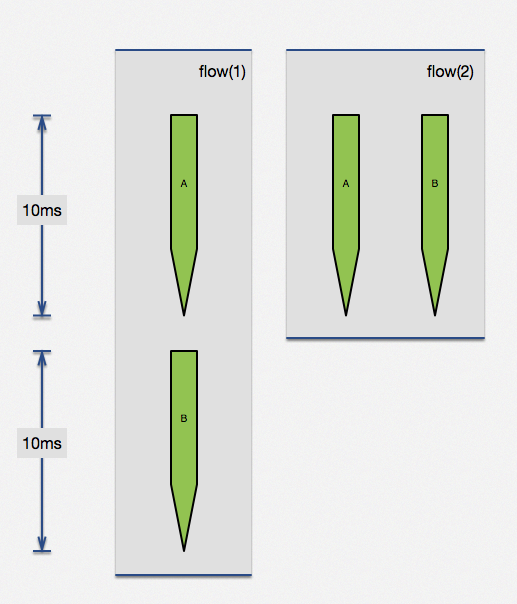
该方法,可以被广泛应用于广告系统(1:N模型,一个请求,后端从N家供应商中获取条件最优广告)、高并发前端页面展示(并行无依赖界面、降级开关等)。






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号