c语言分析和循坏对应的汇编定义格式(Debug版本)
c语言if单分支结构所对应的汇编代码结构
#include "stdafx.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if(argc > 8 )
{
printf("argc > 8");
if(argc > 50)
{
printf("argc > 50");
}
}
return 0;
}
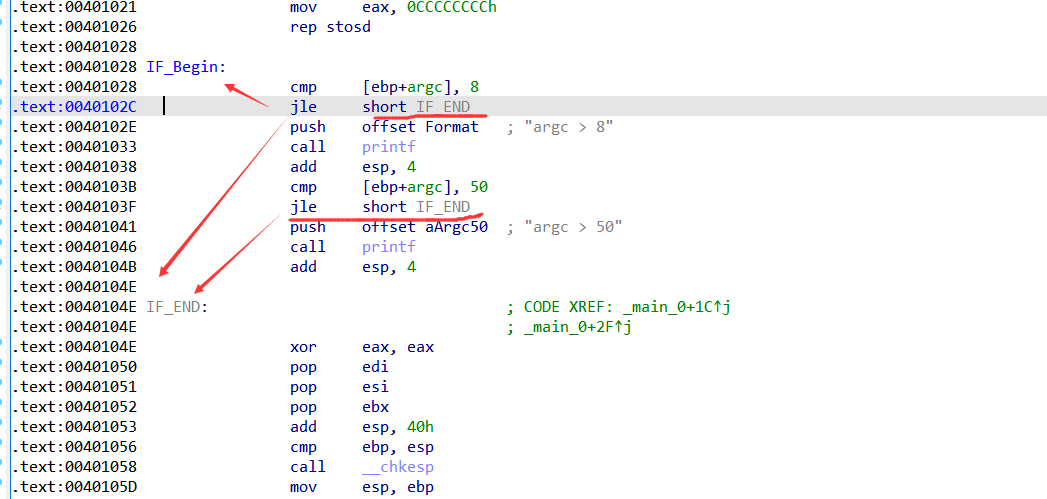

注意这些与语言没有关系,这是编译原理的问题,以后看编译原理
if和else双分支的汇编结构
#include "stdafx.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if(argc> 0 )
{
printf("argc>0\r\n");
}
else
{
printf("argc<=0\r\n");
}
return 0;
}

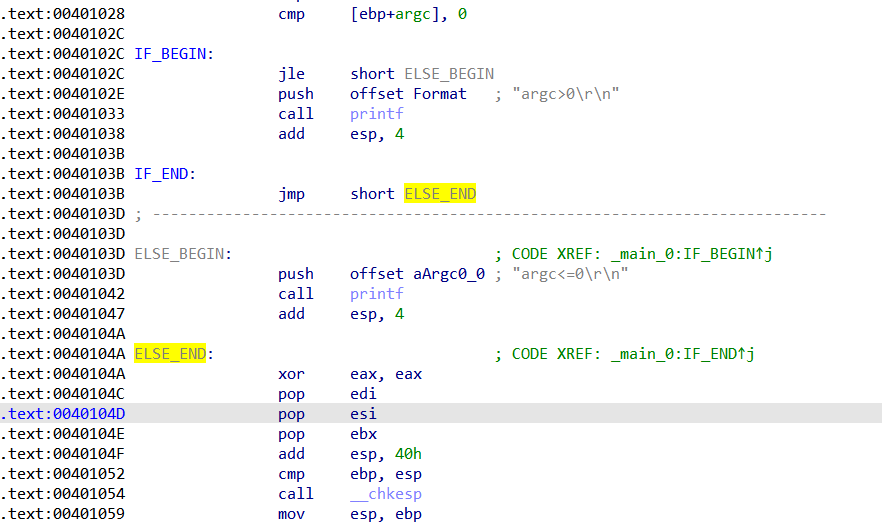
双分支的结构特点:jxx的目标上一行指令为jmp,而且是往高地址去的的jmp
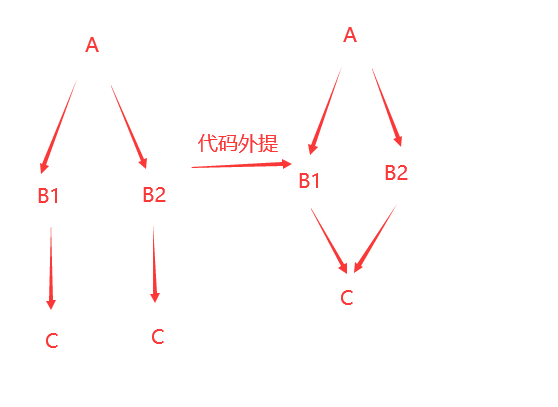
编译原理代码优化外提
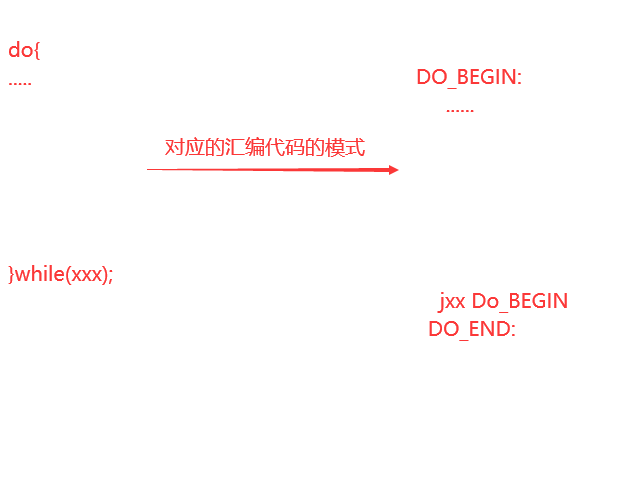
do—while(效率最高,跳转的目标没有检测条件,往上跳)
#include "stdafx.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int n = 1;
int nSum = 0;
do
{
nSum=nSum+n;
n++;
}
while(n<=100);
return 0;
}
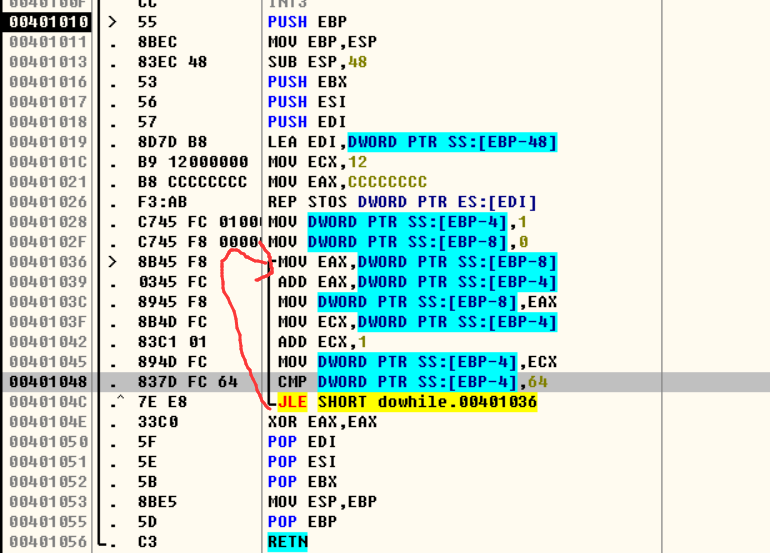
1.识别代码定式
2.如果是do循环,则按jxx同条件还原等价高级代码
3.其余的代码还原则按相反的规则还原
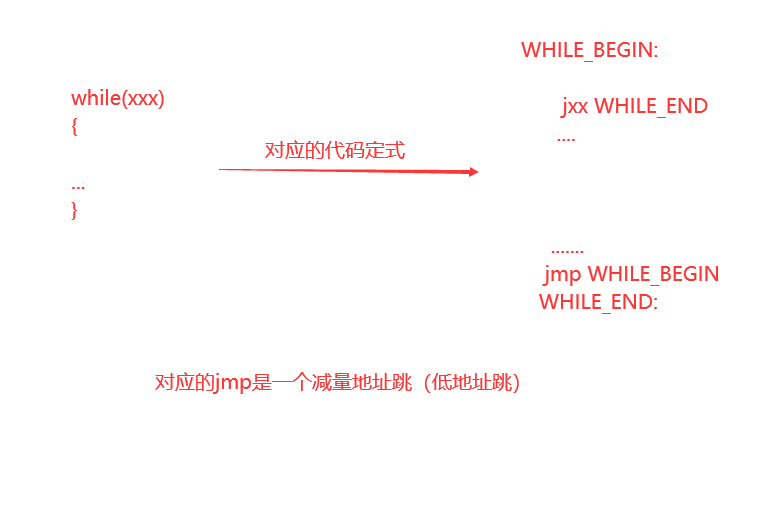
while循环的代码定式(地址减量跳,两跳)
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int n = 1;
int nSum = 0;
while(n<=100){
nSum = nSum + n;
n++;
}
printf("%d",nSum);
return 0;
}
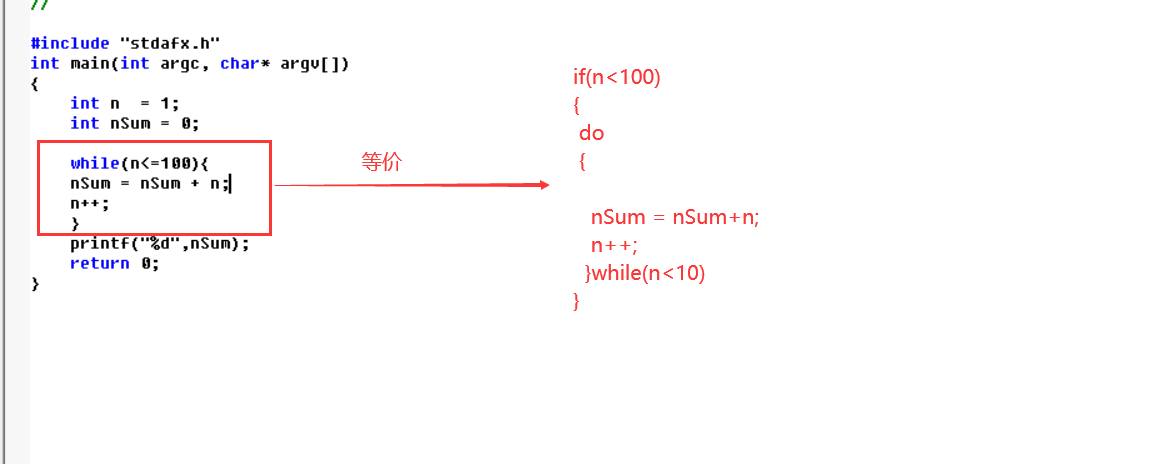
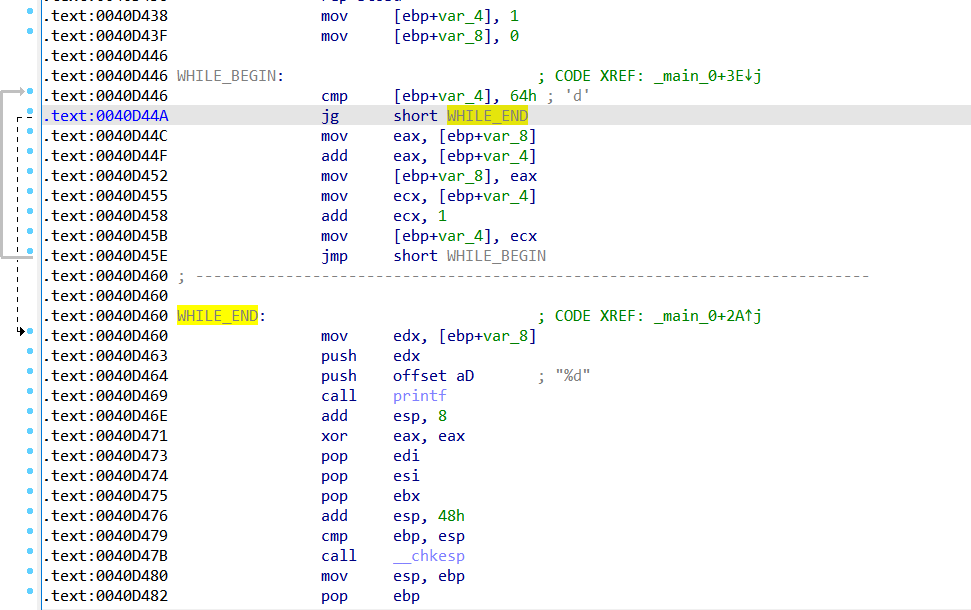
关键比较是比较的是常量,常量在是可以在编译期间预知其结果。常量传播
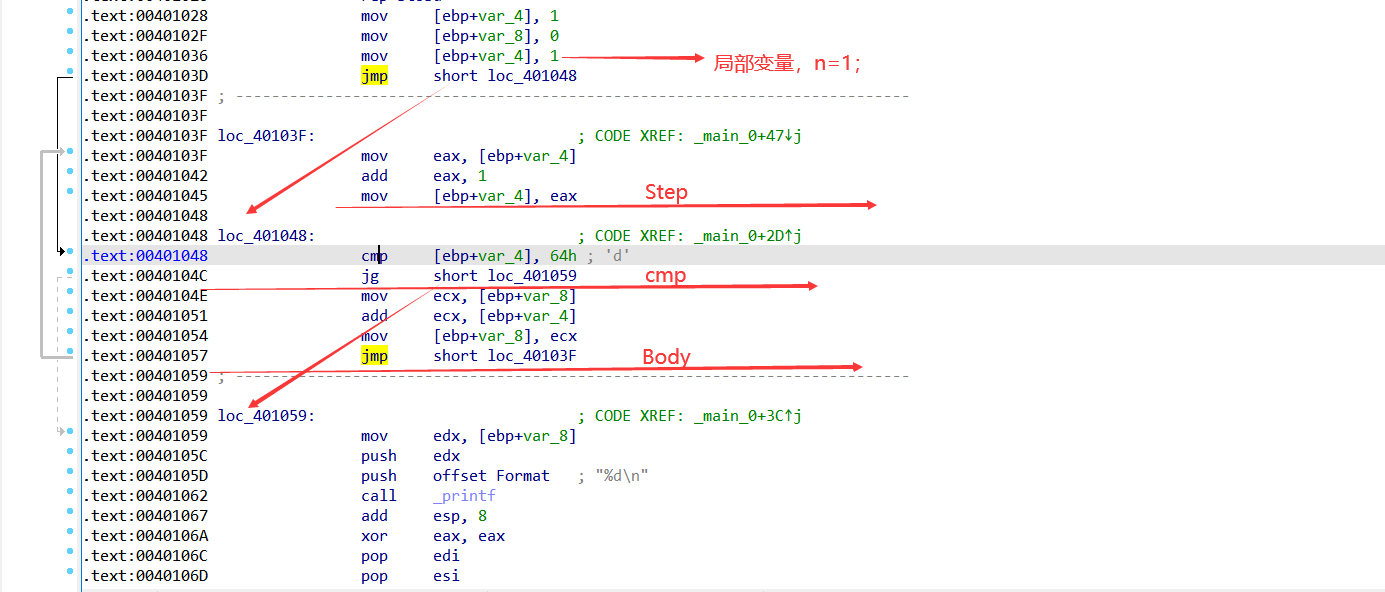
for循环
#include "stdafx.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int i = 1; ;
int nSum = 0;
for(i=1; i<=100; i++)
{
nSum = nSum+ i ;
}
printf("%d\n",nSum);
return 0;
}

if和else if
#include "stdafx.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int nSum = 0 ;
if(argc ==1)
{
nSum = nSum+1;
}
else if(argc == 2)
{
nSum = nSum-1;
}
else if(argc == 3)
{
nSum = nSum*argc;
}
else
{
nSum = nSum / argc;
}
return 0;
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号