牛客 周赛83 20250304
牛客 周赛83 20250304
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/102896
A:
题目大意:给定字符,不同输出
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define cintie ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define Trd int T;cin>>T;while (T--)solve();
#define LLinf 9e18;
#define Iinf 2e9
#define LL long long
#define Lc p<<1
#define Rc p<<1|1
#define lc(x) tr[x].ch[0]
#define rc(x) tr[x].ch[1]
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char c;
cin>>c;
if (c=='U'||c=='D') cout<<'L';
else cout<<'U';
return 0;
}
签到
B:
题目大意:有 \(n\) 个格子与 \(3\times n\) 个石头,每个格子中的石头与相邻格子的石头数相差 \(1\) ,给出一种放石头的方案,石头可以不用完
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define cintie ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define Trd int T;cin>>T;while (T--)solve();
#define LLinf 9e18;
#define Iinf 2e9
#define LL long long
#define Lc p<<1
#define Rc p<<1|1
#define lc(x) tr[x].ch[0]
#define rc(x) tr[x].ch[1]
using namespace std;
void solve(void){
int n;
cin>>n;
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if (i%2) cout<<1<<' ';
else cout<<2<<' ';
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
Trd;
return 0;
}
贪心构造,\(1,2,1,\cdots\) 这样的序列用石头一定最少且一定小于 \(3\times n\)
C:
题目大意:

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define cintie ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define Trd int T;cin>>T;while (T--)solve();
#define LLinf 9e18;
#define Iinf 2e9
#define LL long long
#define Lc p<<1
#define Rc p<<1|1
#define lc(x) tr[x].ch[0]
#define rc(x) tr[x].ch[1]
using namespace std;
void solve(void){
string x;
cin>>x;
int d=x.size();
cout<<1;
for (int i=1;i<d;i++)
cout<<0;
cout<<1<<endl;
}
int main()
{
Trd;
return 0;
}
差点卡死,一开始想复杂了
假设给定的数为 \(A\) ,那么 \(AA\) 的数域一定和 \(A\) 是相同的,所以构造 \(y=100\cdots001\) 即可,中间的 \(0\) 的个数取决于 \(A\) 的长度
D:
题目大意:

求解 \(t\) 时刻的坐标
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define cintie ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define Trd int T;cin>>T;while (T--)solve();
#define LLinf 9e18;
#define Iinf 2e9
#define LL long long
#define Lc p<<1
#define Rc p<<1|1
#define lc(x) tr[x].ch[0]
#define rc(x) tr[x].ch[1]
using namespace std;
LL t;
bool judge(LL x){
LL sum=x*x;
return sum<t;
}
void solve(void){
cin>>t;
LL l=0,r=1e9+1;
while (l+1!=r){
LL mid=l+r>>1;
if (judge(mid))
l=mid;
else
r=mid;
}
LL stp=t-l*l;
if (l%2==1){
LL x=l/2,y=l/2;
if (stp==0)
cout<<x<<' '<<y<<endl;
else if (stp==1)
cout<<x+1<<' '<<y<<endl;
else if (stp>1&&stp<=l)
cout<<x+1<<' '<<y-(stp-1)<<endl;
else
cout<<x+1-(stp-l-1)<<' '<<y-l<<endl;
}else{
LL x=-l/2+1,y=-l/2;
if (stp==0)
cout<<x<<' '<<y<<endl;
else if (stp==1)
cout<<x-1<<' '<<y<<endl;
else if (stp>1&&stp<=l)
cout<<x-1<<' '<<y+stp-1<<endl;
else
cout<<x-1+(stp-l-1)<<' '<<y+l<<endl;
}
}
int main()
{
Trd;
return 0;
}
找规律+模拟
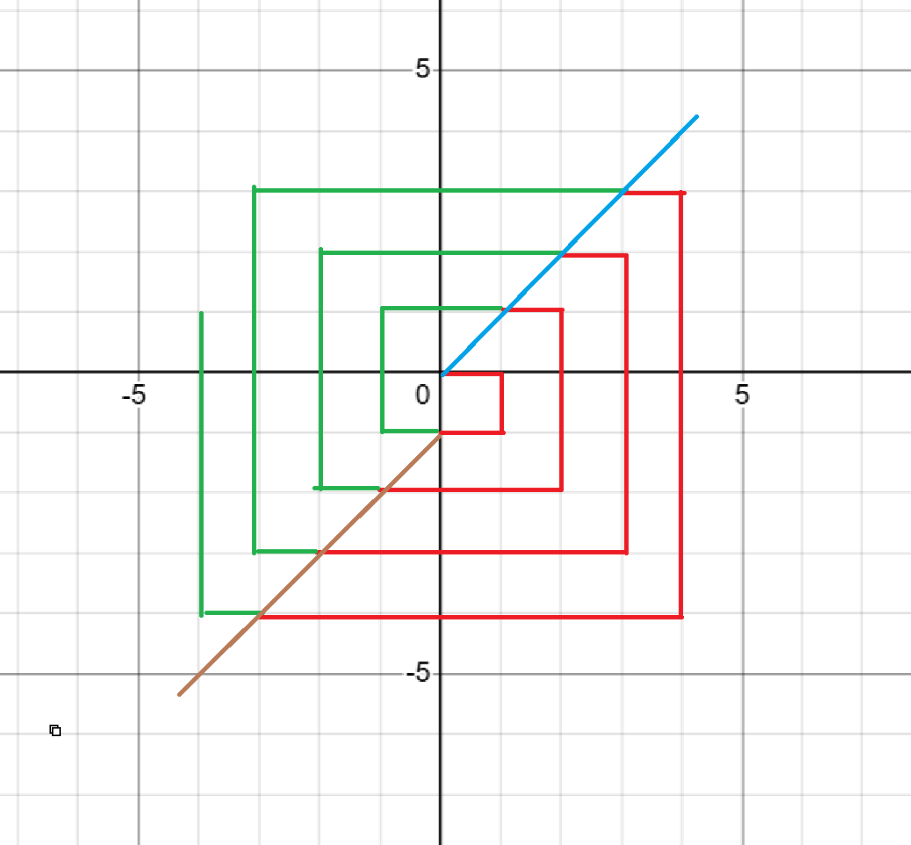
规律有点玄学,手玩出前几段的图像后,在蓝线上的点都满足 \(x=y\) ,棕线上的点都满足 \(x=y+1\)
那么给定的 \(t\) 必然在红绿其中一段上,图像可以看作许多层正方形叠加,由蓝线确定的正方形边长以 \(2n+1\) 递增,棕线确定的正方形以 \(2n\) 递增
蓝棕线与轨迹的交点确定的路程为 \(n^2\) ,所以可以二分时间 \(t\) ,判断处于哪两个交点之间
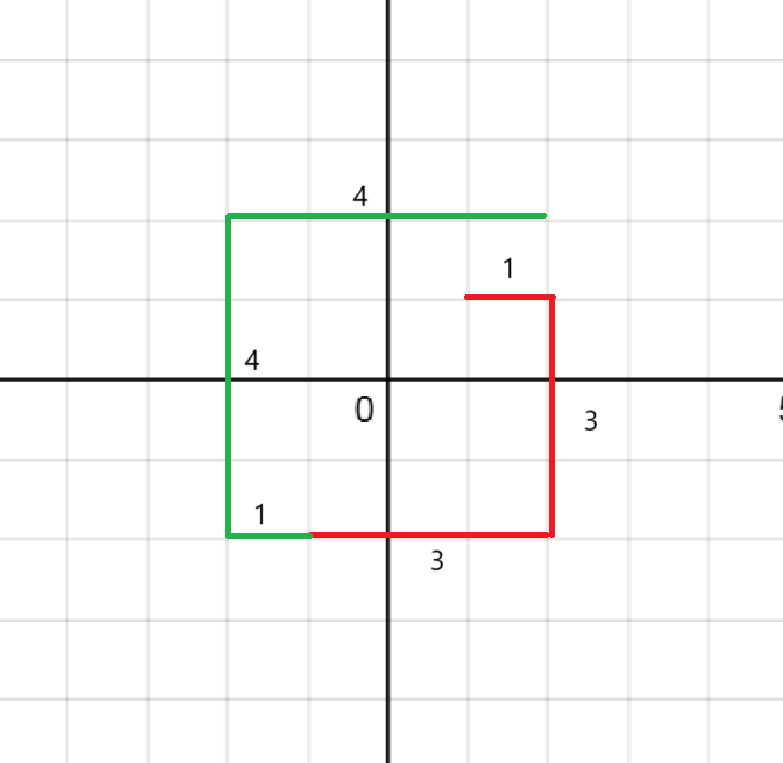
考虑在红绿段上的路径规律,都是从交点右移或左移一步,然后向下或向上移动 \(n\) 步,最后向左或向右移动 \(n\) 步
我们下取整交点,通过 \(t-n^2\) 计算出这一段还剩余的步数,按照步数进行分类讨论
-
\(stp=1\) 在红色段向右移动一次,在绿色段向左移动一次
-
\(stp\le n\) 在红色段向下移动 \(stp-1\) 次,在绿色段向左移动 \(stp-1\) 次
-
\(stp>n\) 在红色段再向左移动 \(stp-1-n\) 次,在绿色段再向左移动 \(stp-1-n\) 次
E:
题目大意:
有 \(n\) 个格子,每个格子内都有数值,必须使用 \(k\) 次机会,每次可以选择走 \([1,6]\) 格,求最后数值的最大和
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define cintie ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define Trd int T;cin>>T;while (T--)solve();
#define LLinf 9e18;
#define Iinf 2e9
#define LL long long
#define Lc p<<1
#define Rc p<<1|1
#define lc(x) tr[x].ch[0]
#define rc(x) tr[x].ch[1]
using namespace std;
LL a[10010];
LL dp[1010][10010];
void solve(void){
int n,k;
cin>>n>>k;
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i];
for (int i=0;i<=k;i++)
for (int j=0;j<=n;j++)
dp[i][j]=-LLinf;
dp[0][0]=0;
for (int i=1;i<=k;i++){
for (int j=0;j<=n;j++){
for (int u=j+1;u<=min(j+6,n);u++){
dp[i][u]=max(dp[i][u],dp[i-1][j]+a[u]);
}
}
}
LL ans=-LLinf;
for (int i=0;i<=n;i++) ans=max(ans,dp[k][i]);
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
int main()
{
solve();
return 0;
}
dp预设值太小被卡了
经典的动态规划,考虑 \(dp_{i,j}\) 表示用 \(i\) 次机会走到 \(j\) 格的最大总和,每次循环内考虑步数 \([1,6]\) ,注意不能超出 \(n\)
状态转移方程可以为
对每个 \(j\) 点都取当前的值和从 \(j-step\) 转移过来的值的最优解
for (int u=j+1;u<=min(j+6,n);u++){
dp[i][u]=max(dp[i][u],dp[i-1][j]+a[u]);
}
最后遍历次数为 \(k\) 的所有状态,输出最大值即可



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号