go的相关包time、os、rand、fmt
time
1、time包
2、time.Time类型, 用来表示时间
3、取当前时间, now := time.Now()
4、time.Now().Day(),time.Now().Minute(),time.Now().Month(),time.Now().Year(),
second := now.Unix() //按秒计
5、格式化,fmt.Printf(“%02d/%02d%02d %02d:%02d:%02d”, now.Year()…)
package main
import(
"time"
"fmt"
)
func testTime() {
for {
now := time.Now()
fmt.Printf("type of now is:%T\n", now)
year := now.Year()
month := now.Month()
day := now.Day()
str := fmt.Sprintf("%04d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d\n", year, month, day, now.Hour(), now.Minute(), now.Second())
fmt.Println(str)
fmt.Printf("timestamp:%d\n", now.Unix()) //时间戳
}
}
6、time.Duration 用来表示纳秒
7、 一些常量量:
const (
Nanosecond Duration = 1
Microsecond= 1000 * Nanosecond //纳秒
Millisecond= 1000 * Microsecond //微妙
Second= 1000 * Millisecond //毫秒
Minute= 60 * Second
Hour= 60 * Minute
)
package main
import(
"time"
"fmt"
)
func testTimeConst() {
fmt.Printf("Nanosecond :%d\n", time.Nanosecond) //1
fmt.Printf("Microsecond:%d\n", time.Microsecond) //1000
fmt.Printf("Millisecond:%d\n", time.Millisecond) //1000000
fmt.Printf("second :%d\n", time.Second)
fmt.Printf("Minute :%d\n", time.Minute)
fmt.Printf("Hour :%d\n", time.Hour)
}
8. 格式化:
now := time.Now()
fmt.Println(now.Format(“02/1/2006 15:04:05”)) //02/1/2006 03:04:05 十二小时制
fmt.Println(now.Format(“2006/1/02 15:04:05”))
fmt.Println(now.Format(“2006/1/02”))
package main
import(
"time"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
now := time.Now()
str := now.Format("2006-01-02 03:04:05")
fmt.Printf("format result:%s\n", str)
}
练习:写 一个程序,统计一段代码的执行耗时,单位精确到微秒
package main
import(
"time"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
start := time.Now().UnixNano() //纳秒为单位
/*
业务代码
*/
time.Sleep(10*time.Millisecond)
end := time.Now().UnixNano()
cost := (end - start)/1000
fmt.Printf("cost:%dus\n", cost)
}
os
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
var goos string = os.Getenv("OS") //操作系统的名字
fmt.Printf("The operating system is: %s\n", goos)
path := os.Getenv("PATH") //GOPATH的路径
fmt.Printf("Path is %s\n", path)
}
math/rand
 View Code
View Code View Code
View Code
fmt
各种方法集合:
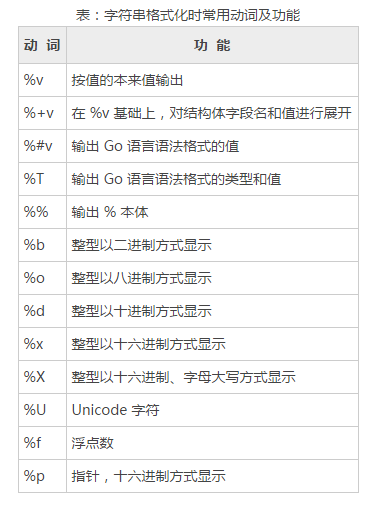
格式化输出:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var a int = 100
var b bool
c := 'a'
fmt.Printf("%+v\n", a) //类似%v,但输出结构体时会添加字段名
fmt.Printf("%#v\n", b) //相应值的Go语法表示
fmt.Printf("%T\n", c) //值的类型的Go语法表示
fmt.Printf("90%%\n") //字面上的%
fmt.Printf("%t\n", b) //布尔值
fmt.Printf("%b\n", 100) //二进制
fmt.Printf("%f\n", 199.22) //浮点型,有小数点,但没有指数
fmt.Printf("%q\n", "this is a test") //双引号围绕的字符字面值
fmt.Printf("%x\n", 39839333) //每个字节用两字符十六进制数表示(使用a-f)
fmt.Printf("%p\n", &a) //传入指针,表示为十六进制,并加上前导的0x
fmt.Printf("%c\n", 87) //相应Unicode码所表示的字符
str := fmt.Sprintf("a=%d", a) // 将a转化为字符串
fmt.Printf("%q\n", str)
}
格式化输入:
package main
import "fmt"
var number int
var str string
func main() {
fmt.Scanf("%d", &number)
fmt.Scanf("%s", &str)
fmt.Println(number, str)
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号