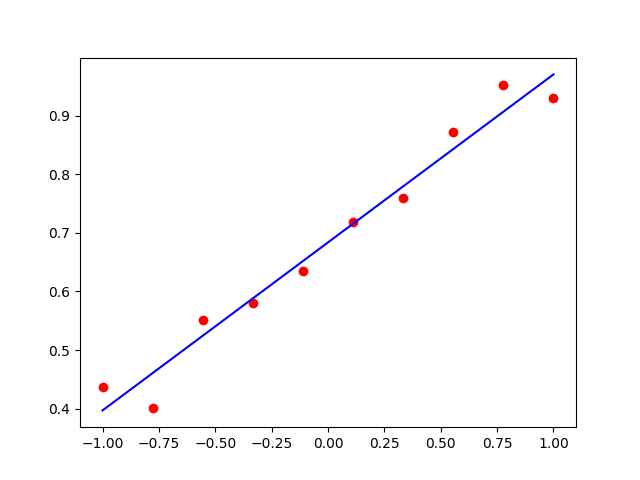
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plot # 定义数据数量 xdata = [] ydata = [] # 生成数据 xdata = np.linspace(-1., 1., 10) # 线性等分生成100个数据 # 拟合 y = a*x + b 的线性回归函数 # 定义 a=0.3,b=0.7,加上随机噪声 ydata = [0.3 * v + 0.7 + np.random.normal(0.0, 0.05) for v in xdata] # 定义变量 a = tf.Variable(initial_value=0., dtype=tf.float32) b = tf.Variable(initial_value=0., dtype=tf.float32) variables = [a, b] # 声明梯度下降优化算法 optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.01) # 声明循环迭代次数 num = 100 history_loss = [] # 记录每一次更新的loss值的变化 # 进行迭代,更新参数 for s in range(num): with tf.GradientTape() as tape: # 预测值 y_pred = a * xdata + b # 损失函数 loss = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(y_pred - ydata)) history_loss.append(loss) # 计算梯度 grads = tape.gradient(loss, variables) # 更新参数 optimizer.apply_gradients(grads_and_vars=zip(grads, variables)) # 每隔100次输出一次结果 if s % 10 == 0: print("step: %i, loss: %f, a: %f, b: %f" % (s, loss, a.numpy(), b.numpy())) print(a.numpy(), b.numpy()) plot.scatter(xdata, ydata, c='r') plot.plot(xdata, a * xdata + b, c='b') plot.show() # 画出loss曲线 plot.plot(np.arange(num), history_loss) plot.title('loss') plot.show()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号