MySQL查询(一)
题一:现有strings表如下:
id指序列号;
string列中存放的是字符串,且字符串中仅包含数字、字母和逗号类型的字符。
|
id |
string |
|
1 2 3 |
10,A,B,C,D A,B,C,D,E,F A,11,B,C,D,E,G |
请你统计每个字符串中逗号出现的次数cnt。
以上例子的输出结果如下:
|
id |
cnt |
|
1 2 3 |
4 5 6 |

方法一:
用到的函数:
length(s)函数: s是字符串, 返回的是所求的字符串s的长度。
replace(a,b,c): 在字符串a中,将a中出现的b,替换成c。再把这个替换之后的串的结果返回。
select id,
length(string)-length(replace(string,',','')) as cnt
from strings
方法二:
SELECT
id,
length(
regexp_replace(STRING, '[A-Z 0-9]', '')
)
FROM
strings;
使用正则表达是把字母数字删除。取长度即可
题2:现有employees表如下:
|
emp_no |
birth_date |
first_name |
last_name |
gender |
hire_date |
|
10001 |
1953-09-02 |
Georgi |
Facello |
M |
1986-06-26 |
|
10002 |
1964-06-02 |
Bezalel |
Simmel |
F |
1985-11-21 |
|
10003 |
1959-12-03 |
Parto |
Bamford |
M |
1986-08-28 |
|
10004 |
1954-05-01 |
Christian |
Koblick |
M |
1986-12-01 |
|
10005 |
1955-01-21 |
Kyoichi |
Maliniak |
M |
1989-09-12 |
|
10006 |
1953-04-20 |
Anneke |
Preusig |
F |
1989-06-02 |
|
10007 |
1957-05-23 |
Tzvetan |
Zielinski |
F |
1989-02-10 |
|
10008 |
1958-02-19 |
Saniya |
Kalloufi |
M |
1994-09-15 |
|
10009 |
1952-04-19 |
Sumant |
Peac |
F |
1985-02-18 |
|
10010 |
1963-06-01 |
Duangkaew |
Piveteau |
F |
1989-08-24 |
|
10011 |
1953-11-07 |
Mary |
Sluis |
F |
1990-01-22 |
请你将employees中的first_name,并按照first_name最后两个字母升序进行输出。
以上示例数据的输出如下:
|
first_name |
|
Christian |
|
Tzvetan |
|
Bezalel |
|
Duangkaew |
|
Georgi |
|
Kyoichi |
|
Anneke |
|
Sumant |
|
Mary |
|
Parto |
|
Saniya |
思路:
substr(string,start,length)
string - 指定的要截取的字符串。
start - 必需,规定在字符串的何处开始。正数 - 在字符串的指定位置开始,负数 - 在从字符串结尾的指定位置开始,0 - 在字符串中的第一个字符处开始。
length - 可选,指定要截取的字符串长度,缺省时返回字符表达式的值结束前的全部字符。
例如:select substr('abcdefg',3,4) from dual; 结果是cdef
select substr('abcdefg',-3,4) from dual; 结果efg
注意:字符串中的第一个位置始终为1。以下两个sql查询的结果相同:
例如:select substr('abcdefg',0,3) from dual; 结果是abc
select substr('abcdefg',1,3) from dual; 结果是abc
right(str, num) 函数。从右边开始截取str字符串num长度
方法一:
select first_name
from employees
order by substring(first_name,-2)
或者
select first_name
from employees
order by substring(first_name,-2,2)
方法二:
#select first_name from (
#select first_name,right(first_name,2) as sort
#from employees ) t
#order by t.sort
或者
select first_name
from employees
order by right(first_name,2)
题3:
按照dept_no进行汇总,属于同一个部门的emp_no按照逗号进行连接,结果给出dept_no以及连接出的结果employees
CREATE TABLE `dept_emp` (
`emp_no` int(11) NOT NULL,
`dept_no` char(4) NOT NULL,
`from_date` date NOT NULL,
`to_date` date NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`emp_no`,`dept_no`));
输出格式:
|
dept_no |
employees |
|
d001 |
10001,10002 |
|
d002 |
10006 |
|
d003 |
10005 |
|
d004 |
10003,10004 |
|
d005 |
10007,10008,10010 |
|
d006 |
10009,10010 |
方法:
group_concat()函数返回X的非null值的连接后的字符串。如果给出了参数Y,将会在每个X之间用Y作为分隔符。如果省略了Y,“,”将作为默认的分隔符。每个元素连接的顺序是随机的。
注意:要求连接符就是逗号时,省略Y,不然会出现两个逗号。
SELECT
dept_no,
group_concat(emp_no) employees
FROM
dept_emp
GROUP BY
dept_no
补充:
一、concat()函数
1.功能:将多个字符串连接成一个字符串
语法:concat(str1, str2,...)
返回结果为连接参数产生的字符串,如果有任何一个参数为null,则返回值为null
数据库表结构:
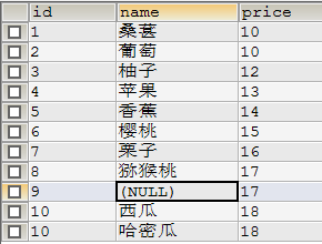
SELECT CONCAT(id,NAME,price) FROM demo;
SELECT CONCAT(id,NAME) FROM demo WHERE price ='17';
给拼接的字符串添加分隔符:
SELECT CONCAT(NAME,',',price) FROM demo WHERE id='1';
二、group_concat()函数
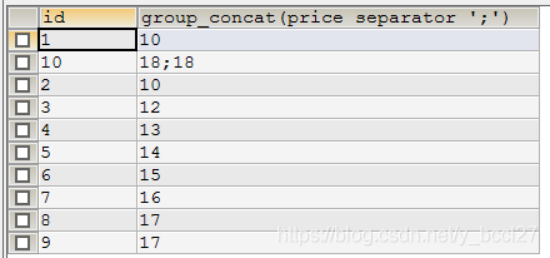
以id分组,把price字段的值在一行打印出来,分号分隔。 其中GROUP_CONCAT()函数中SEPARATOR后面接的字符表示分隔符
SELECT id,GROUP_CONCAT(price SEPARATOR ';') FROM demo GROUP BY id;
示例效果:
题4:查找排除在职(to_date = '9999-01-01' )员工的最大、最小salary之后,其他的在职员工的平均工资avg_salary。
CREATE TABLE `salaries` ( `emp_no` int(11) NOT NULL,
`salary` int(11) NOT NULL,
`from_date` date NOT NULL,
`to_date` date NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`emp_no`,`from_date`));
如:
INSERT INTO salaries VALUES(10001,85097,'2001-06-22','2002-06-22');
INSERT INTO salaries VALUES(10001,88958,'2002-06-22','9999-01-01');
INSERT INTO salaries VALUES(10002,72527,'2001-08-02','9999-01-01');
INSERT INTO salaries VALUES(10003,43699,'2000-12-01','2001-12-01');
INSERT INTO salaries VALUES(10003,43311,'2001-12-01','9999-01-01');
INSERT INTO salaries VALUES(10004,70698,'2000-11-27','2001-11-27');
INSERT INTO salaries VALUES(10004,74057,'2001-11-27','9999-01-01');
输出格式:
|
avg_salary |
|
73292 |
#方法一
select avg(salary) as avg_salary
from salaries
where salary > (select min(salary) from salaries where to_date = '9999-01-01')
and salary < (select max(salary) from salaries where to_date = '9999-01-01')
and to_date = '9999-01-01'
#方法二
#select avg(salary) as avg_salary from salaries
#where to_date = '9999-01-01'
#and salary not in (select max(salary) from salaries where to_date = '9999-01-01')
#and salary not in (select min(salary) from salaries where to_date = '9999-01-01')
#方法三
#SELECT AVG(salary)
#FROM (
# SELECT *,
# RANK() OVER(ORDER BY salary) r1,
# RANK() OVER(ORDER BY salary DESC) r2
# FROM salaries
# WHERE to_date = '9999-01-01'
#) a
#WHERE r1!=1 AND r2!=1



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号