快速幂优化高精度乘法
NOI 1.6 12
题目描述
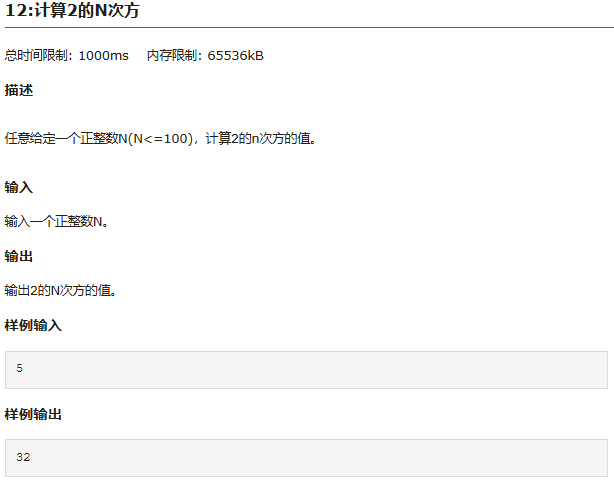
题目给出的 \(n\) 最大可以取到 \(100\) ,即计算 \(2^{100}\) ,明显是超过 long long 的 \(2^{63}-1\),所以需要使用高精度来计算幂次方的乘法
- 简单的高精度,即每次计算一个小整数乘上一个大整数
循环 \(n\) 次,每次对上一次的积都乘以 \(2\)
vector<int> ans = { 1 };//注意,需要对ans的第一位进行赋初值为1
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
ans = highdouble(ans);
然后就是简单高精度乘法的模板
vector<int> highdouble(vector<int> x) {
vector<int> res;//定义返回数组
int t = 0;//进位变量
for (int i = 0; i < x.size(); i++) {
t += 2 * x[i];//计算乘2的积
res.push_back(t % 10);//取尾数放入
t /= 10;
}
while (t) {//如果进位t还有值,就继续放入
res.push_back(t % 10);
t /= 10;
}
return res;//返回答案
}
以上的代码仅只用于大整数乘一个小整数,不能完成对两个大整数求积的操作、
简单的高精度计算的时间复杂度大约在 \(O(n^2)\) ,我们也可以使用快速幂的办法将时间复杂度优化到更低
- 快速幂高精度计算
vector<int> quickpower(int b) {//快速幂函数
vector<int> res, a;//使用vector来存储数据
res.push_back(1);//对res第一项继续预处理
a.push_back(2);//放入底数2
while (b)//快速幂模板
{
if (b & 1) res = highplus(res, a);//使用高精度乘法计算
a = highplus(a, a);//高精度倍增计算因子
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
这里的高精度乘法需要计算两个大整数的积,采用错位相乘法
vector<int> highplus(vector<int>& x, vector<int>& y) {
vector<int> temp(x.size() + y.size() + 1, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < x.size(); i++)
for (int j = 0; j < y.size(); j++)
temp[i + j] += x[i] * y[j];
int t = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < temp.size(); i++) {
t += temp[i];
temp[i] = t % 10;
t /= 10;
}
while (t > 0) {
temp.push_back(t % 10);
t /= 10;
}
while (temp.size() > 1 && temp.back() == 0) temp.pop_back();
return temp;
}
其中,将 temp 赋值一个最大长度,即两个因子的长度和加 \(1\) ,并赋初值都为 \(0\)
循环两层计算相应位置上的乘积 temp[i + j] += x[i] * y[j] (原理这里不做赘述)
最后处理进位的问题,遍历整个 temp 数组,对每一位都继续进位操作
t += temp[i];
temp[i] = t % 10;
t /= 10;
while (t > 0) {//如果进位t还有值,就继续放入
temp.push_back(t % 10);
t /= 10;
}
对 temp 数组去除前导 \(0\) 后返回高精度乘法的结果
经过实测,朴素的高精度乘法在规定的 \(1s\) 内最多只能计算到 \(2^{11438}\),而采用快速幂则可以计算到 \(2^{2^{15-1}}=2^{32767}\)
是一种极大的优化方案,如果我们的底数更大的话,快速幂的优势会变得更大
完整AC代码:
朴素算法
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int n;
vector<int> ans = { 1 };
vector<int> highdouble(vector<int> x) {
vector<int> res;
int t = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < x.size(); i++) {
t += 2 * x[i];
res.push_back(t % 10);
t /= 10;
}
while (t) {
res.push_back(t % 10);
t /= 10;
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
ans = highdouble(ans);
for (int i = ans.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) cout << ans[i];
return 0;
}
快速幂
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int n;
vector<int> highplus(vector<int>& x, vector<int>& y) {
vector<int> temp(x.size() + y.size() + 1, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < x.size(); i++)
for (int j = 0; j < y.size(); j++)
temp[i + j] += x[i] * y[j];
int t = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < temp.size(); i++) {
t += temp[i];
temp[i] = t%10;
t /= 10;
}
while (t > 0) {
temp.push_back(t % 10);
t /= 10;
}
while (temp.size() > 1 && temp.back() == 0) temp.pop_back();
return temp;
}
vector<int> quickpower(int b) {
vector<int> res, a;
res.push_back(1);
a.push_back(2);
while (b)
{
if (b & 1) res = highplus(res, a);
a = highplus(a, a);
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
auto ans = quickpower(n);
for (int i = ans.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) cout << ans[i];
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号