【源码】浅看Dictionary(.Net Framework)源码
注:本文参考的源码来自mscorlib.dll,会有部分代码逻辑不同于.Net Core的Dictionary,已在另一篇博文对比介绍【源码】浅看Dictionary(System.Private.CoreLib)源码
在自定义类重写Equals()和GetHashCode()的时候有些好奇,所以想看看Dictionary查找Key和存储键值对的原理。
下面通过看看几个最常用的Dictionary的方法,了解一下Dictionary的实现原理。
GetHashCode
首先看看如果在重写Equals()的时候不重写GetHashCode()会出现什么情况
class Cat
{
public string Name;
public string Birth;
public bool Equals(Cat cat)
{
if (cat is null)
return false;
Console.WriteLine("自定义_Cat");
return Name == cat.Name && Birth == cat.Birth;
}
public override bool Equals(object obj) => Equals(obj as Cat);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Dictionary<Cat, string> cats = new Dictionary<Cat, string>()
{
{ new Cat { Name="小黑", Birth = "2020-2-1" }, "小黑" },
{ new Cat { Name="小黄", Birth = "2020-4-1" }, "小黄" },
{ new Cat { Name="憨豆", Birth = "2020-5-1" }, "憨豆" },
{ new Cat { Name="小黑", Birth = "2020-2-1" }, "小黑2" },
};
var xiaohei = new Cat { Name = "小黑", Birth = "2020-2-1" };
Console.WriteLine(cats.ContainsKey(xiaohei));
}
// 输出
// False
可以看到虽然有两个“一样”的Key,{ new Cat { Name="小黑", Birth = "2020-2-1" }, "小黑" }和{ new Cat { Name="小黑", Birth = "2020-2-1" }, "小黑2" },但是Dictionary还是正常初始化了,而在ContainsKey()时找不到Key。
ContainsKey
源码中的ContainsKey()直接returnFindEntry(key) >= 0;,再看看FindEntry()的实现
private int FindEntry(TKey key) {
if( key == null) {
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.key);
}
if (buckets != null) {
int hashCode = comparer.GetHashCode(key) & 0x7FFFFFFF;
for (int i = buckets[hashCode % buckets.Length]; i >= 0; i = entries[i].next) {
if (entries[i].hashCode == hashCode && comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key)) return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
if (entries[i].hashCode == hashCode && comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key)) return i;
所以需要hashCode相同并且comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key)返回true才认为两个Key一样,因为重写了Equals(),所以comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key)返回的是true,而在没有重写GetHashCode()时,默认使用Object.GetHashCode()获取hashCode,我没有找到这个函数的实现,但基本可以确定跟对象的存储地址是有关系的,而我们是new了一个对象去找Key的,所以得到的hashCode必然跟字典中的Key的hashCode不一致,所以会出现这样的现象。
所以必须同时重写Equals()和GetHashCode(),比如在这个例子中,根据Name和Birth确定是否同一只Cat,
public override int GetHashCode() {
return Name.GetHashCode() ^ Birth.GetHashCode();
}
此时调用的是string.GetHashCode(),生成的哈希值只与string有关,只要string一样,得到的hashCode是一样的。
Dictionary的基本原理其实就是利用一个hash表对Key和Key_Value进行存储和寻址。要看懂源码先要有点哈希表相关的基础,没有数据结构基础的慢慢看也不难懂。
Add
先上图
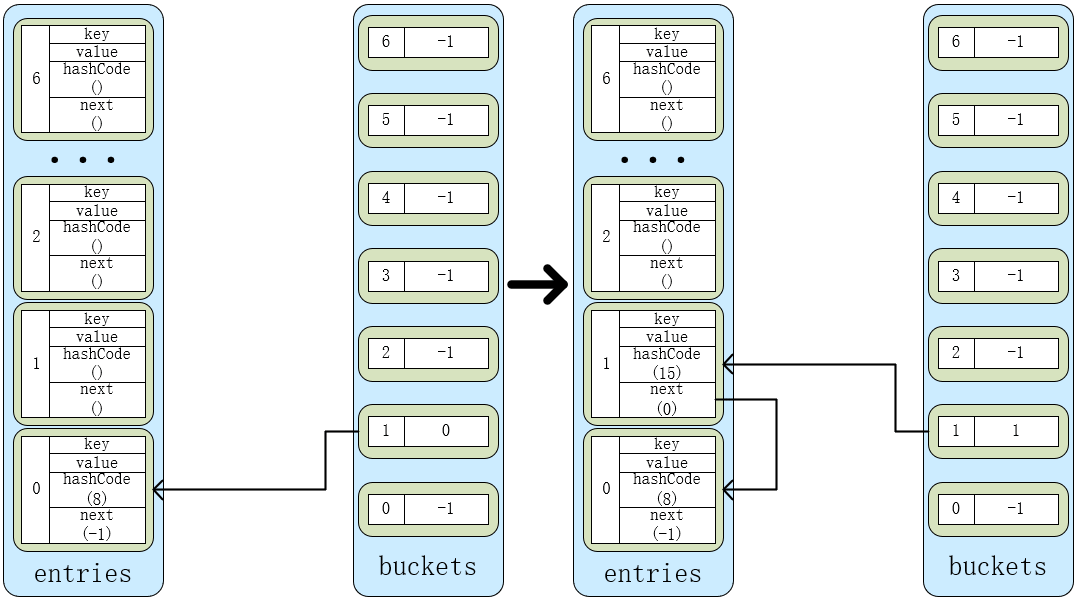
左边的Dictionary有一个元素,entries[0].hashCode = 8,8 % buckets.Length = 1,因此,entries[0].next = buckets[1] = -1,buckets[1] = 0,实际指向entries[0]。
此时插入第二个元素,entries[1].hashCode = 15,15 % buckets.Length = 1,因此,entries[1].next = buckets[1] = 0,buckets[1] = 1,实际指向entries[1]。
带着图看源码
public void Add(TKey key, TValue value) {
Insert(key, value, true);
}
再看Insert()
这里有两个关键的变量entries和buckets
private Entry[] entries; // 按下标顺序存储每一个元素、对应的hashCode、下一个entry的下标
private int[] buckets; // 存储entries下标的哈希表,用元素的hashCode对buckets.Length取余作为下标可快速找到对应的entry
private struct Entry {
public int hashCode; // Lower 31 bits of hash code, -1 if unused
public int next; // Index of next entry, -1 if last
public TKey key; // Key of entry
public TValue value; // Value of entry
}
private void Insert(TKey key, TValue value, bool add) {
if( key == null ) {
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.key);
}
if (buckets == null) Initialize(0); // 如果buckets为null要先初始化
int hashCode = comparer.GetHashCode(key) & 0x7FFFFFFF;
int targetBucket = hashCode % buckets.Length;
// hashCode取余作为新元素的buckets下标
#if FEATURE_RANDOMIZED_STRING_HASHING
int collisionCount = 0;
#endif
// 下面整个for从buckets[targetBucket]开始,取entries[buckets[targetBucket]]跟新元素的Key对比,如果没有遇到相同的Key才添加新元素
for (int i = buckets[targetBucket]; i >= 0; i = entries[i].next) {
// 只有在hashCode相等和Equals返回true的同时才认为两个元素相同
if (entries[i].hashCode == hashCode && comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key)) {
if (add) { // 在用`[]`进行操作时add为false,更新元素value
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentException(ExceptionResource.Argument_AddingDuplicate); // 存在相同元素抛出异常
}
entries[i].value = value;
version++; // 当对Dictionary进行Add或Update或Remove“增、改、删”操作时,Dictionary的version加一
return;
}
#if FEATURE_RANDOMIZED_STRING_HASHING
collisionCount++; // 记录冲突数,理解这个需要先了解上面提到的哈希表结构
#endif
}
int index;
// freeCount只有在Remove元素之后才可能大于0,此时将新元素插入entries空位
if (freeCount > 0) {
index = freeList; // 取上次被Remove的元素的下标
freeList = entries[index].next; // 指向上一个被Remove的元素的坐标,若没有则为-1
freeCount--; // 闲置数减一
}
else {
// 如果entries空间不够用了,就对entries和buckets进行扩容
if (count == entries.Length)
{
Resize();
targetBucket = hashCode % buckets.Length;
}
index = count;
count++;
}
entries[index].hashCode = hashCode;
entries[index].next = buckets[targetBucket]; // [1]
entries[index].key = key;
entries[index].value = value;
buckets[targetBucket] = index; // [2]
// 这里标记的[1][2]两句是关键,
// 当存储的元素作为当前hashCode的第一个元素时,next = buckets[targetBucket] = -1,buckets[targetBucket]置为该元素的下标
// 而后每一次存储有带着相同哈希值Key的元素时,next指向上一个带着相同哈希值Key的元素,buckets[targetBucket]置为新元素的下标
version++; // 当对Dictionary进行Add或Update或Remove“增、改、删”操作时,Dictionary的version加一
// 下面代码是当collisionCount(新增元素Key的hashCode的冲突数) > HashHelpers.HashCollisionThreshold(设定的最大冲突数)时会进行对表的Resize处理,我懒得细看了。
#if FEATURE_RANDOMIZED_STRING_HASHING
#if FEATURE_CORECLR
// In case we hit the collision threshold we'll need to switch to the comparer which is using randomized string hashing
// in this case will be EqualityComparer<string>.Default.
// Note, randomized string hashing is turned on by default on coreclr so EqualityComparer<string>.Default will
// be using randomized string hashing
if (collisionCount > HashHelpers.HashCollisionThreshold && comparer == NonRandomizedStringEqualityComparer.Default)
{s
comparer = (IEqualityComparer<TKey>) EqualityComparer<string>.Default;
Resize(entries.Length, true);
}
#else
if(collisionCount > HashHelpers.HashCollisionThreshold && HashHelpers.IsWellKnownEqualityComparer(comparer))
{
comparer = (IEqualityComparer<TKey>) HashHelpers.GetRandomizedEqualityComparer(comparer);
Resize(entries.Length, true);
}
#endif // FEATURE_CORECLR
#endif
}
Resize
Resize()会在字典,也就是entries容量不够时执行,对字典进行扩展。
private void Resize() {
Resize(HashHelpers.ExpandPrime(count), false);
// HashHelpers.ExpandPrime(count)方法调用GetPrime(2 * oldSize)取大于当前元素数量2倍的最小素数作为新哈希表的长度。
}
private void Resize(int newSize, bool forceNewHashCodes) {
Contract.Assert(newSize >= entries.Length);
int[] newBuckets = new int[newSize];
for (int i = 0; i < newBuckets.Length; i++) newBuckets[i] = -1; // 初始化哈希表内坐标
Entry[] newEntries = new Entry[newSize];
Array.Copy(entries, 0, newEntries, 0, count); // 复制旧元素到新表
if(forceNewHashCodes) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if(newEntries[i].hashCode != -1) {
newEntries[i].hashCode = (comparer.GetHashCode(newEntries[i].key) & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
}
}
// // 对所有元素hashCode重新取余,重设下标
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (newEntries[i].hashCode >= 0) { // 过滤Remove后的闲置位
int bucket = newEntries[i].hashCode % newSize;
newEntries[i].next = newBuckets[bucket];
newBuckets[bucket] = i;
}
}
buckets = newBuckets;
entries = newEntries;
}
Remove
public bool Remove(TKey key) {
if(key == null) {
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.key);
}
if (buckets != null) {
int hashCode = comparer.GetHashCode(key) & 0x7FFFFFFF;
int bucket = hashCode % buckets.Length;
int last = -1;
for (int i = buckets[bucket]; i >= 0; last = i, i = entries[i].next) {
if (entries[i].hashCode == hashCode && comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key)) {
if (last < 0) {
buckets[bucket] = entries[i].next;
}
else {
entries[last].next = entries[i].next;
}
entries[i].hashCode = -1; // hashCode设为-1,做个标记
entries[i].next = freeList; // next指向上一个被Remove的元素的坐标,若没有则为-1
entries[i].key = default(TKey);
entries[i].value = default(TValue);
freeList = i; // 置为最新被移除元素的坐标
freeCount++; // entries闲置数加一
version++; // 当对Dictionary进行Add或Update或Remove(“增、改、删”)操作时,Dictionary的version加一
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
Clear
为了提高效率,Clear函数没有对entries和buckets置null,只是把相关的变量重新初始化了。也符合逻辑,如果置null,那我为什么不直接new一个新的Dictionary呢。
public void Clear() {
if (count > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < buckets.Length; i++) buckets[i] = -1;
Array.Clear(entries, 0, count);
freeList = -1;
count = 0;
freeCount = 0;
version++;
}
}
官方源码:Dictionary.cs


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号