连续登录计算
题目一:
11月结束后,小牛同学需要对其在某宝的网店就11月份用户交易情况和产品情况进行分析以更好的经营小店。
11月份销售数据表sales_tb如下(其中,sales_date表示销售日期,user_id指用户编号,item_id指货号,sales_num表示销售数量,sales_price表示结算金额):
|
sales_date |
user_id |
item_id |
sales_num |
sales_price |
|
2021-11-01 |
1 |
A001 |
1 |
90 |
|
2021-11-01 |
2 |
A002 |
2 |
220 |
|
2021-11-01 |
2 |
B001 |
1 |
120 |
|
2021-11-02 |
3 |
C001 |
2 |
500 |
|
2021-11-02 |
4 |
B001 |
1 |
120 |
|
2021-11-03 |
5 |
C001 |
1 |
240 |
|
2021-11-03 |
6 |
C002 |
1 |
270 |
|
2021-11-04 |
7 |
A003 |
1 |
180 |
|
2021-11-04 |
8 |
B002 |
1 |
140 |
|
2021-11-04 |
9 |
B001 |
1 |
125 |
|
2021-11-05 |
10 |
B003 |
1 |
120 |
|
2021-11-05 |
10 |
B004 |
1 |
150 |
|
2021-11-05 |
10 |
A003 |
1 |
180 |
|
2021-11-06 |
11 |
B003 |
1 |
120 |
|
2021-11-06 |
10 |
B004 |
1 |
150 |
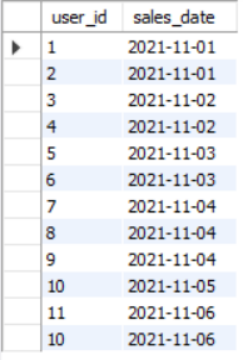
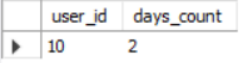
请你统计连续2天及以上在该店铺购物的用户及其对应的次数(若有多个用户,按user_id升序排序),以上例子的输出结果如下:
|
user_id |
days_count |
|
10 |
2 |
#1.首先进行去重,排除第一天多次登录的情况
select distinct user_id,
sales_date,
from sales_tb
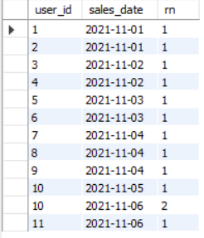
#2.对用户按照日期排序
select distinct user_id,
sales_date,
dense_rank() over (partition by user_id order by sales_date) rn
from sales_tb
#3.将每个用户日期推迟对应的排名数,差值相同则是连续的
date_sub(sales_date ,INTERVAL rn day) as 差值
#4.按照用户和差值分组,其实就是去重,
group by user_id , date_sub(sales_date ,INTERVAL rn day)
#5.选出连续天数大于2的用户
select user_id ,
count(*) days_count
from (select user_id,
sales_date,
ROW_NUMBER() over (partition by user_id order by sales_date) rn
from sales_tb) a
group by user_id , date_sub(sales_date ,INTERVAL rn day)
having days_count >=2
注意:数据量太少,解法可能存在漏洞,比如用户A,日期12,456登陆了,连续登录日期有2和3,这个时候还要考虑要3还是要2还是都要。
题目二:
现有某乎问答创作者信息表author_tb如下(其中author_id表示创作者编号、author_level表示创作者级别,共1-6六个级别、sex表示创作者性别):
|
author_id |
author_level |
sex |
|
101 |
6 |
m |
|
102 |
1 |
f |
|
103 |
1 |
m |
|
104 |
3 |
m |
|
105 |
4 |
f |
|
106 |
2 |
f |
|
107 |
2 |
m |
|
108 |
5 |
f |
|
109 |
6 |
f |
|
110 |
5 |
m |
创作者回答情况表answer_tb如下(其中answer_date表示创作日期、author_id指创作者编号、issue_id指回答问题编号、char_len表示回答字数):
|
answer_date |
author_id |
issue_id |
char_len |
|
2021-11-01 |
101 |
E001 |
150 |
|
2021-11-01 |
101 |
E002 |
200 |
|
2021-11-01 |
102 |
C003 |
50 |
|
2021-11-01 |
103 |
P001 |
35 |
|
2021-11-01 |
104 |
C003 |
120 |
|
2021-11-01 |
105 |
P001 |
125 |
|
2021-11-01 |
102 |
P002 |
105 |
|
2021-11-02 |
101 |
P001 |
201 |
|
2021-11-02 |
110 |
C002 |
200 |
|
2021-11-02 |
110 |
C001 |
225 |
|
2021-11-02 |
110 |
C002 |
220 |
|
2021-11-03 |
101 |
C002 |
180 |
|
2021-11-04 |
109 |
E003 |
130 |
|
2021-11-04 |
109 |
E001 |
123 |
|
2021-11-05 |
108 |
C001 |
160 |
|
2021-11-05 |
108 |
C002 |
120 |
|
2021-11-05 |
110 |
P001 |
180 |
|
2021-11-05 |
106 |
P002 |
45 |
|
2021-11-05 |
107 |
E003 |
56 |
请你统计最大连续回答问题的天数大于等于3天的用户及其等级(若有多条符合条件的数据,按author_id升序排序),以上例子的输出结果如下:
|
author_id |
author_level |
days_cnt |
|
101 |
6 |
3 |
相同思路:
select author_id,author_level,count(*) as cnt
from
(
select distinct b.author_id,answer_date,a.author_level ,
dense_rank()over(partition by b.author_id order by answer_date) rk
from author_tb a,answer_tb b
where a.author_id = b.author_id
) c
group by author_id,author_level, date_sub(answer_date,interval rk day)
having cnt >=3
更严谨:
select author_id,author_level,max(cnt)
from
(select author_id,author_level,count(*) as cnt
from
(
select distinct b.author_id,answer_date,a.author_level ,
dense_rank()over(partition by b.author_id order by answer_date) rk
from author_tb a,answer_tb b
where a.author_id = b.author_id
) c
group by author_id,author_level, date_sub(answer_date,interval rk day)
having cnt >=3
) d
group by author_id,author_level



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号